Eppendorf 012: Microinjection of plasmid DNA or double stranded RNA User Manual
Userguide, C. elegans
Microinjection of plasmid DNA or double
stranded RNA into the gonads of
C. elegans
FemtoJet express | No 012/06
Userguide
Author: Ryuji Minasaki, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology,
Abteilung IV (Evolutionsbiologie), Tübingen, Germany
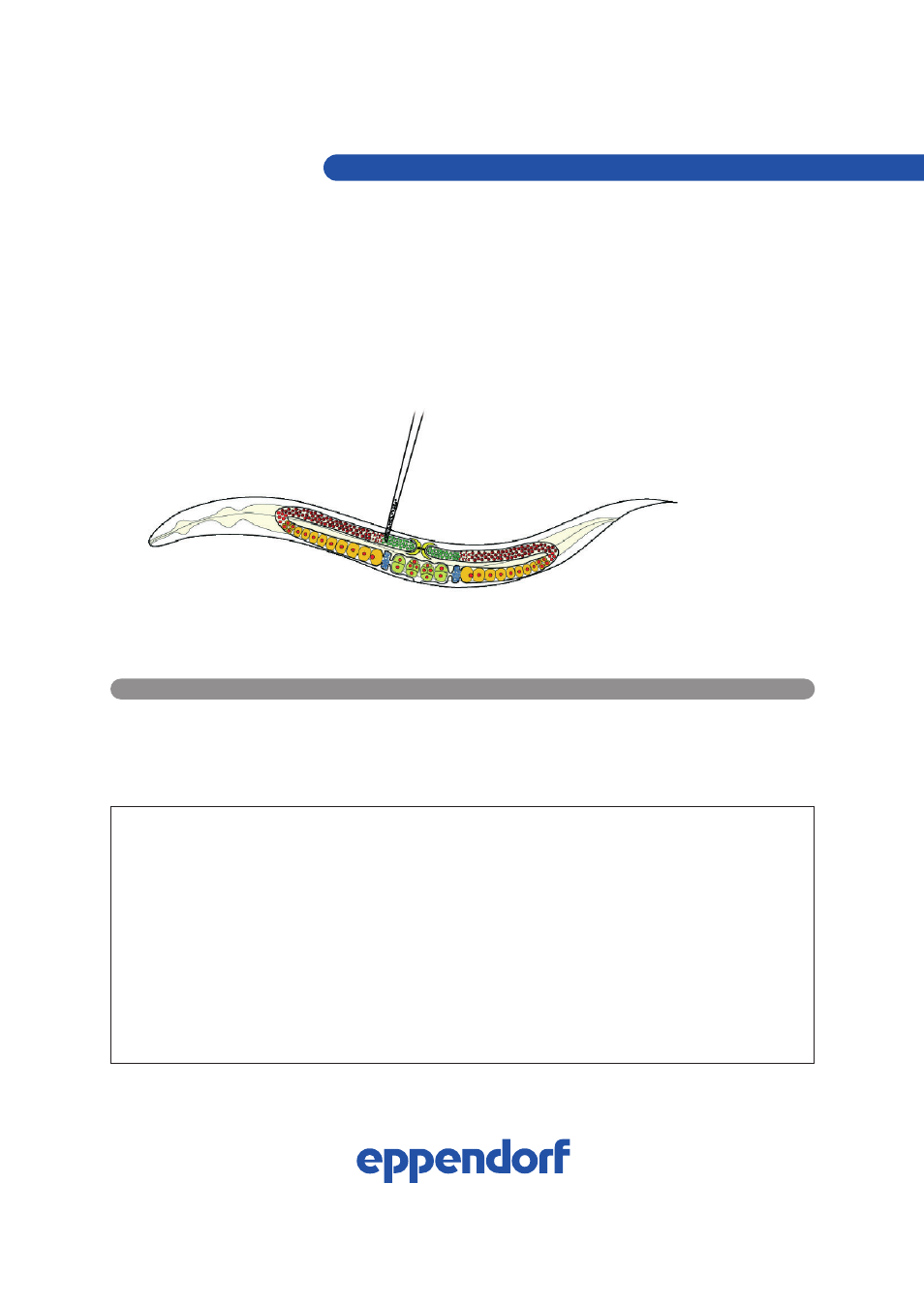
FIG. 1: Intragonadal injection in C. elegans
Introduction
C. elegans was established as a model organism three decades ago by Sydney Brenner (Brenner 1974).
Two major applications for microinjection in C. elegans are the production of transgenic worms (Mello et al.
1991) and the knockdown of genes by RNA interference (Fire et al. 1998).
Here, we describe a microinjection technique that has been established in our laboratory for these purposes.
Applications for microinjection in C. elegans
•
Injection of DNA to generate transgenic lines
•
Injection of dsRNA to induce RNAi
•
Injection of proteins
Research interests
Transgenic animals can be generated for a wide range of purposes. Some of the more popular uses are outlined below:
•
Direct transformation of mutant strains using cloned DNA by germline microinjection
•
Expression pattern analysis (e.g., GFP fusion constructs)
•
Structure/function analysis
•
Promoter Bashing
•
Identification of gain-of-function phenotype through overexpression / ectopic expression of an endogenous
or foreign gene
Table 1: Applications for microinjection in worm
