Ball bearings – Hale CSD User Manual
Page 16
d) Pull a prime until the compound gauge reaches about 20 inches of vacuum.
e) Watch gauge - if vacuum drops more than one inch in 10 minutes, an air leak is present. All air
leaks must be corrected before the pump may be considered fully serviceable.
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are the most common anti-friction bearings used today and offer a major contribution
to the life of a fire pump, during major maintenance you will have an occasion to remove or replace
ball bearings. Often an attempt is made to reuse them and sometimes they can be; however, when
doing so you are taking a serious gamble, particularly when you have invested a great deal of time
and money to dismantle, repair and reinstall the equipment only to have a bearing fail after a few
short hours of operation, again requiring further downtime and additional money spent. We do not
recommend this practice under any circumstance, however, we realize at times this must be
considered, when doing so they must be examined very carefully for pits, abrasion or other
damage, check the raceways very carefully for metal transfer and pits. When cleaning ball
bearings, be sure to use clean solvent; do not use contaminated solvent. Use clean air to blow the
solvent and foreign matter from the inside raceway, do not hold the inner race rigid and spin the
outer race with air pressure; this can cause metal transfer or embed small particles. Hold both
inner and outer races and blow through the open sections around the separation. After examination
and the bearing appears to be satisfactory, lubricate the raceway with light oil and then holding the
inner race between the fingers slowly rotate the outer race and feel for any catch, rough spots or
binds. If any are found then discard the bearing and secure a correct replacement. Your best
supply for the correct type and size is the pump manufacturer. If locally supplied bearings are used,
be sure it is an exact replacement. Do not interchange bearing types; they may also fail
prematurely.
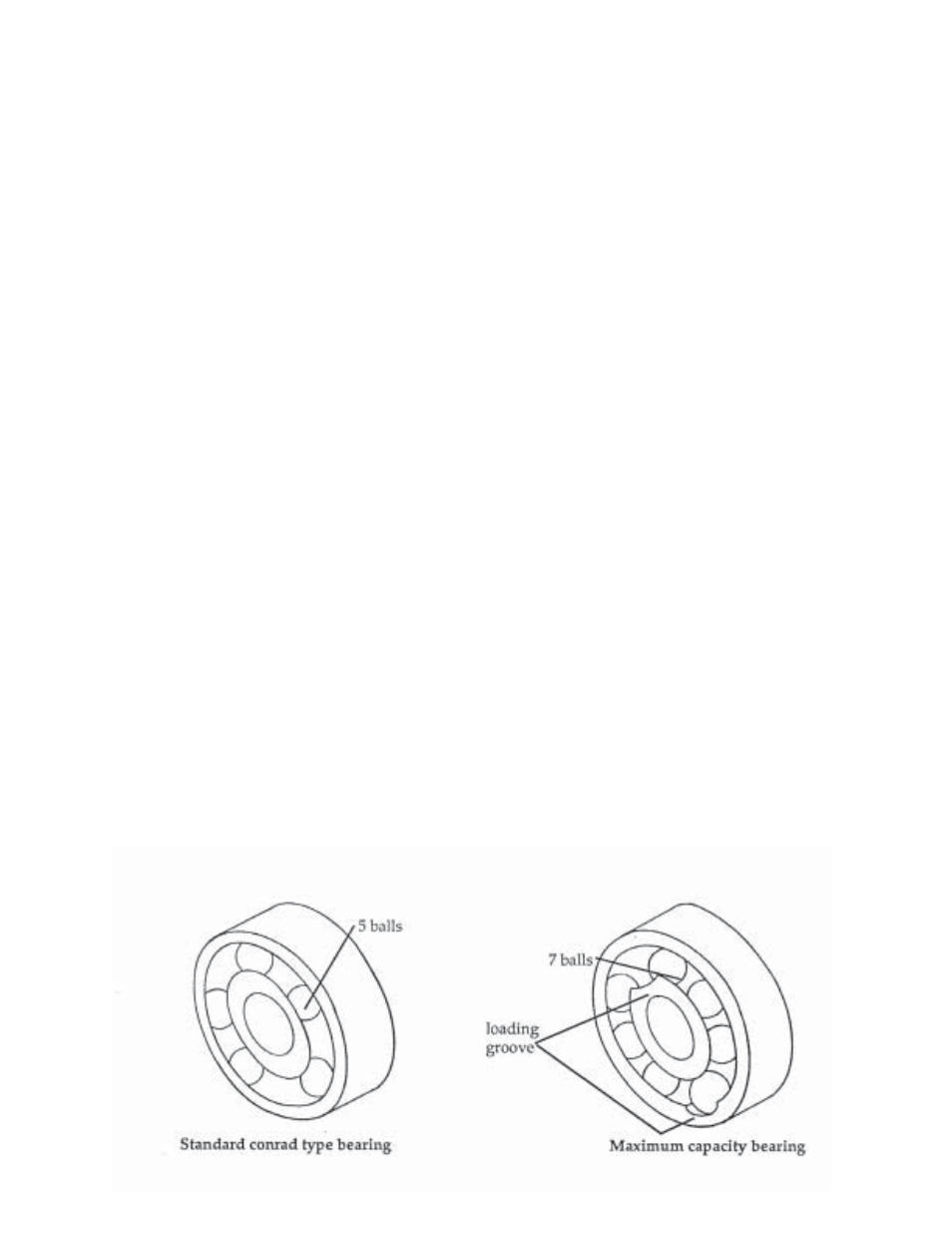
We have sketched two similar bearings that have the same outside diameter, same inside diameter
and the same width, but if one of these bearings is used to replace the other one you may be
asking for trouble. Design engineers and bearing manufacturers have spent a great deal of time
and effort to achieve the correct combinations of loads, speeds and other contributing factors to
assure long and dependable service. When a bearing is inadvertently or hastily replaced without
due consideration, you should not expect your equipment to operate as designed.
The standard Conrad type bearing shown on the left contains five balls and is a so-called standard
bearing. It will withstand moderate radial and combined thrust loads; however, the maximum
capacity bearing shown on the right contains more balls due to the loading groove and will
withstand considerable higher radial loads but less thrust loading. This bearing can replace the
Conrad type when very little or no thrust load is present; however, never replace the maximum type
with a standard Conrad type, when a bearing has the loading groove as shown, it most certainly
indicates high radial and very little thrust loads are present.
