Troubleshooting – Belkin F9L1109V1 User Manual
Page 33
31
TROUBLESHOOTING
What’s the difference between 802.11n and 802.11ac?
Currently there are three commonly used wireless networking standards, which transmit data at very different maximum speeds.
Each is based on the designation for certifying network standards. The most common wireless networking standard, 802.11n,
can transmit information up to 450Mbps; 802.11a also supports up to 54Mbps, but in the 5GHz frequency; and 802.11ac draft
specification can connect at up to 1.3Gbps (3x3, 256 QAM). See the following chart for more detailed information.
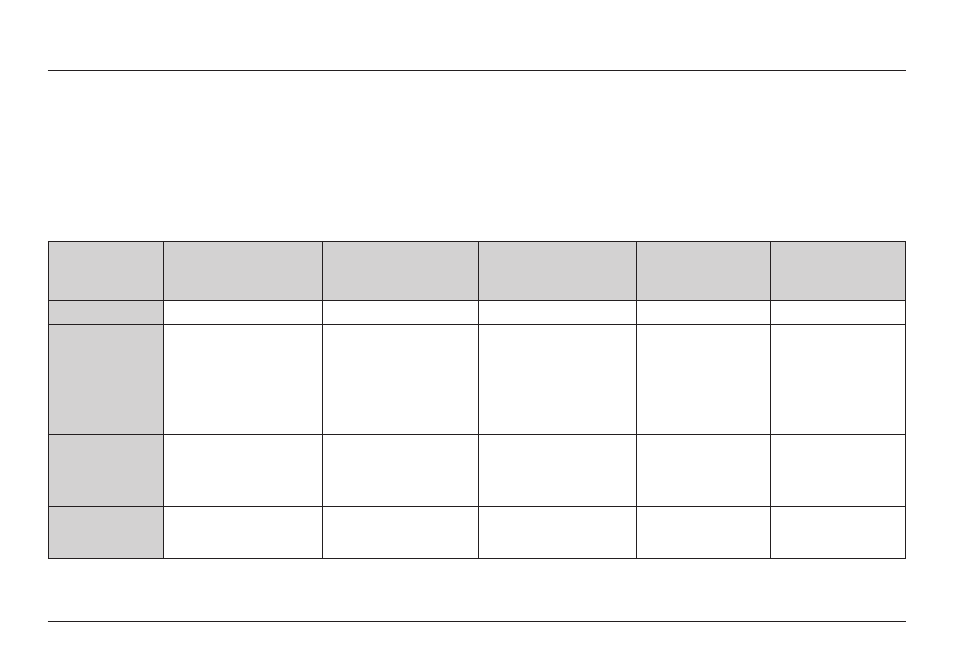
Belkin Wireless Comparison Chart
Wireless
Technology
G
(802.11g)
N150
(1x1 802.11n)
N300 MIMO
802.11n
N750 Dual-Band
MIMO
802.11n
AC Wi-Fi Dual-Band
USB Adapter
Speed/Data Rate* Up to 54Mbps*
Up to 150Mbps*
Up to 300Mbps*
Up to 450Mbps*
Up to 867Mbps*
Frequency
Common household
devices such as cordless
phones and microwave
ovens may interfere with
the unlicensed band
2.4GHz
Common household
devices such as cordless
phones and microwave
ovens may interfere with
the unlicensed band
2.4GHz
Common household
devices such as cordless
phones and microwave
ovens may interfere with
the unlicensed band
2.4GHz
Uses both 2.4GHz
and 5GHz bands for
less interference and
better throughput
Uses wider channel
bandwidth and higher
modulation for a
faster connection and
greater throughput.
Compatibility
Compatible with
802.11b/g
Compatible with
802.11b/g
Compatible with 802.11n
and 802.11b/g
Compatible with
802.11n and
802.11a/b/g
Compatible with
802.11ac draft,
802.11n, and
802.11a/b/g
Advantage
Common—widespread
use for Internet sharing
Better coverage and
consistent speed and
range
Good speed and
coverage
High-performance
coverage and
throughput
Leading-edge,
best coverage and
throughput available
*AC link rates require an 11ac access point and are only available on the 5GHz band.
