B&B Electronics Mini POE Ethernet to RS-232 Converter PESV1A User Manual
Page 59
Manual Documentation Number: PES1A/PESV1A-2907m
49
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
A
A
p
p
p
p
e
e
n
n
d
d
i
i
x
x
F
F
:
:
P
P
o
o
w
w
e
e
r
r
o
o
v
v
e
e
r
r
E
E
t
t
h
h
e
e
r
r
n
n
e
e
t
t
(
(
P
P
o
o
E
E
)
)
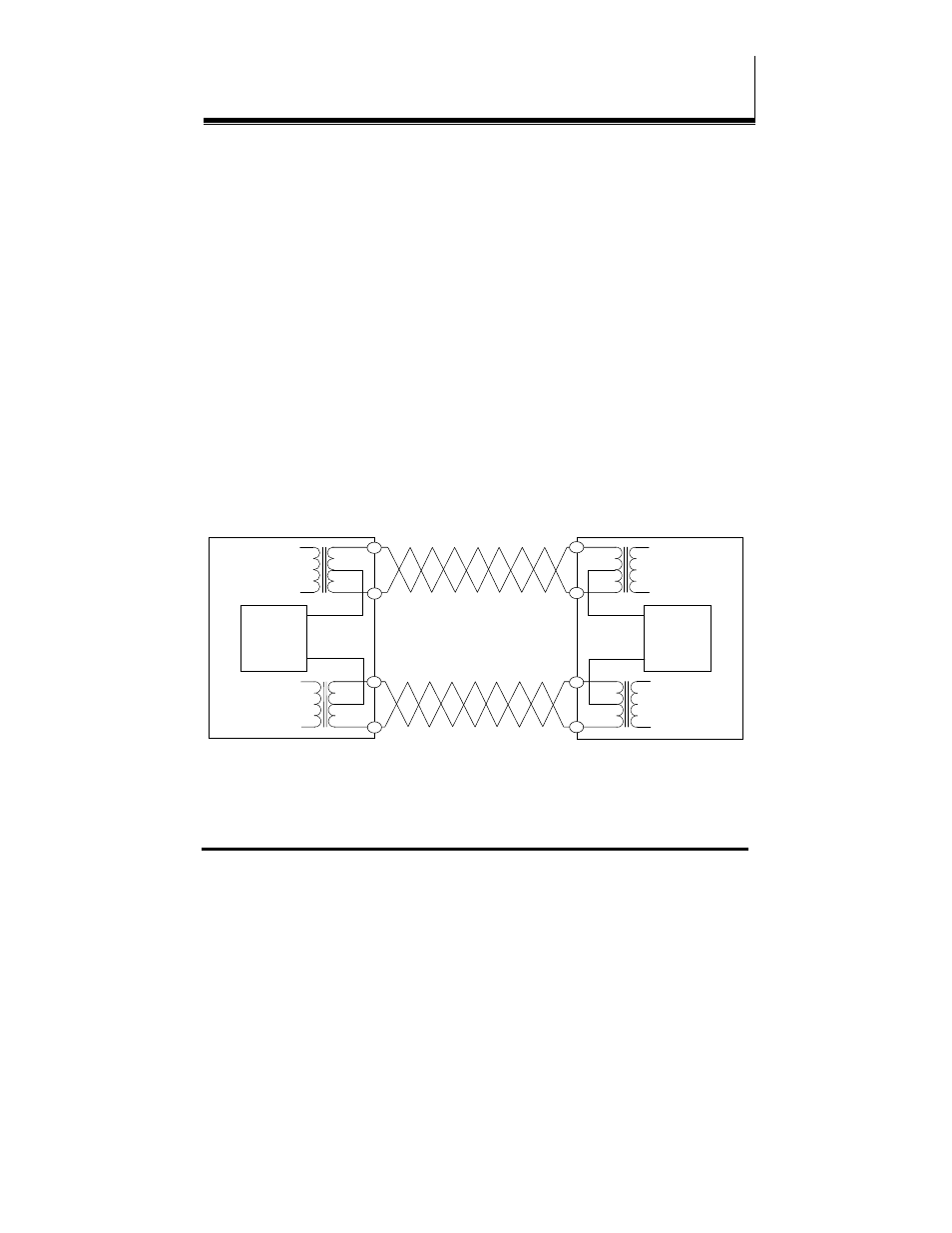
Power over Ethernet is a technique (defined by the IEEE802.3af standard) for
providing power to Ethernet enabled devices over standard Category 5e
cabling. Two techniques (Alternative A and Alternative B) are defined by the
standard and supported by the PES1A/PESV1A.
Alternative A implements a simplex, or ‘phantom feeding’ method for
delivering power to the end device. Power is carried on the same conductors
as data. Cabling for standard 10BaseT and 100BaseTX Ethernet (typically
Category 5 cable with RJ-45 connectors) uses two data/signal pairs. The
power sourcing equipment (PSE) applies positive DC voltage (simplexed) to
pins 3 and 6. Negative voltage is applied to pins 1 and 2. The powered device
(PD) derives the power from these lines.
Alternative B carries power over spare wire pairs in the cable. The power
sourcing equipment applies positive voltage to pins 4 and 5. Negative voltage
is applied to pins 7 and 8.
Operating voltage is typically 48 volts but may vary from 44 volts to 57
volts.
Power
Sourcing
Equipment
(PSE)
Powered
Device
(PD)
Data Pair
Data Pair
6
2
Device with Power Source
Data Pair
Data Pair
Powered End Station
6
2
Negative (-)
Positive(+)
Negative (-)
Positive(+)
3
3
1
1
Figure 23. Power over Ethernet Alternative A
