Ami post code, Ami post code -3, Ami post c – MSI I3-945GSE User Manual
Page 57
4-3
MS-9856
aMi poSt c
ode
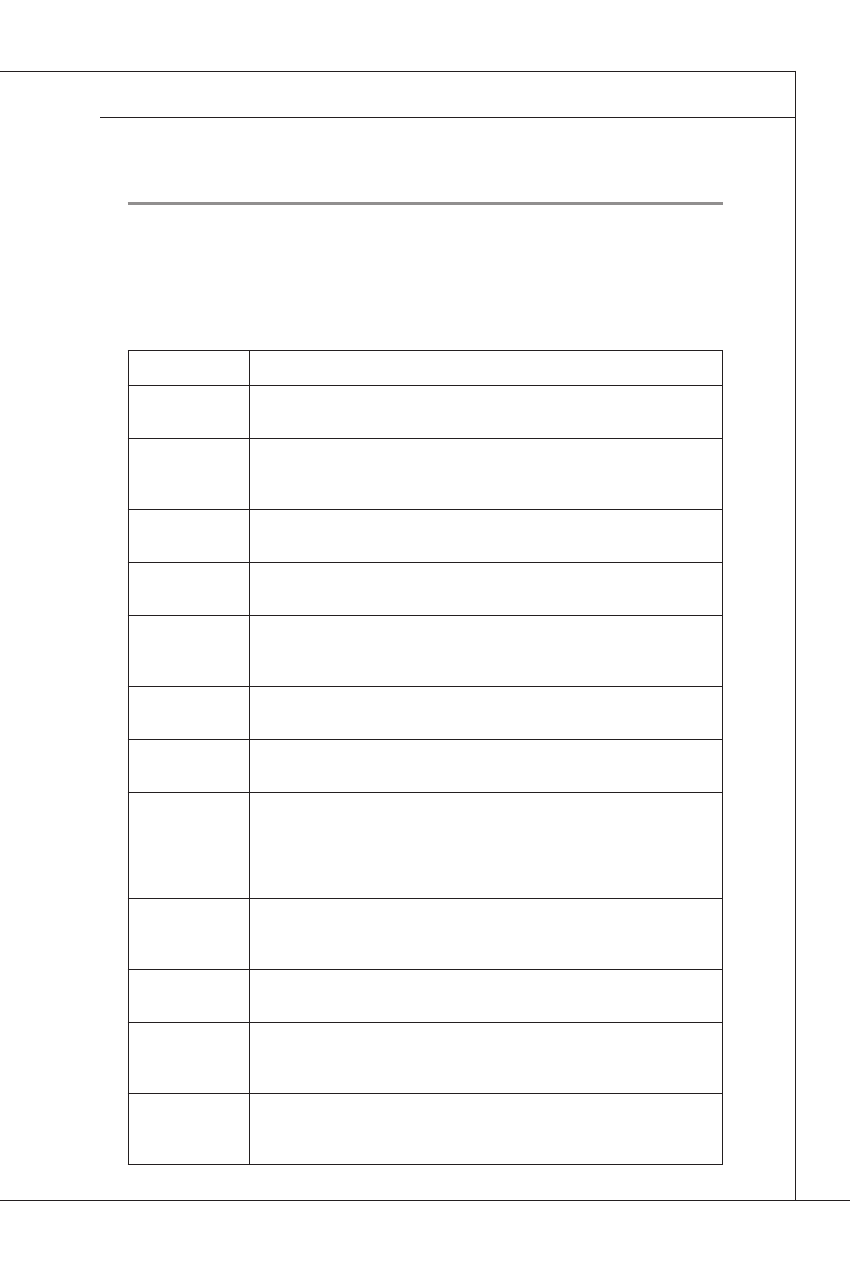
Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints
The Bootblock initialization code sets up the chipset, memory and other
components before system memory is available. The following table de-
scribes the type of checkpoints that may occur during the bootblock initial-
ization portion of the BIOS:
Checkpoint
Description
Before D1
Early chipset initialization is done. Early super I/O initialization is
done including RTC and keyboard controller. NMI is disabled.
D1
Perform keyboard controller BAT test. Check if waking up from
power management suspend state. Save power-on CPUID value
in scratch CMOS.
D0
Go to flat mode with 4GB limit and GA20 enabled. Verify the boot-
block checksum.
D2
Disable CACHE before memory detection. Execute full memory siz-
ing module. Verify that flat mode is enabled.
D3
If memory sizing module not executed, start memory refresh and do
memory sizing in Bootblock code. Do additional chipset initialization.
Re-enable CACHE. Verify that flat mode is enabled.
D4
Test base 512KB memory. Adjust policies and cache first 8MB. Set
stack.
D5
Bootblock code is copied from ROM to lower system memory and
control is given to it. BIOS now executes out of RAM.
D6
Both key sequence and OEM specific method is checked to deter-
mine if BIOS recovery is forced. Main BIOS checksum is tested. If
BIOS recovery is necessary, control flows to checkpoint E0. See
Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoints section of document for
more information.
D7
Restore CPUID value back into register. The Bootblock-Runtime
interface module is moved to system memory and control is given to
it. Determine whether to execute serial flash.
D8
The Runtime module is uncompressed into memory. CPUID infor-
mation is stored in memory.
D9
Store the Uncompressed pointer for future use in PMM. Copying
Main BIOS into memory. Leaves all RAM below 1MB Read-Write
including E000 and F000 shadow areas but closing SMRAM.
DA
Restore CPUID value back into register. Give control to BIOS POST
(ExecutePOSTKernel). See POST Code Checkpoints section of
document for more information.
