Operational principles, 1 measurement – Campbell Scientific LWS Decagon Leaf Wetness Sensor User Manual
Page 8
LWS-L Dielectric Leaf Wetness Sensor
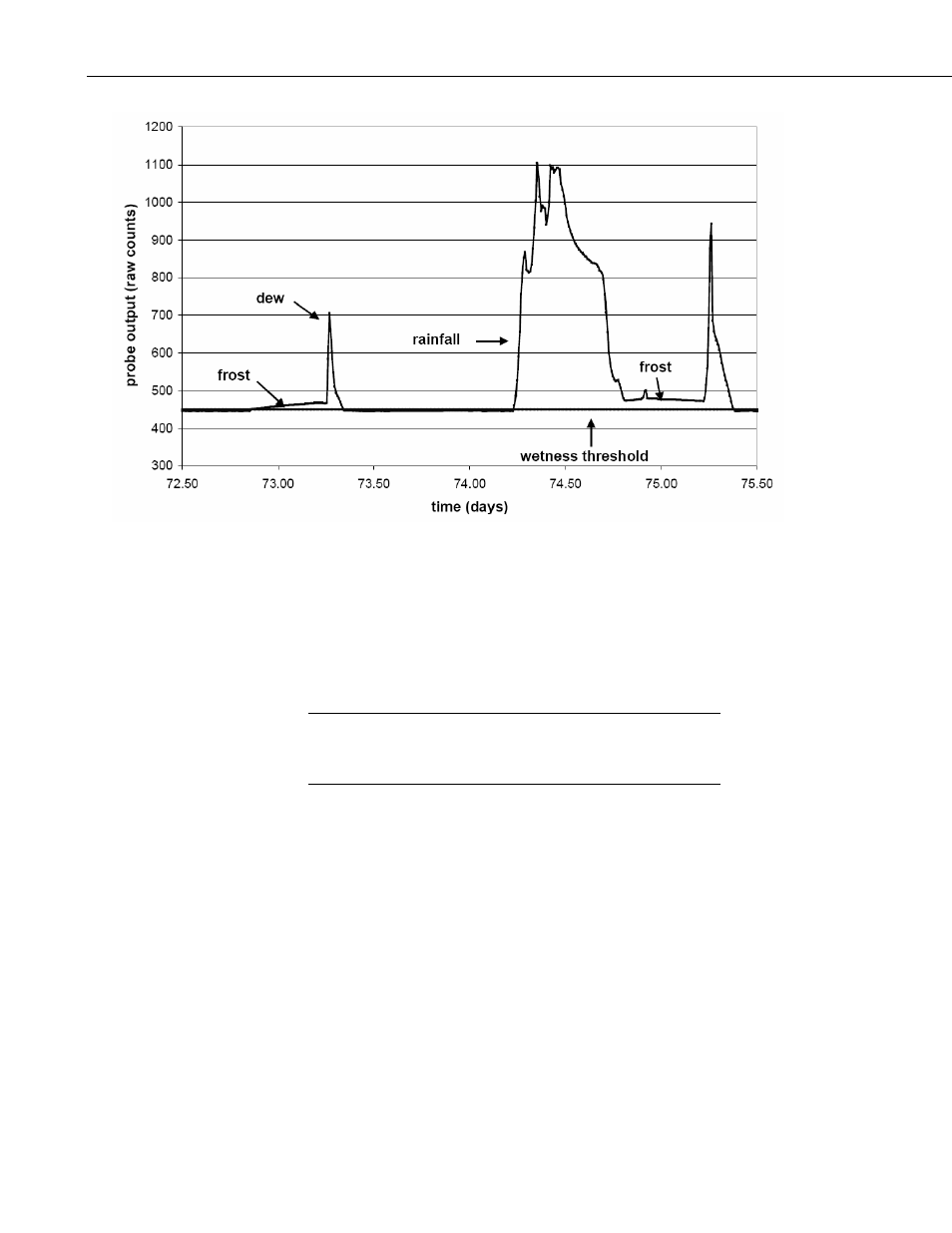
FIGURE 3. Typical LWS-L Response
Duration of leaf wetness can be determined either by post processing of data,
or by programming the datalogger to accumulate time of wetness based on the
Boolean threshold. Accumulation of dust and debris, such as avian fecal
matter, will change the Boolean threshold. So, while having the datalogger
accumulate time of leaf wetness, or time of frost, may be convenient, assurance
of data quality requires retention of the base mV measurements.
Collect data frequently enough to capture changes in surface
wetness. A sample frequency of 15 minutes or less is usually
necessary to accurately capture leaf wetness duration.
NOTE
7. Operational Principles
7.1 Measurement
The LWS-L measures the dielectric constant of a zone approximately 1 cm
from the upper surface of the sensor. The dielectric constant of water (≈80)
and ice (≈5) are much higher than that of air (≈1), so the measured dielectric
constant is strongly dependent on the presence of moisture or frost on the
sensor surfaces. The sensor outputs a mV signal proportional to the dielectric
of the measurement zone, and therefore proportional to the amount of water or
ice on the sensor surface.
4
