Thermo Fisher Scientific Ion Selective Electrodes Cadmium User Manual
Page 10
Cadmium Electrode
Instruction Manual
10
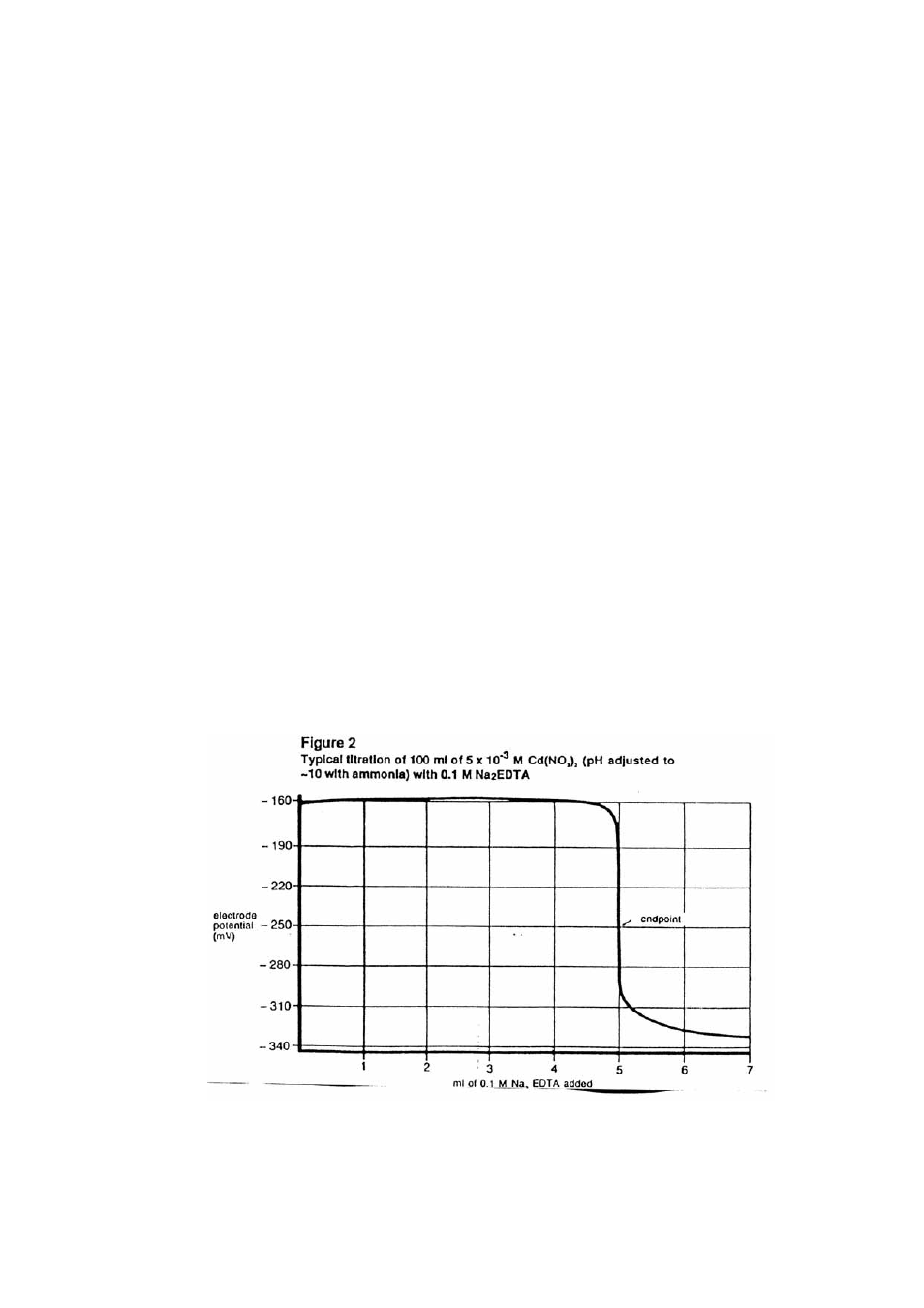
Titration of Cadmium
The method outlined in this section makes use of the cadmium ion electrode as a highly sensitive
endpoint detector for cadmium-containing samples. The titrant used is EDTA.
EDTA complexes cadmium as well as other cations. The sample pH can be adjusted to pH 10 by
adding ammonia to eliminate unwanted ion complexes. Masking agents may be added in some
cases.
1.
Prepare the stock EDTA titrant as given in the section
Required Solutions
. Dilute the
EDTA to 10 to 20 times as concentrated as the suspected sample concentration. The
sample should contain at least 1.0X10
-4
M cadmium for a good detection of the endpoint.
2.
Fill a 50 ml burette with the EDTA solution. Pipet 100 ml of the sample into a 150 ml
beaker, place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a constant rate. Adjust
the sample to pH 10 by adding ammonia.
3.
Position the burette tip in the beaker, slightly above the liquid level in the beaker and
slightly off center. Position the electrode tips in the solution about halfway between the
center of the beaker and the beaker wall.
4.
Begin adding the EDTA in 0.5 ml to 1.0 ml increments and about 0.1 ml to 0.2 ml
increments as the potential begins to change more rapidly. Record the mV potential after
each addition. Continue the additions several milliliters past the endpoint until little
change is noted in the mV reading even when adding 0.5 - 1.0 ml increments.
5.
Plot the milliliters of EDTA added against the mV potential on standard coordinate graph
paper. (See Figure 2.) The point of greatest potential change is the endpoint.
6.
The cadmium ion concentration of the sample is calculated as follows:
VtMt
