Schaefer Series U User Manual
Page 12
www.schaeferpower.de
Technical Notes
Technical Notes
AC output
Operational Characteristics
DC output voltage stabilization
Soft start
The application of the input power permits the unit to
generate an AC output. The output power increases linearly
until it reaches its calibrated value. This delay from initial
output generation until the nominal value is defined as the
soft start.
No load operation
Inverters require no minimum load for operation within tolerance.
Short circuit protection
The inverter current limitation circuit provides a protection
against an external short circuit. Due to the need for crest
factor and pulse power requirement in many applications, the
current limitation permits twice the nominal output current
to be extracted for up to 1 second. The current limitation
will then be reduced to typically 105% of the nominal value.
Should the overloading persist, and the output voltage reduce
to less than 20% of nominal, then the unit will perceive an
overload condition and turn off. Recycling the input voltage
will remove this latched off condition.
Crest factor
The ability of an inverter to deliver to a load an inrush current
is related to the crest factor. The crest factor is the ratio
between the nominal and the peak current.
Over voltage protection (OVP)
The high power units have this feature. It will shut down the
primary power circuit after a continued OVP operation.
The
input power must be re-cycled in order to remove the unit
from shut down.
The output voltage is measured internally.
This measured value is compared against a reference value.
When the reference value has been reached, this circuit turns
off the power circuit. Once the measured value has reduced
below the reference value the power circuit is once again
permitted to be activated.
Sense leads
Sense leads are internally connected in all standard configurations.
Harmonic distortion
The generated inverter output is designed to follow a true
sine wave signal. Deviation from this sine wave is measured
as distortion. The level of deviation is defined as harmonic
distortion. The total harmonic distortion THD is the
relationship between the harmonic and fundamental wave
forms.
Surge power
The AC output may facilitate the output load through its
ability to provide more then the nominal current for up to 1
second.
Power factor
The AC output may facilitate complex or other loads, through
its ability to provide a phase shifted output current at nominal
power rating. This is once again due to the ability to provide
more than the nominal output current for a limited period of
time.
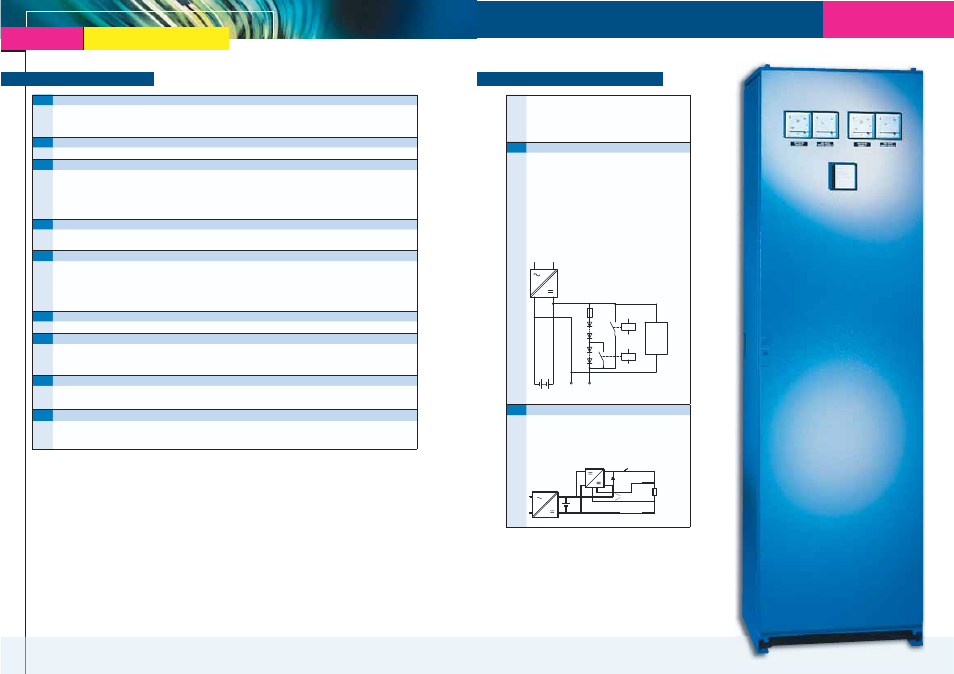
The output voltage of a battery charger with parallel
connected batteries varies substantially with the
charging condition of the battery. For many applications,
however, the load circuit requires a more stabilized
voltage which can be accomplished by:
Voltage dropping diodes
being interconnected between battery and load, reduce
the voltage to a value suitable for the load. They are
short-circuited by one or more contactors only if a partial
reduction or no voltage reduction is required. A control
circuit senses the battery voltage and energizes the
contactors. Voltage dropping diodes cause substantial
power losses as the excess voltage is absorbed by the
diodes. However, due to simplicity, this method is
frequently used, especially if the voltage reduction
is needed only during the short periods of high-rate
charging.
AC input
battery
-
+
battery
charger
DC-load
K1
K2
control
circuit
K1 and K2
for
Switchmode step-up converters
are DC/DC converters supplied from the battery with the
output connected in series to the battery. They present a
very economical solution as they only add voltage when
the battery is discharged. Details see page 47/ 83.
battery
charger
+
-
step-up converter
(long) cable to load
+
-
sense leads
load
