Cartridge operation/features, Shade guide settings – Lincoln Electric IM10039 VIKING 750S AUTO-DARKENING HELMETS User Manual
Page 7
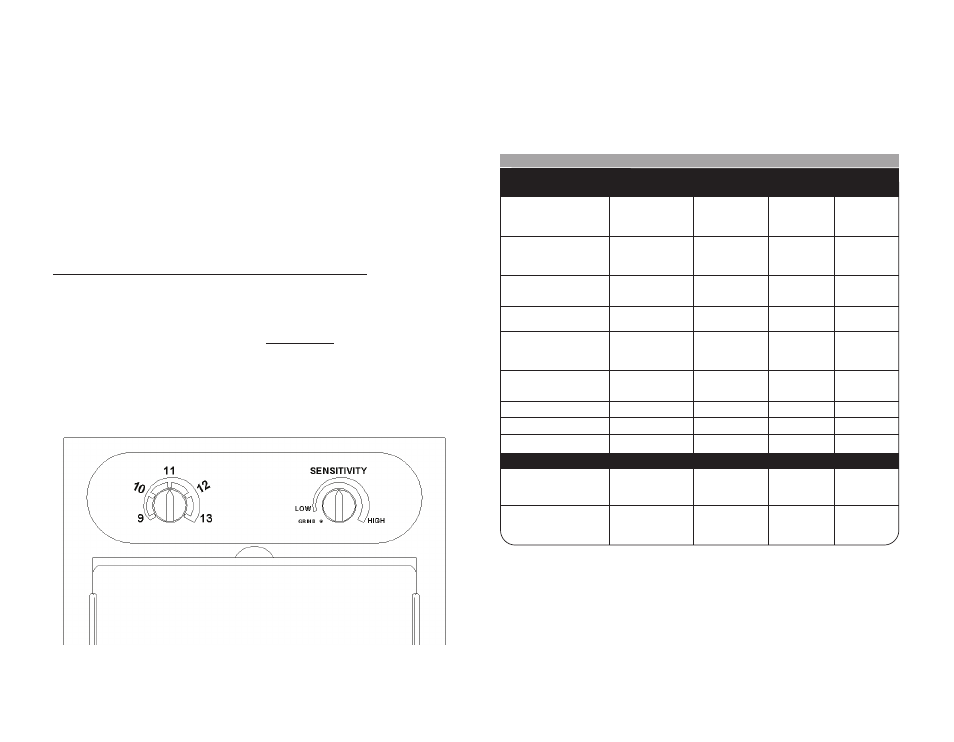
CARTRIDGE OPERATION/FEATURES
Variable Shade Control
The shade can be adjusted from shade 9 to 13 based upon welding process or
application (refer to shade selection chart on page 6). The variable shade con-
trol knob is located on the ADF cartridge as shown below.
Sensitivity Knob
Adjust the light sensitivity by turning the Sensitivity knob to the left or right as
shown in figure below. Turning the knob all the way to the right, the highest set-
ting, is typically selected for normal use. When helmet is used in the presence of
excess ambient light or with another welding machine close by, improved helmet
performance can be obtained with a lower setting by turning the knob to the left to
reduce the sensitivity.
Do not rotate Sensitivity knob to Grind position for welding. See Grind mode
below for more information.
Grind mode
Grind mode can be selected by rotating the Sensitivity knob to left till an audible
click is heard. Grind mode is intended for grinding only not for welding.
Solar Power
This helmet is powered by solar energy. There are no user replaceable batteries.
5
ALWAYS TEST TO BE SURE THE ADF CARTRIDGE IS CHARGED
BEFORE WELDING. The helmet can be placed in sunlight to charge. Do not
store the helmet in a dark cabinet or other storage area for long periods.
While welding, the arc also charges the ADF cartridge.
SHADE GUIDE SETTINGS
If your helmet does not include any one of the shades referenced above, it is
recommended you use the next darker shade.
6
NT 1
GUIDE FOR SHADE NUMBERS
OPERATION
ELECTRODE SIZE
ARC
MINIMUM
SUGGESTED(1)
1/32 in. (mm)
CURRENT (A)
PROTECTIVE
SHADE NO.
SHADE
(COMFORT)
Shielded metal arc
Less than 3 (2.5)
Less than 60
7
–
welding
3-5 (2.5–4)
60-160
8
10
5-8 (4–6.4)
160-250
10
12
More than 8 (6.4)
250-550
11
14
Gas metal arc
Less than 60
7
–
welding and flux
60-160
10
11
cored arc welding
160-250
10
12
250-500
10
14
Gas tungsten arc
Less than 50
8
10
welding
50-150
8
12
150-500
10
14
Air carbon
(Light)
Less than 500
10
12
Arc cutting
(Heavy)
500-1000
11
14
Plasma arc welding
Less than 20
6
6 to 8
20-100
8
10
100-400
10
12
400-800
11
14
Plasma arc cutting
(Light)
(2)
(2)
(2)
Less than 300
8
9
(Medium)
300-400
9
12
(Heavy)
400-800
10
14
Torch brazing
–
–
3 or 4
Torch soldering
–
–
2
Carbon arc welding
–
–
14
PLATE THICKNESS
in.
mm
Gas welding
Light
Under 1/8
Under 3.2
4 or 5
Medium
1/8 to 1/2
3.2 to 12.7
5 or 6
Heavy
Over 1/2
Over 12.7
6 or 8
Oxygen cutting
Light
Under 1
Under 25
3 or 4
Medium
1 to 6
25 to 150
4 or 5
Heavy
Over 6
Over 150
5 or 6
(1)
As a rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark, then go to a lighter shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going
below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas welding or cutting where the torch produces a high yellow light, it is desirable to use a filter lens that absorbs
the yellow or sodium line the visible light of the (spectrum) operation
(2)
These values apply where the actual arc is clearly seen. Experience has shown that lighter filters may be used when the arc is hidden by the
workpiece.
.
Data from ANSI Z49.1-2005
