GC EUROPE Unifil Bond User Manual
Page 9
GC
UniFil Bond Technical manual version 1.10, November 2005, 9/23
6.0 Test results
GC UniFil Bond is part of the GC UniFil range of products, successfully introduced in
1998
by GCC in the domestic market, Japan.
GC UniFil comprises a high quality range of resin bonding agents and composite
materials and is well appreciated, like GC Fuji glass ionomers, for ease of use and
reliable results. In Europe only GC UniFil Bond and GC UniFil Flow are sold.
Due to the availability in Japan for a long period, several publications can be found in
the literature. In the chapter 8 a small selection taken from available data is listed.
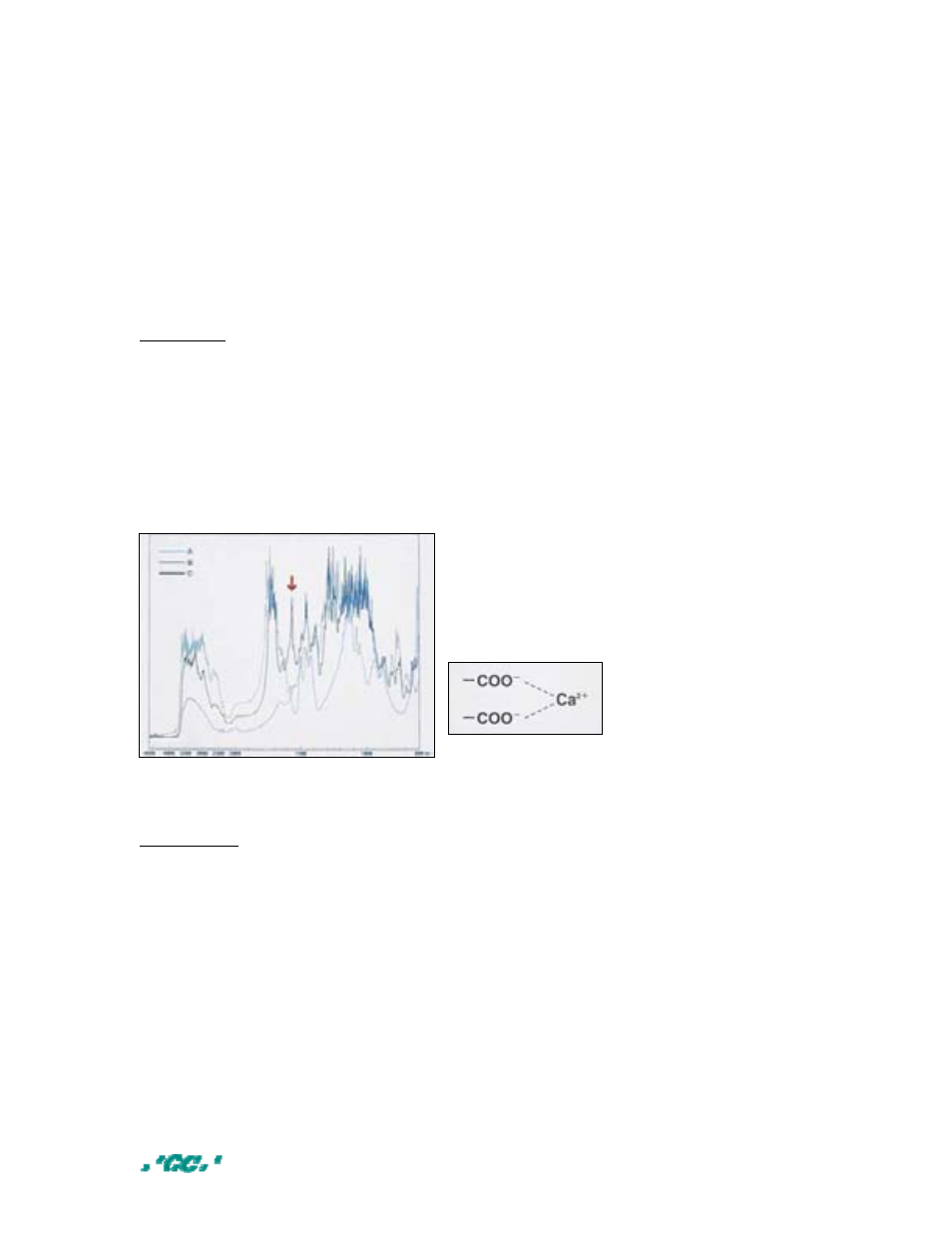
IR analysis
To verify the formation of calcium carboxylate, IR analysis was performed. Bovine
enamel was ground into apatite powder (A). GC UniFil Bond self etching primer was
kept in a container at 45 °C and alcohol and water were removed. After light curing,
the hardened primer was ground and used as control powder (B). Self etching
primer was applied to apatite powder, kept and stored in a container at 45 °C and
water and alcohol were removed. Primed powder was light cured and ground into
test powder (C) .
From the IR analysis it can be concluded that
only powder C shows a peak near 1550 cm
-1
.
This peak represents the formation of Calcium
carboxylate when the self etching primer
comes into contact with hydroxyapatite from
the tooth
.
XPS analysis
In the study “Bonding Mechanism and Micro-Tensile Bond Strength of a 4-MET based
self-Etching Adhesive“, B.Van Meerbeek, Y.Yoshida and others analyzed the bonding
mechanism chemically using XPS. It was concluded that the bonding mechanism of
UniFil Bond to dentine is twofold. Micro-mechanical bonding was established by
monomer interdiffusion into a shallow, partially demineralized dentine layer.
Chemical bonding was obtained by ionic interaction of the carboxyl group of 4-MET
with calcium of hydroxyapatite that remained around collagen.
