GC EUROPE Unifil Bond User Manual
Page 7
GC
UniFil Bond Technical manual version 1.10, November 2005, 7/23
5.0 Adhesion mechanism
At the heart of GC UniFil Bond’s performance is the 4-MET molecule in the primer
solution.
4-MET is derived from 4-META by hydrolysis during the manufacturing process and
compared to the latter is more hydrophilic and acidic. The functional monomer 4-
MET is characterized by self etching and adhesive properties and inherently has very
good diffusion properties.
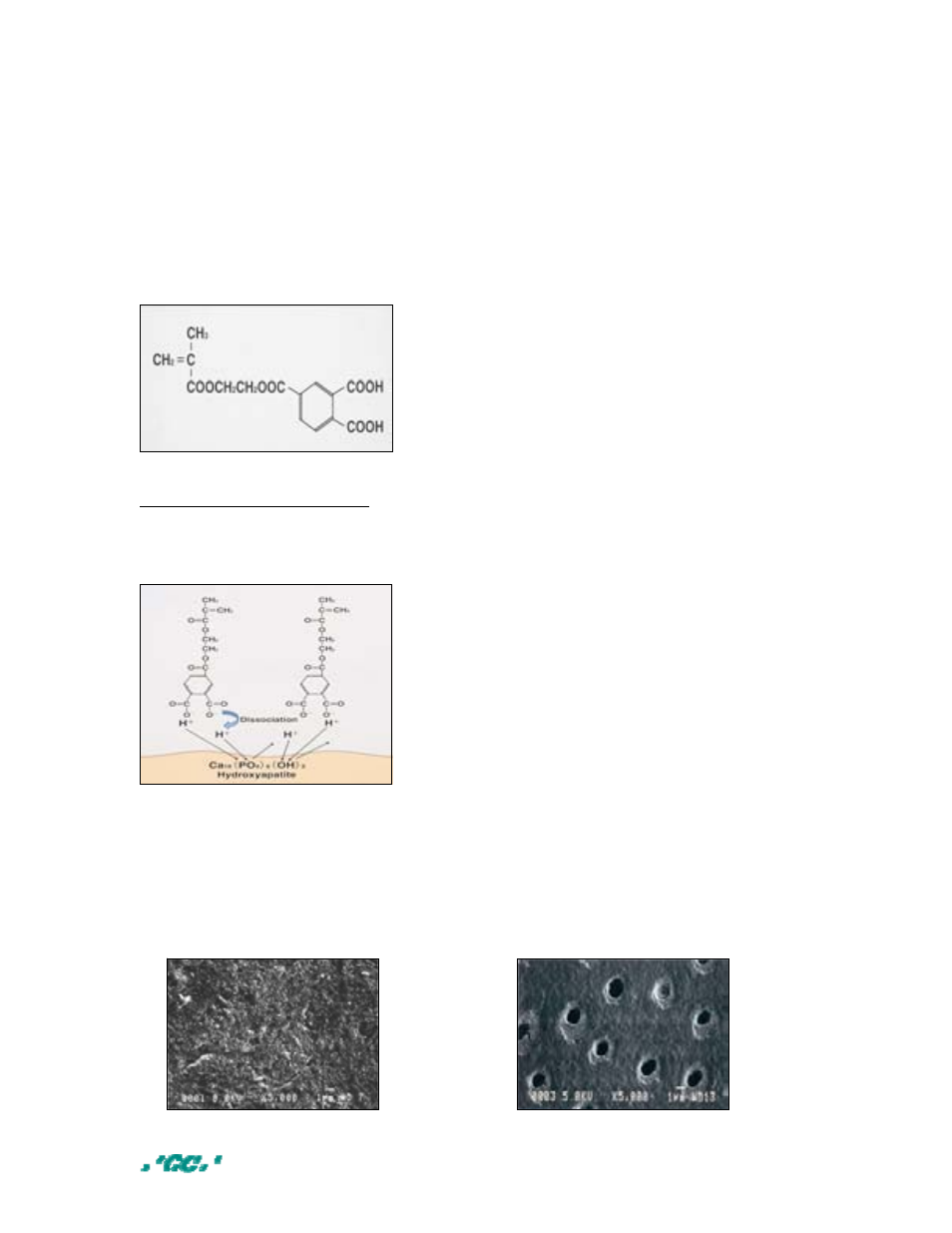
Self-etching primer / 4 - MET
As can be seen from the figure below, the carboxyl group (COOH) of 4-MET can
dissociate into hydrogen (H
+
) and carboxylic (COO
-
) ions.
This dissociation will result in both (self) etching of tooth surfaces and chemical
adhesion to calcium.
• Self-etching properties
Both enamel and dentine surfaces will be decalcified due to the freely available
hydrogen ions and consequently dissolution of the outer surfaces (≤1µm) of the
hydroxyapatite will take place. The pH of GC UniFil Bond Primer is 2.0.
4-MET
Dissociation of 4-MET when applied to tooth surfaces
