3B Scientific Electrostatic Equipment Set User Manual
Page 2
5
3. Instructions for use
• The equipment only produces satisfactory experi-
mental results if kept clean and dry.
• Discharge experiment components before use.
• When the weather is damp, it is advisable to use a
fan.
• Assemble the experiments on the stand and con-
nect to the Wimshurst machine or Van der Graaf
generator with connection chains.
• Observe safety advice.
4. Example experiments
4.1 Discharge from points (Fig.1)
•
Place the triskelion wheel (3) on the needle bearing
attached to the stand. Connect to the source of
charge to charge up the wheel.
•
The triskelion wheel starts to turn because a jet
of charge flows rapidly out of the points and
propels the wheel.
•
Increasing the charge causes the wheel to spin
more quickly.
4.2 Double pendulum (Fig.2)
•
A double pendulum made of elder pith (7) is at-
tached to the hook stand. Connect to the source
of charge to charge up the pendulum.
•
Since the pieces of elder pith assume the same
charge, they repel one another.
•
The double pendulum is a simple electroscope.
4.3 Bundle of tissue paper (Fig.3)
•
Attach the bundle of tissue paper (8) to the stand,
connect to the source of charge and gradually in-
crease the charge.
•
The strips of paper all repel one another and
spread out to all sides to look like an umbrella
frame.
•
The bundle of tissue paper is also a simple elec-
troscope.
4.4 Bell chimes (Fig.4)
•
Attach the bell chimes (16) to the stand, connect
to the source of charge and gradually increase the
charge until the hammers strike the bells.
•
Be careful. Excessive charge can cause sparks be-
tween the mountings.
•
The supply of charge causes the hammers to
charge up and be attracted or repelled by the bells.
•
When the hammers touch the bells, they discharge
and swing back. The process starts again when
they are loaded with the opposite charge.
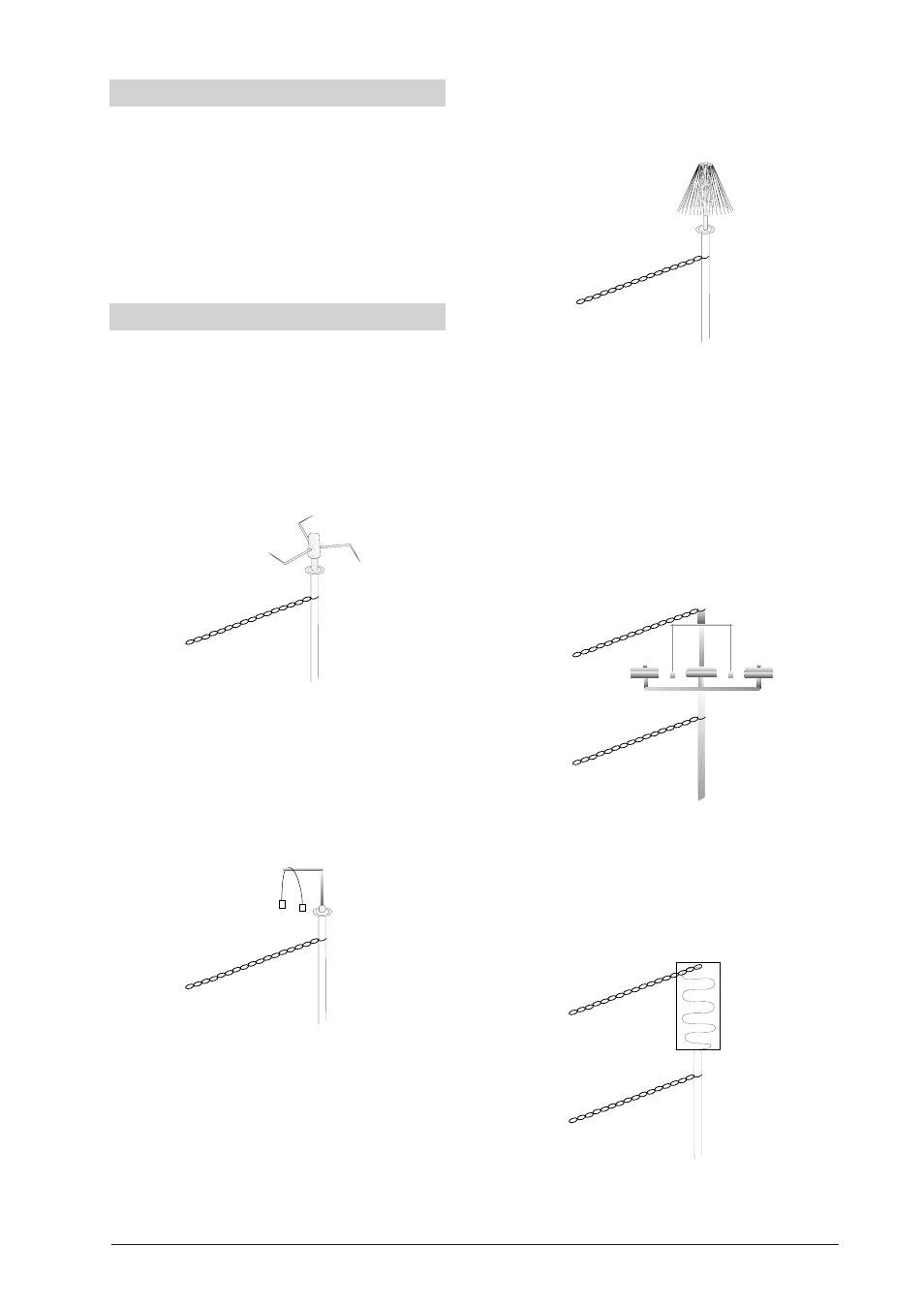
4.5 Luminous pane (Fig.5)
•
Attach the luminous plane (1) to the stand, connect
to the source of charge and gradually increase the
charge.
•
When the voltage is large sparks cross the spaces
between the conductors of the pane.
(Fig. 1)
(Fig. 2)
(Fig. 3)
(Fig. 4)
(Fig. 5)
