Retrieving data from ram or clock, Writing data to ram or clock – Rainbow Electronics DS1747P User Manual
Page 5
DS1747/DS1747P
5 of 18
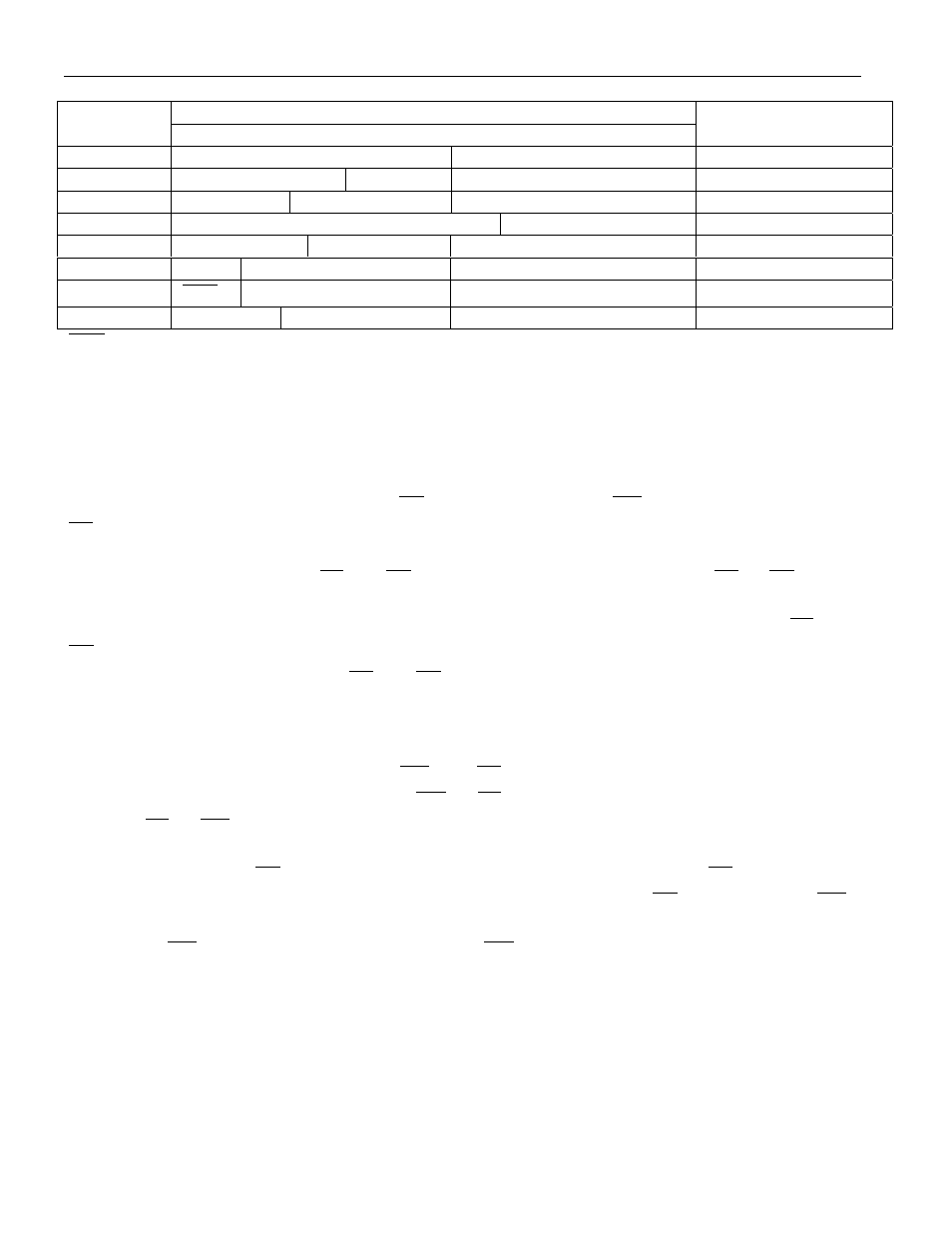
DS1746 REGISTER MAP Table 2
DATA
ADDRESS
B
7
B
6
B
5
B
4
B
3
B
2
B
1
B
0
FUNCTION/RANGE
7FFFF
10 YEAR
YEAR
YEAR
00-99
7FFFE
X X X
10 MO
MONTH
MONTH
01-12
7FFFD
X X
10 DATE
DATE
DATE
01-31
7FFFC
BF FT X X X
DAY
DAY
01-07
7FFFB
X X
10 HOUR
HOUR
HOUR
00-23
7FFFA
X
10 MINUTES
MINUTES
MINUTES
00-59
7FFF9
OSC
10 SECONDS
SECONDS
SECONDS
00-59
7FFF8
W R
10 CENTURY
CENTURY
CENTURY
00-39
OSC = STOP BIT
R = READ BIT
FT = FREQUENCY TEST
W = WRITE BIT
X = SEE NOTE BELOW
BF = BATTERY FLAG
NOTE:
All indicated “X” bits are not dedicated to any particular function and can be used as normal RAM bits.
RETRIEVING DATA FROM RAM OR CLOCK
The DS1747 is in the read mode whenever OE (output enable) is low, WE (write enable) is high, and
CE (chip enable) is low. The device architecture allows ripple-through access to any of the address
locations in the NV SRAM. Valid data will be available at the DQ pins within t
AA
after the last address
input is stable, providing that the CE and OE access times and states are satisfied. If CE or OE access
times and states are not met, valid data will be available at the latter of chip enable access (t
CEA)
or at
output enable access time (t
OEA)
. The state of the data input/output pins (DQ) is controlled by CE and
OE . If the outputs are activated before t
AA,
the data lines are driven to an intermediate state until t
AA.
If
the address inputs are changed while CE and OE remain valid, output data will remain valid for output
data hold time (t
OH
)
but will then go indeterminate until the next address access.
WRITING DATA TO RAM OR CLOCK
The DS1747 is in the write mode whenever WE , and CE are in their active state. The start of a write is
referenced to the latter occurring transition of WE or CE . The addresses must be held valid throughout
the cycle. CE or WE must return inactive for a minimum of t
WR
prior to the initiation of another read or
write cycle. Data in must be valid t
DS
prior to the end of write and remain valid for t
DH
afterward. In a
typical application, the OE signal will be high during a write cycle. However, OE can be active
provided that care is taken with the data bus to avoid bus contention. If OE is low prior to WE
transitioning low the data bus can become active with read data defined by the address inputs. A low
transition on WE will then disable the output t
WEZ
after WE goes active.
