Pin description, Detailed description – Rainbow Electronics MAX859 User Manual
Page 6
MAX856–MAX859
3.3V/5V or Adjustable-Output,
Step-Up DC-DC Converters
6
_______________________________________________________________________________________
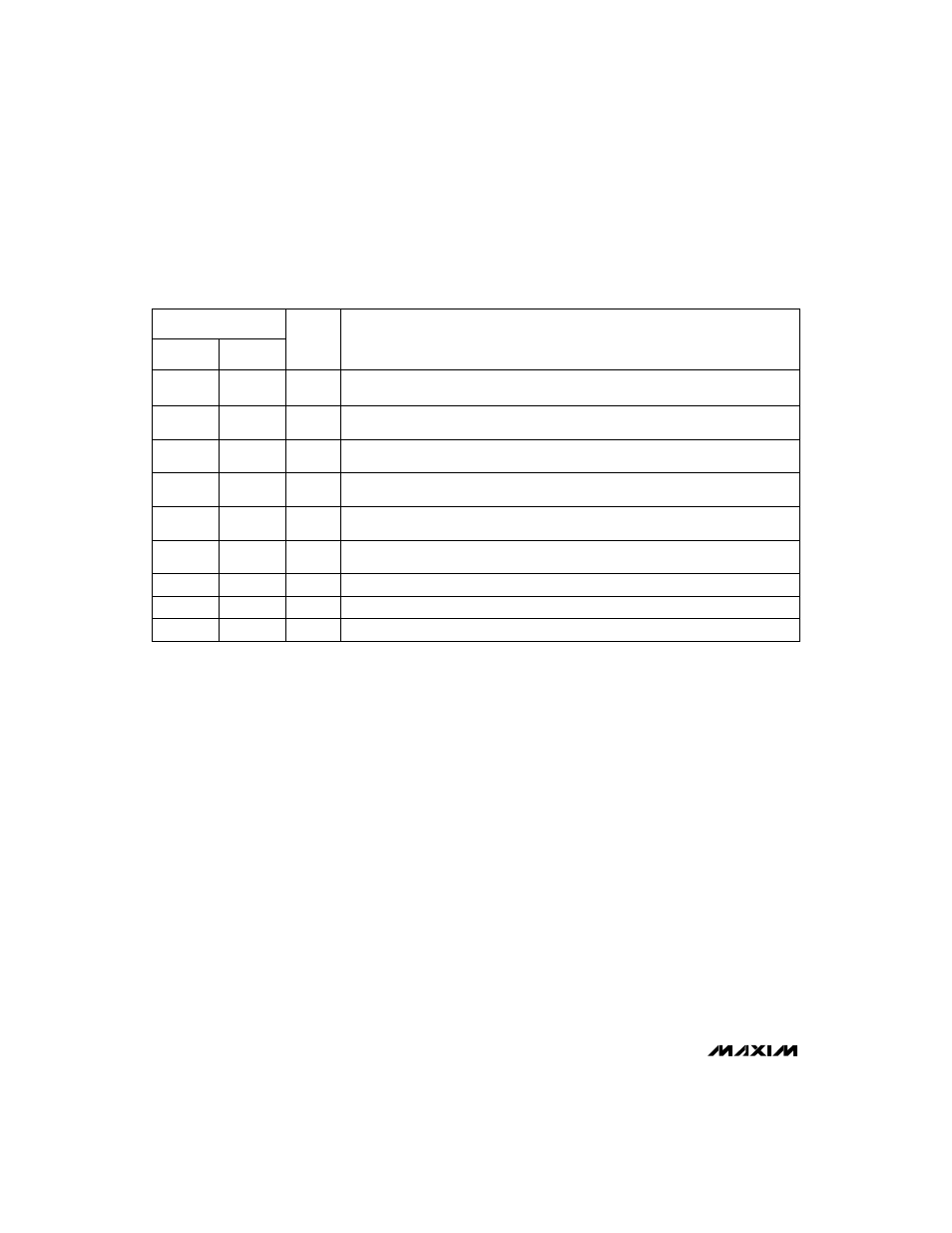
______________________________________________________________Pin Description
N-Channel Power-MOSFET Drain
8
8
Low-Battery Output. An open-drain N-channel MOSFET sinks current when the voltage at
LBI drops below 1.25V.
4
4
Low-Battery Input. When the voltage on LBI drops below 1.25V, LBO sinks current.
If not used, connect to V
IN
.
5
5
Connect OUT to the regulator output. OUT provides bootstrap power to the IC.
6
6
Power Ground. Must be low impedance; solder directly to ground plane.
7
7
1.25V Reference Voltage Output. Bypass with 0.22µF to GND (0.1µF if there is no external
reference load). Maximum load capability is 250µA source, 20µA sink.
3
3
Feedback Input for adjustable-output operation. Connect to an external resistor voltage
divider between OUT and GND.
2
—
Selects the output voltage; connect to GND for 5V output, and to OUT for 3.3V
output.
—
2
Shutdown Input. When low, the entire circuit is off and V
OUT
= V
IN
- V
D,
where V
D
is the
forward voltage drop of the external Schottky rectifier.
1
1
FUNCTION
PIN
LX
LBO
LBI
OUT
GND
REF
FB
3/
–
5
–
–
S
—
H
—
D
—
N
–
NAME
MAX856
MAX858
MAX857
MAX859
_______________Detailed Description
Operating Principle
The MAX856–MAX859 combine a switch-mode regula-
tor, N-channel power MOSFET, precision voltage refer-
ence, and power-fail detector in a single monolithic
device. The MOSFET is a “sense-FET” type for best
efficiency, and has a very low gate threshold voltage to
ensure start-up with low battery voltages (0.8V typ).
PFM Control Scheme
A unique minimum-off-time, current-limited pulse-fre-
quency modulation (PFM) control scheme is a key fea-
ture of the MAX856 series (Figure 1). This scheme
combines the high output power and efficiency of a
pulse-width modulation (PWM) device with the ultra-low
quiescent current of a traditional PFM pulse-skipper.
There is no oscillator; at heavy loads, switching is
accomplished through a constant-peak-current limit in
the switch, which allows the inductor current to vary
between this peak limit and some lesser value. At light
loads, switching frequency is governed by a pair of
one-shots, which set a minimum off-time (1µs) and a
maximum on-time (4µs). The switching frequency
depends upon the load and the input voltage, and can
range up to 500kHz.
The peak switch current of the internal MOSFET power
switch is fixed at 500mA ±100mA (MAX856/MAX857)
or 125mA ±25mA (MAX858/MAX859). The switch’s on-
resistance is typically 1
Ω
(MAX856/MAX857) or 4
Ω
(MAX858/MAX859), resulting in a switch voltage drop
(V
SW
) of about 500mV under high output loads. The
value of V
SW
will decrease with light current loads.
Conventional PWM converters generate constant-fre-
quency switching noise, whereas the unique architec-
ture of the MAX856–MAX859 produces variable-fre-
quency switching noise. However, unlike conventional
pulse-skippers (where noise amplitude varies with input
voltage), noise in the MAX856 series does not exceed
the switch current limit times the filter-capacitor equiva-
lent series resistance (ESR).
Voltage Reference
The precision voltage reference is suitable for driving
external loads, such as an analog-to-digital converter.
The voltage-reference output changes less than ±2%
when sourcing up to 250µA and sinking up to 20µA. If
the reference drives an external load, bypass it with
0.22µF to GND. If the reference is unloaded, bypass it
with at least 0.1µF.
