Rainbow Electronics MAX1299 User Manual
Page 12
MAX1298/MAX1299
12-Bit Serial-Output Temperature Sensors
with 5-Channel ADC
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
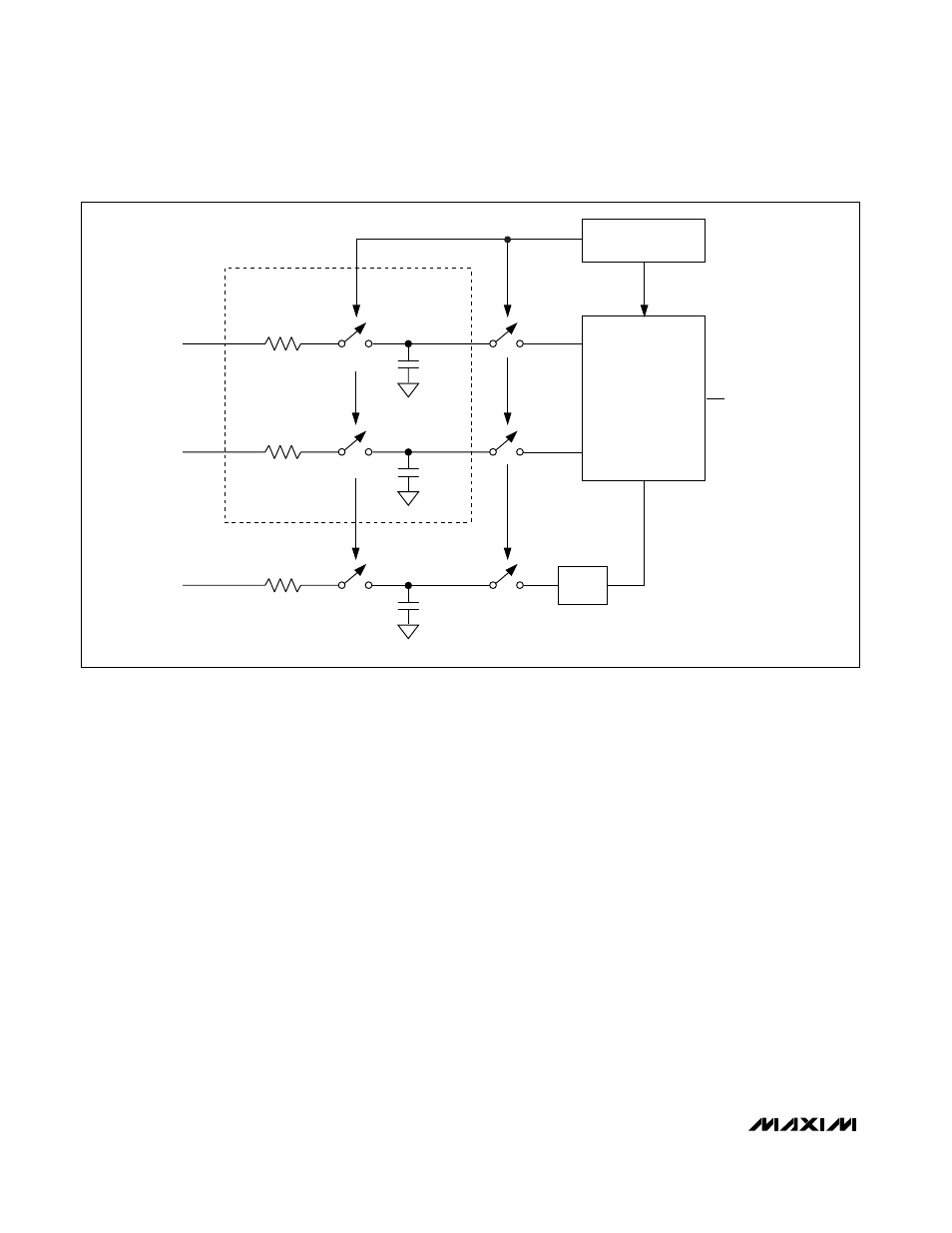
Converter Operation
Figure 2 shows a simplified model of the converter
input structure. Once initiated, a voltage conversion
requires 64 f
CLK
periods, where f
CLK
is the internal
master clock. Each conversion is preceded by 13 f
CLK
periods of warm-up time, performed in twelve 4 f
CLK
period cycles, and followed by 3 f
CLK
periods to load
the output register. SSTRB falls at the beginning of a
conversion and rises at the end of a conversion.
Inputs IN+ and IN- charge capacitors C
HOLDP
and
C
HOLDN
, respectively, during the acquisition interval
that occurs during the first f
CLK
period of the first con-
version cycle. In the second f
CLK
period, the T/H
switches open so that charge is retained on C
HOLDP
and C
HOLDN
as a sample of the differential voltage
between IN+ and IN-. This charge is transferred to the
ADC during the third and fourth f
CLK
periods.
The reference sampling process begins in the second
conversion cycle and continues until the conversion is
complete. Sampling occurs during the second and
fourth f
CLK
periods to yield an effective doubling of the
reference voltage. The reference sampling requirement
is signal dependent and may or may not occur in every
subsequent conversion cycle.
Temperature conversion is essentially nothing more than
subtracting the results of two sequential voltage conver-
sions. The only difference is that output registers are not
loaded at the end of the first conversion. Thus, tempera-
ture conversions require 2 x 64 - 3 = 125 f
CLK
periods.
Figures 3a and 3b show timing diagrams for voltage
and temperature conversions, respectively.
Track/Hold
The T/H stage for the MAX1298/MAX1299 is a simple
switched-capacitor sampling operation. The time
required for the T/H stage to acquire an input signal is
a function of how fast its input capacitance is charged.
If the signal source impedance is high, the acquisition
time lengthens and more time must be allowed
between conversions. The acquisition time (t
ACQ
) is the
maximum time the device takes to acquire the signal.
Calculate this with the following equation:
t
ACQ
= 7 (R
s
+ R
IN
) C
IN
where R
s
is the source impedance of the input signal,
R
IN
is the T/H input impedance (40k
Ω), and C
IN
is the
TIMING/CONTROL
LOGIC
FULLY
DIFFERENTIAL
A/D
OUTPUT
GAIN
OF 2
IN+
IN-
REF
TRACK AND HOLD
CHOLDP
4pF
CHOLDN
4pF
CREF
4pF
RR
30k
RIN
40k
RIN
40k
T/H
T/H
Figure 2. Converter Input Structure
