Inverting dc-dc controllers – Rainbow Electronics MAX776 User Manual
Page 12
MAX774/MAX775/MAX776
Choosing an Inductor
Practical inductor values range from 10µH to 50µH.
The maximum inductor value is not particularly critical.
For highest current at high
V
OUT
to V+ ratios, the
inductor should not be so large that the peak current
never reaches the current limit. That is:
[
V+(min) - V
SW
(max)
]
x 12µs
L(max)
≤
_______________________________
I
LIM
(max)
This is only important if
V
IN
1
t
OFF
(min)
_______
< — = ___________
V
OUT
6
t
ON
(max)
More important is that the inductor not be so small that the
current rises much faster than the current-limit comparator
can respond. This would be wasteful and reduce effi-
ciency. Calculate the minimum inductor value as follows:
[
V+(max) - V
SW
(min)
]
x 0.3µs
L(min)
≥
_______________________________
δ
(I) x I
LIM
(min)
Where L is in µH, 0.3µs is an ample time for the com-
parator response, I
LIM
is the current limit (see
Current-
Sense Resistor section), and
δ
(I) is the allowable per-
centage of overshoot. As an example, Figure 2's circuit
uses a 3A peak current. If we allow a 15% overshoot
and 15V is the maximum input voltage, then L(min) is
16µH. The actual value of L above this limit has minimal
effect on this circuit's operation.
For highest efficiency, use a coil with low DC resistance.
Coils with 30m
Ω
or lower resistance are available. To
minimize radiated noise, use a torroid, pot-core, or shield-
ed-bobbin inductor. Inductors with a ferrite core or equiv-
alent are recommended. Make sure that the inductor’s
saturation current rating is greater than I
LIM
(max).
Diode Selection
The ICs’ high switching frequencies demand a high-
speed rectifier. Schottky diodes such as the 1N5817 to
1N5822 families are recommended. Choose a diode
with an average current rating approximately equal to
or greater than I
LIM
(max) and a voltage rating higher
than V
IN
(max) + V
OUT
. For high-temperature applica-
tions, Schottky diodes may be inadequate due to their
high leakage currents; instead, high-speed silicon
diodes may be used. At heavy loads and high temper-
ature, the benefits of a Schottky diode’s low forward
voltage may outweigh the disadvantages of its high
leakage current.
Current-Sense Resistor
The current-sense resistor limits the peak switch cur-
rent to 210mV/R
SENSE
, where R
SENSE
is the value of
the current-sense resistor, and 210mV is the current-
sense comparator threshold (see Current-Limit Trip
Level in the
Electrical Characteristics).
To maximize efficiency and reduce the size and cost of
external components, minimize the peak current.
However, since the output current is a function of the
peak current, do not set the limit too low. Refer to
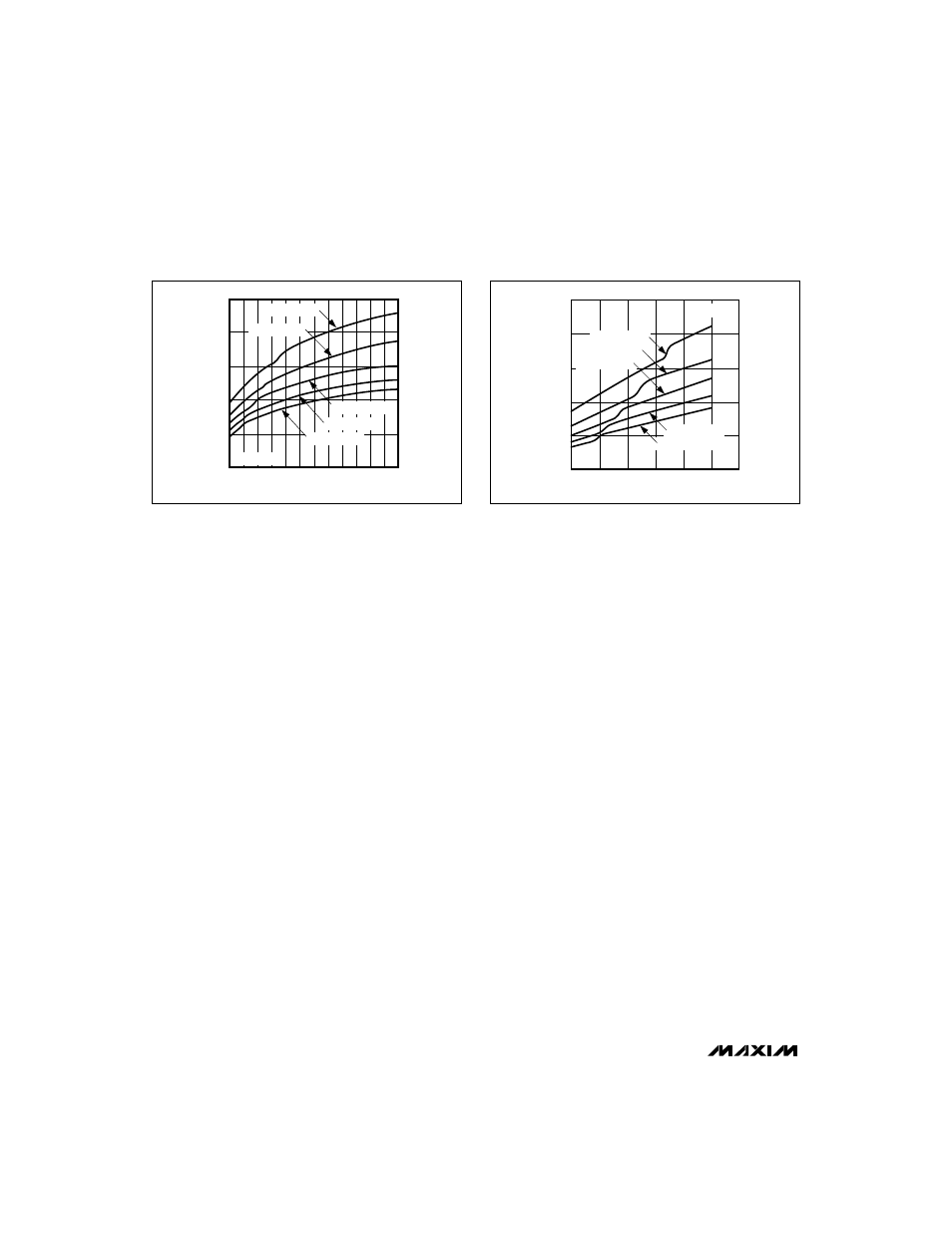
Figures 6–9 to determine the sense resistor (and, there-
fore, peak current) for the required load current.
-5V/-12V/-15V or Adjustable,
High-Efficiency, Low I
Q
Inverting DC-DC Controllers
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
MAXIMUM OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3 4
5 6
7
8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15
V
OUT
= -5V
R
SENSE
= 0.05
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.06
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.08
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.09
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.07
Ω
MAX775-fig6
Figure 6. MAX774 Maximum Output Current vs. Input Voltage
(V
OUT
= -5V)
Figure 7. MAX775 Maximum Output Current vs. Input Voltage
(V
OUT
= -12V)
MAXIMUM OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
0
200
400
600
800
1000
9
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
MAX775-FIG07
3
4
5
6
7
8
R
SENSE
= 0.05
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.06
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.07
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.08
Ω
R
SENSE
= 0.09
Ω
V
OUT
= -12V
