Rainbow Electronics DS1720 User Manual
Page 3
DS1720
030598 3/12
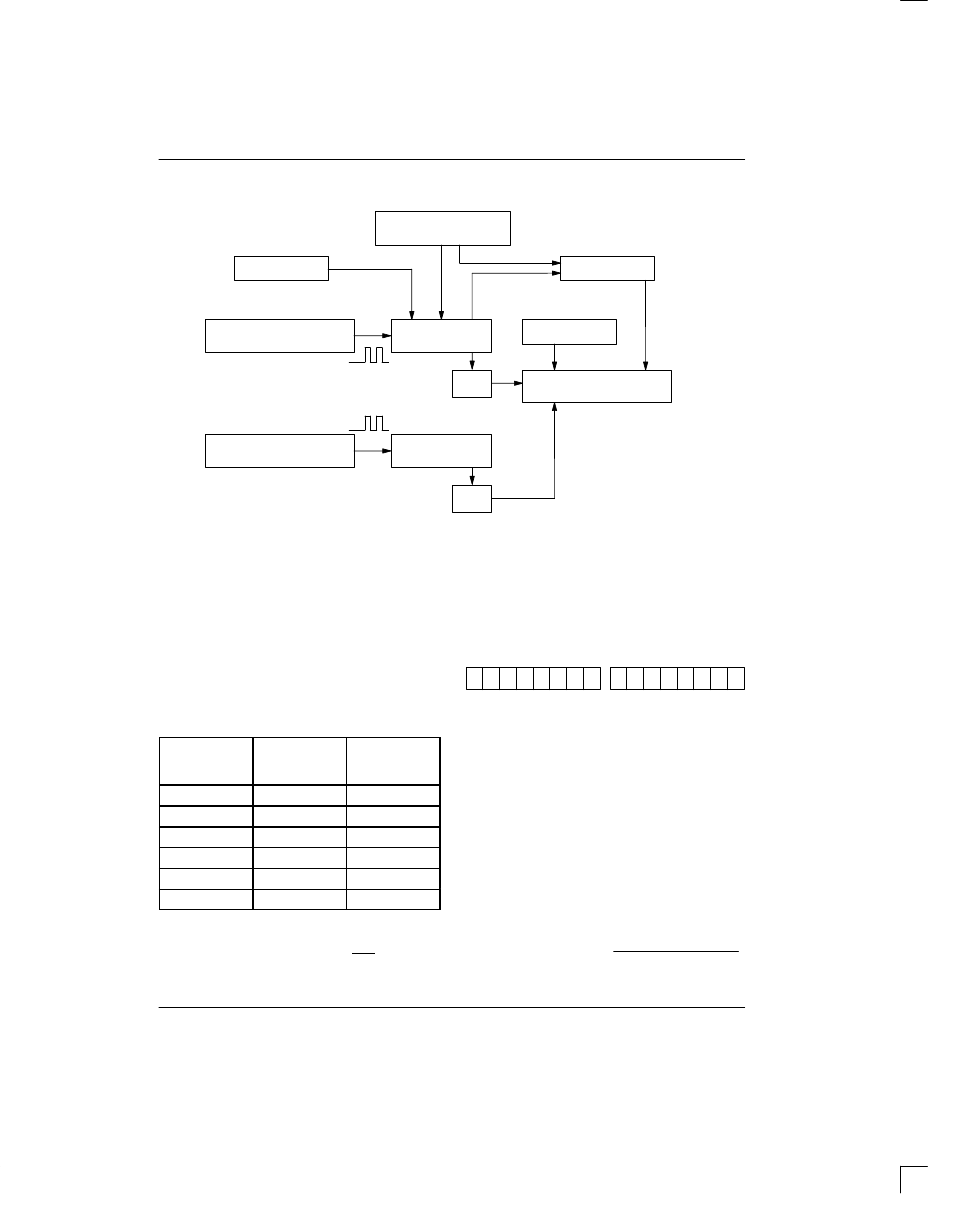
TEMPERATURE MEASURING CIRCUITRY Figure 2
SLOPE ACCUMULATOR
PRESET
PRESET
COUNTER
COUNTER
=0
=0
STOP
INC
COMPARE
TEMPERATURE REGISTER
LOW TEMPERATURE
COEFFICIENT OSCILLATOR
HIGH TEMPERATURE
COEFFICIENT OSCILLATOR
SET/CLEAR
LSB
This calculation is done inside the DS1720 to provide
0.5
°
C resolution. The temperature reading is provided
in a 9–bit, two’s complement reading by issuing a READ
TEMPERATURE command. Table 1 describes the
exact relationship of output data to measured tempera-
ture. The data is transmitted serially through the 3–wire
serial interface, LSB first. The DS1720 can measure
temperature over the range of –55
°
C to +125
°
C in 0.5
°
C
increments. For Fahrenheit usage, a lookup table or con-
version factor must be used.
TEMPERATURE/DATA RELATIONSHIPS
Table 1
TEMP
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
(Binary)
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
(Hex)
+85
°
C
0 10101010
00AA
+25
°
C
0 00110010
0032h
+
1
/2
°
C
0 00000001
0001h
+0
°
C
0 00000000
0000h
–
1
/
2
°
C
1 11111111
01FFh
–25
°
C
1 11001110
01CEh
Since data is transmitted over the 3–wire bus LSB first,
temperature data can be written to/read from the
DS1720 as either a 9–bit word (taking RST low after the
9th (MSB) bit), or as two transfers of 8–bit words, with
the most significant 7 bits being ignored or set to zero,
as illustrated in Table 1. After the MSB, the DS1720 will
output 0s.
Note that temperature is represented in the DS1720 in
terms of a
1
/
2
°
C LSB, yielding the following 9–bit format:
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
MSB
LSB
T = –25
°
C
Higher resolutions may be obtained by reading the tem-
perature, and truncating the 0.5
°
C bit (the LSB) from the
read value. This value is TEMP_READ. The value left in
the counter may then be read by issuing a READ
COUNTER command. This value is the count remain-
ing (COUNT_REMAIN) after the gate period has
ceased. By loading the value of the slope accumulator
into the count register (using the READ SLOPE com-
mand), this value may then be read, yielding the number
of counts per degree C (COUNT_PER_C) at that tem-
perature. The actual temperature may be then be calcu-
lated by the user using the following:
TEMPERATURE = TEMP_READ – 0.25
)
(COUNT_PER_C – COUNT_REMAIN)
COUNT_PER_C
