Read/write time slots – Rainbow Electronics DS1996 User Manual
Page 15
DS1996
15 of 18
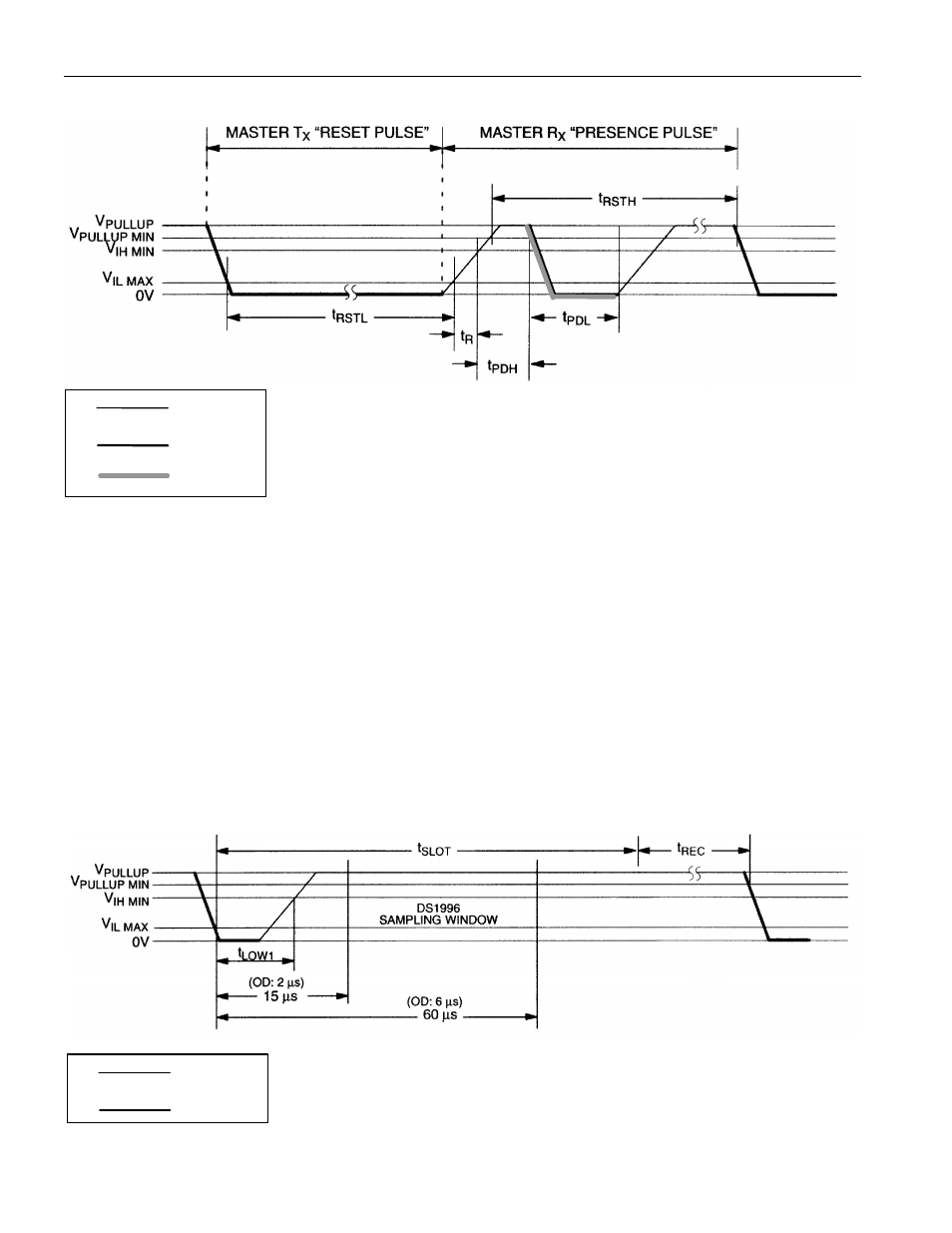
INITIALIZATION PROCEDURE “RESET AND PRESENCE PULSES” Figure 10
Regular Speed
Overdrive Speed
480
µ
s
≤
t
RSTL
<
∞
*
48
µ
s
≤
t
RSTL
< 80
µ
s
480
µ
s
≤
t
RSTH
<
∞
(includes recovery time)
48
µ
s
≤
t
RSTH
<
∞
15
µ
s
≤
PDH
< 60
µ
s
2
µ
s
≤
t
PDH
< 6
µ
s
60
µ
s
≤
t
PDL
< 240
µ
s
8
µ
s
≤
t
PDL
< 24
µ
s
* In order not to mask interrupt signaling by other devices on the 1-Wire bus, t
RSTL
+ t
R
should always be
less than 960
µ
s.
READ/WRITE TIME SLOTS
The definitions of write and read time slots are illustrated in Figure 11. All time slots are initiated by the
master driving the data line low. The falling edge of the data line synchronizes the DS1996 to the master
by triggering a delay circuit in the DS1996. During write time slots, the delay circuit determines when the
DS1996 will sample the data line. For a read data time slot, if a ”0” is to be transmitted, the delay circuit
determines how long the DS1996 will hold the data line low overriding the 1 generated by the master. If
the data bit is a ”1”, the iButton will leave the read data time slot unchanged.
READ/WRITE TIMING DIAGRAM Figure 11
Write-One Time Slot
Regular Speed
Overdrive Speed
60
µ
s
≤
t
SLOT
< 120
µ
s
6
µ
s
≤
t
SLOT
< 16
µ
s
1
µ
s
≤
t
LOW1
< 15
µ
s
1
µ
s
≤
t
LOW1
< 2
µ
s
1
µ
s
≤
t
REC
<
∞
1
µ
s
≤
t
REC
<
∞
RESISTOR
MASTER
DS1996
RESISTOR
MASTER
