Design procedure – Rainbow Electronics MAX15031 User Manual
Page 12
MAX15031
80V, 300mW Boost Converter and Current
Monitor for APD Bias Applications
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
Design Procedure
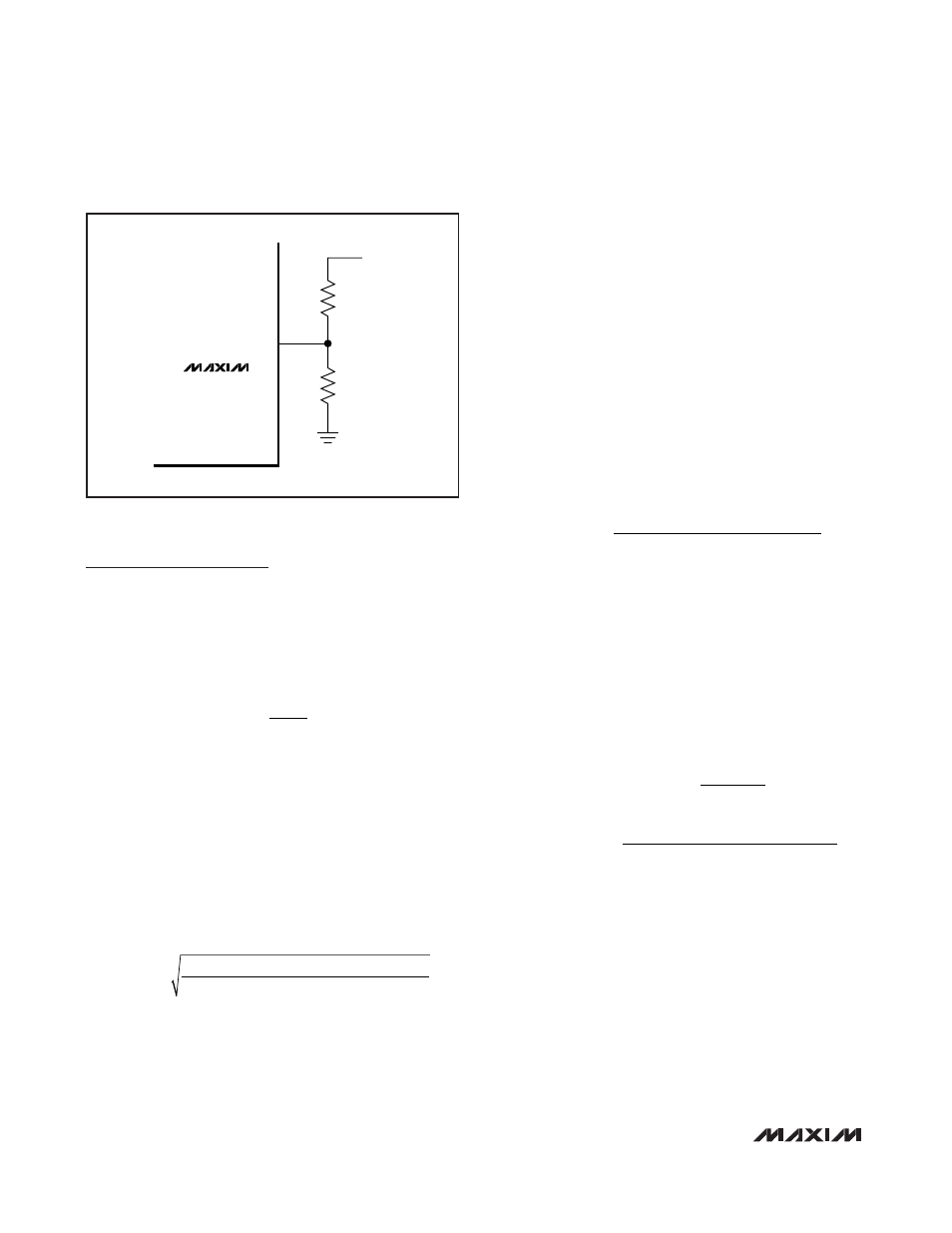
Setting the Output Voltage
Set the MAX15031 output voltage by connecting a resis-
tive divider from the output to FB to SGND (Figure 1).
Select R
1
(FB to SGND resistor) between 200k
Ω and
400k
Ω. Calculate R
2
(V
OUT
to FB resistor) using the fol-
lowing equation:
where V
OUT
can range from (V
IN
+ 1V) to 76V and V
REF
= 1.245V or V
CNTRL
depending on the V
CNTRL
value.
For V
CNTRL
> 1.5V, the internal 1.245V (typ) reference
voltage is used as the feedback set point (V
REF
=
1.245V) and for V
CNTRL
< 1.25V, V
REF
= V
CNTRL
.
Determining Peak Inductor Current
If the boost converter remains in the discontinuous
mode of operation, then the approximate peak inductor
current, I
LPEAK
(in amperes), is represented by the for-
mula below:
where T
S
is the switching period in microseconds,
V
OUT
is the output voltage in volts, V
IN_MIN
is the mini-
mum input voltage in volts, I
OUT_MAX
is the maximum
output current in amperes, L is the inductor value in
microhenrys, and
η is the efficiency of the boost con-
verter (see the
Typical Operating Characteristics
).
Determining the Inductor Value
Three key inductor parameters must be specified for
operation with the MAX15031: inductance value (L),
inductor saturation current (I
SAT
), and DC resistance
(DCR). In general, the inductor should have a saturation
current rating greater than the maximum switch peak
current-limit value (I
LIM-LX
= 1.6A). Choose an inductor
with a low-DCR resistance for reasonable efficiency.
Use the following formula to calculate the lower bound
of the inductor value at different output voltages and
output currents. This is the minimum inductance value
for discontinuous mode operation for supplying full
300mW of output power.
where V
IN_MIN
, V
OUT
(both in volts), and I
OUT
(in
amperes) are typical values (so that efficiency is opti-
mum for typical conditions), T
S
(in microseconds) is the
period,
η is the efficiency, and I
LIM_LX
is the peak
switch current in amperes (see the
Electrical
Characteristics
table).
Calculate the optimum value of L (L
OPTIMUM
) to ensure
the full output power without reaching the boundary
between continuous conduction mode (CCM) and DCM
using the following formula:
For a design in which V
IN
= 3.3V, V
OUT
= 70V, I
OUT
=
3mA,
η = 45%, I
LIM-LX
= 1.3A, and T
S
= 2.5µs: L
MIN
=
1.3µH and L
MAX
= 23µH.
For a worse-case scenario in which V
IN
= 2.9V, V
OUT
=
70V, I
OUT
= 4mA,
η = 43%, I
LIM-LX
= 1.3A, and T
S
=
2.5µs: L
MIN
= 1.8µH and L
MAX
= 15µH.
The choice of 4.7µH is reasonable given the worst-case
scenario above. In general, the higher the inductance,
the lower the switching noise. Load regulation is also
better with higher inductance.
where L
[ H]
V
(V
V
)
T
2
MAX
IN_MIN
2
OUT
IN_MIN
S
µ
η
=
Ч
Ч
−
ЧЧ
Ч
I
V
OUT
OUT
2
L
[ H]
L
OPTIMUM
MAX
µ
µ
=
[
]
.
H
2 25
L
[ H]
2
T
I
(V
V
)
I
MIN
S
OUT
OUT
IN_MIN
LIM-LX
2
µ
η
=
Ч
Ч
Ч
Ч
−
I
2
T
(V
V
) I
L
LPEAK
S
OUT
IN_MIN
OUT_MAX
=
Ч
Ч
Ч
Ч
−
η
R
R
V
V
1
2
1
OUT
REF
=
⎛
⎝⎜
⎞
⎠⎟
⎡
⎣
⎢
⎤
⎦
⎥
−
MAX15031
FB
V
OUT
R
2
R
1
Figure 1. Adjustable Output Voltage
