QSC Audio RAVE 80 User Manual
Page 18
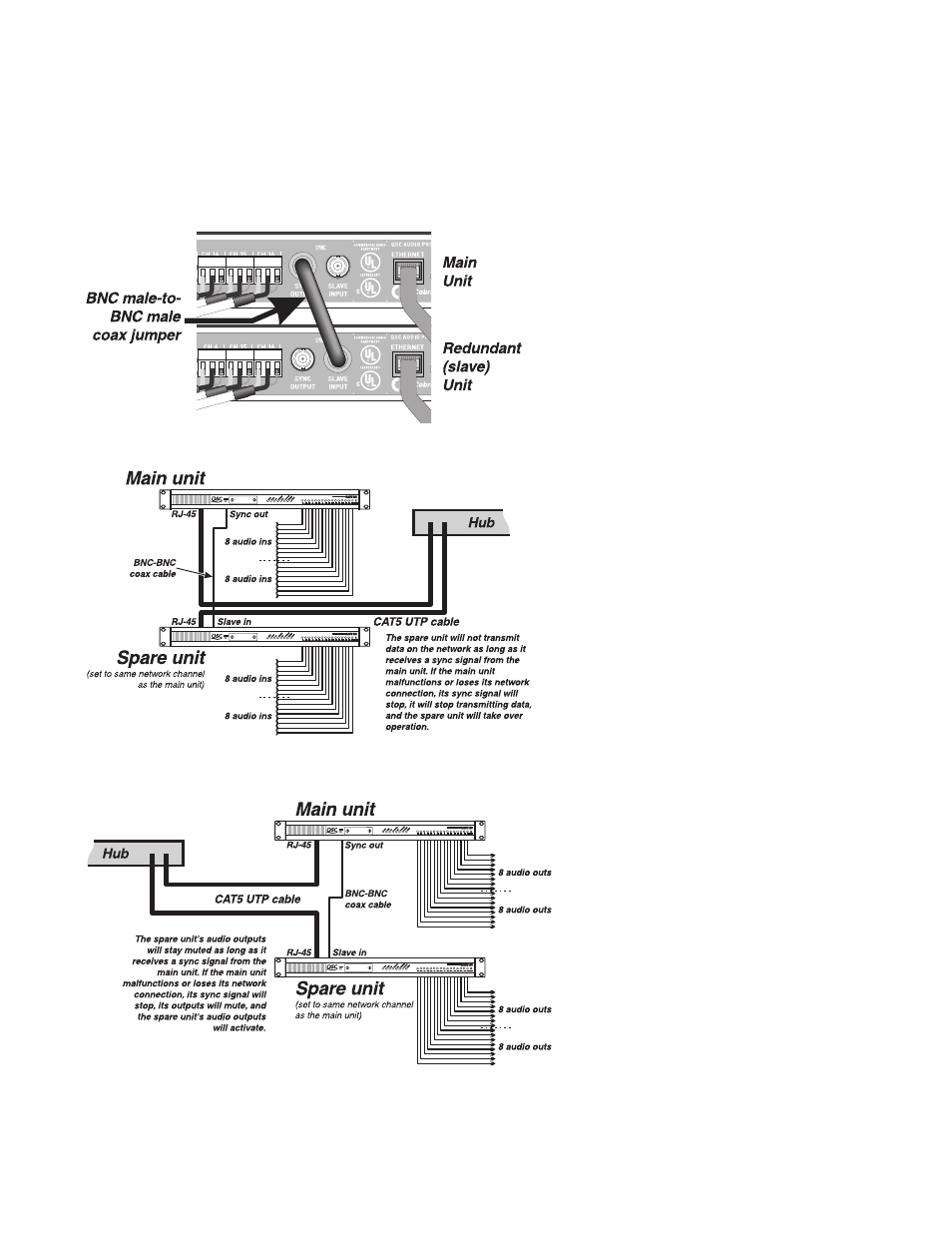
17
SLAVE INPUT
The slave input is another BNC jack. Its use is to allow a RAVE unit to “slave” itself to another RAVE unit, as a
backup in mission-critical applications.
To slave one RAVE unit to another, connect a BNC jumper
cable from the sync output of the main unit to the slave
input of the redundant unit. Select the same network
channel(s) on the slave unit as are selected on the main
unit. As long as the slave input detects the clock signal
from the main RAVE unit, it will maintain a sort of
“standby” mode, i.e., if it has analog audio outputs, the
output relays will stay open to prevent the production of
audio signals; if it has digital audio outputs, the bitstream
will continue, but the audio information will be as if the
audio channels were muted; if it has analog or digital
audio inputs, the unit will not transmit data on the
network.
However, once the clock signal disappears, as would
happen if the main unit detects an internal fault, loses
its network connection, or just fails, the slave unit will
go into normal operation. If the clock signal re-ap-
pears, the slave unit will go back to its standby role.
RS232 PORT
The RS232 port is an auxiliary function which allows
you to transmit serial data over the RAVE network,
from one RAVE unit to another. This is handy for
remotely controlled accessories and processors that
use RS232 data.
Serial data format is fixed at 19,200 baud, 9 bits (or 8
bits w/ parity), 1 stop bit.
Incoming serial data is buffered and broadcast over
the network. All attached stations receive these broad-
casts and transmit the data simultaneously out their
respective serial ports.
When the RS232 electrical connection is in use, the
serial port operates in a half duplex mode.
For pinout information, see the Appendix.
