Astronomical observing – Orion SKYQUEST XT6 User Manual
Page 12
12
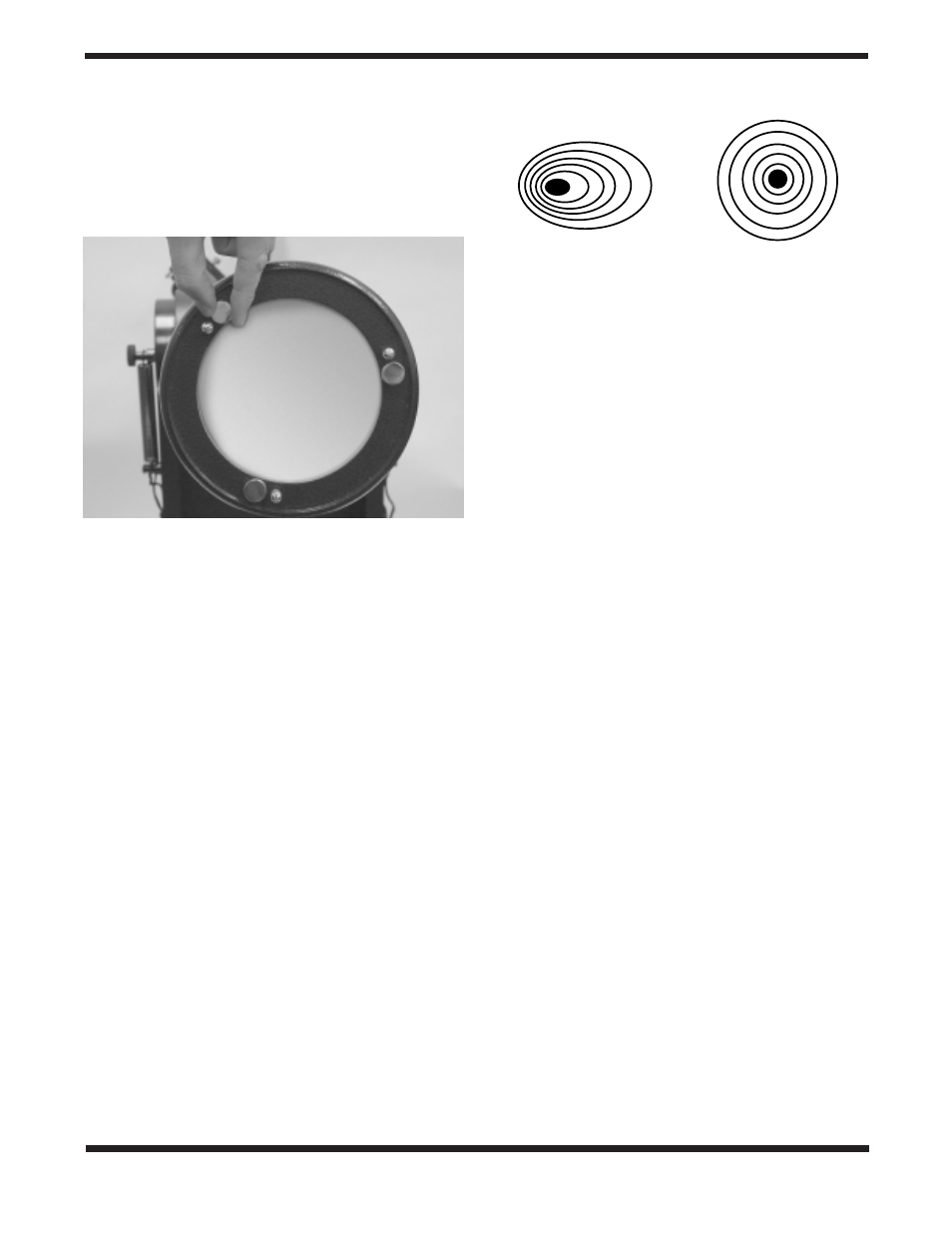
When you have the dot centered as much as possible in the
ring, your primary mirror is collimated. The view through the
collimation cap should resemble Figure 12e. Retighten the
locking thumbscrews.
A simple star test will tell you whether the optics are accurately
collimated.
Star-Testing the Telescope
When it is dark, point the telescope at a bright star and accu-
rately center it in the eyepiece’s field of view. Slowly de-focus
the image with the focusing knob. If the telescope is correctly
collimated, the expanding disk should be a perfect circle
(Figure 17). If the image is unsymmetrical, the scope is out of
collimation. The dark shadow cast by the secondary mirror
should appear in the very center of the out-of-focus circle, like
the hole in a donut. If the “hole” appears off-center, the tele-
scope is out of collimation.
If you try the star test and the bright star you have selected is
not accurately centered in the eyepiece, the optics will always
appear out of collimation, even though they may be perfectly
aligned. It is critical to keep the star centered, so over time you
will need to make slight corrections to the telescope’s position
in order to account for the sky’s apparent motion.
Note About the Collimatable 2" Focuser (XT8)
The 2" focuser of the SkyQuest XT8 can be collimated using
three pairs of push-pull screws located at the base of the
focuser. The focuser was collimated at the factory however,
and should never need to be adjusted. Focuser collimation is
only required under very rare circumstances, but has been
made available for this telescope should such a need arise.
5. Astronomical Observing
For many users, the SkyQuest XT telescope will be a major
leap into the world of amateur astronomy. This section is
intended to get you ready for your first voyage through the
night sky.
Site Selection
Pick a location away from streetlights and bright yard lighting.
Avoid viewing over rooftops and chimneys, as they often have
warm air currents rising from them, which distort the image
seen in the eyepiece.
Similarly, you should not observe through an open window
from indoors. Better yet, choose a site out-of-town, away from
any “light pollution”. You’ll be stunned at how many more stars
you’ll see! Most importantly, make sure that any chosen site
has a clear view of a large portion of the sky.
Cooling the Telescope
All optical instruments need time to reach “thermal equilibri-
um” to achieve maximum stability of the lenses and mirrors,
which is essential for peak performance. When moved from a
warm indoor location to cooler air outside(or vice-versa), a tel-
escope needs time to cool (or warm) to the outdoor
temperature. The bigger the instrument and the larger the
temperature change, the more time will be needed.
Allow at least 30 minutes for your SkyQuest XT to equilibrate.
If the scope experiences more than a 40° temperature change,
allow an hour or more. In the winter, storing the telescope out-
doors in a shed or garage greatly reduces the amount of time
needed for the optics to stabilize. It also is a good idea to keep
the scope covered until the Sun sets so the tube does not heat
greatly above the temperature of the outside air.
The XT8 has the ability to mount a small fan to making cool-
ing the tube faster. On the bottom of the mirror cell there are
four holes where a fan can be screwed on.
Seeing and Transparency
Atmospheric conditions play a huge part in quality of viewing.
In conditions of good “seeing,” star twinkling is minimal and
objects appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is best over-
head, worst at the horizon. Also, seeing generally gets better
after midnight, when much of the heat absorbed by the Earth
Figure 16.
The tilt of the primary mirror is adjusted by turning
one or more of the three larger thumbscrews.
Figure 17.
A star test will determine if a telescope’s optics are
properly collimated. An unfocused view of a bright star through the
eyepiece should appear as illustrated on the right if the optics are
perfectly collimated. If the circle is unsymmetrical, as in the
illustration on the left, the scope needs collimation.
Out of collimation
Collimated
