Amplifier wiring, High-pass crossover, Power connections for the orion cobalt co600.4 – Orion CobaltTM G42110 User Manual
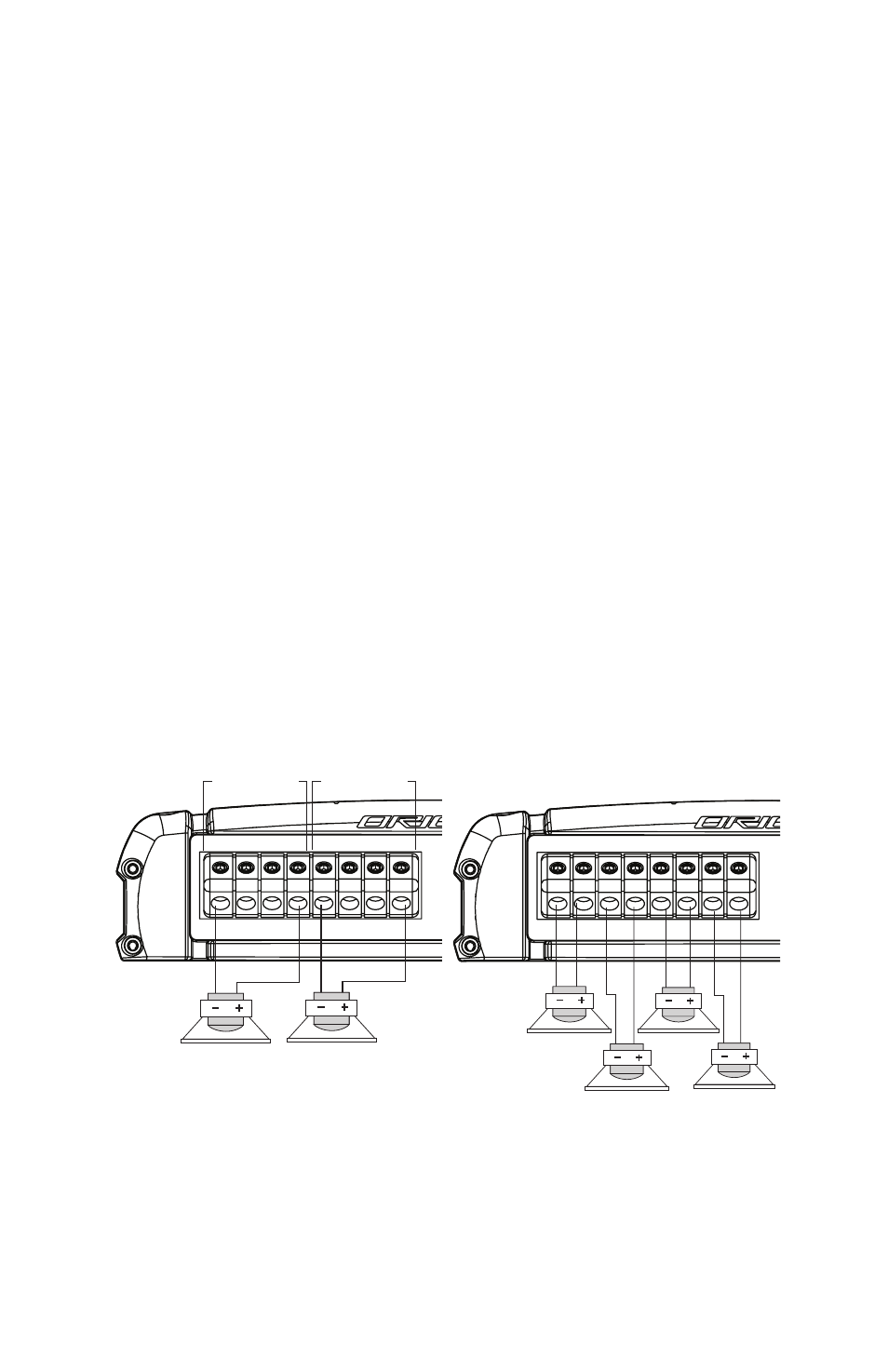
Page 7: Speaker wiring diagram co600.4, Front and rear in tri-mode, Figure 3 figura 3 abbildung 3
6
© 2007 directed electronics—all rights reserved
High-Pass Crossover
When the switch is to the left (FULL position), the high-pass crossover is bypassed . When the
switch is to the right (HPF position), the high-pass crossover is active . The high-pass crossover is
continuously variable from 50Hz to 500Hz .
AMPLIFIEr WIrING
Power Connections for the Orion Cobalt CO600.4
●
Orion Cobalt CO600 .4 Fuse Size: 2 x 25 AMP ATC
●
Power connections accept up to 4 AWG wire .
●
4 AWG power and ground wire recommended for optimal performance .
●
Connect 2V+ to the battery through fuse holder . This connection provides +2V main
power to the amplifier .
●
Power wire must be fused no more than 8" from battery .
●
Ground amplifier to a good chassis ground as close as possible to the amplifier .
●
Connect rEM terminal to remote turn-on lead from source unit . This connection pro-
vides +2V power to turn-on the amplifier .
●
Add extra ground wire between the negative terminal of the battery and the chassis .
Speaker Wiring Diagram CO600.4
The Orion Cobalt CO600 .4 amplifier offers two sets (front and rear) of two positive and two negative
output terminals for ease of connecting the speakers to the amplifier . Each amplifier is stable to 2
Ω
per channel or 4 ohm per bridged channel pair .
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
bridged
bridged
4 channel
2 channels
Bridged Front & Rear
bridged
bridged
4
Ω or 8Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
Front and Rear
in Tri-mode
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
-
- +
+
bridged
bridged
4 channel
2 channels
Bridged Front & Rear
bridged
bridged
4
Ω or 8Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
4
Ω or 8Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
2
Ω or 4Ω
Front and Rear
in Tri-mode
Figure 3
Figura 3
Abbildung 3
