Polk Audio dX8 User Manual
Page 4
Premium Performance Loudspeakers
7
dX
Series
6
Premium Performance Loudspeakers
dX
Series
Parts You Will Need To Build Your Enclosure
When building a subwoofer enclosure you will find that there are numerous materials
recommended for construction.
1) Medium density fiberboard (MDF)
2) Marine grade plywood
3) Particle board (the smaller the particles the better)
These materials range in price as well as availability. Particle board is the most common,
least costly, and can be purchased at most hardware stores. MDF and marine grade plywood,
although preferable, are usually much harder to find, and much more costly. Whichever you
choose, we recommend that its minimum thickness be 3/4". This will provide the rigidity
necessary for optimum performance.
If you’ve never built an enclosure before we are going to try to make this as easy and
painless as possible. If you’ve built enclosures before you can skip this section and go right
to the technical sheet to get your parameters.
Complete Parts List:
1) Wood (particle board, MDF, or marine grade plywood) 4' x 8' x 3/4" sheet
2) Wood glue (one 12-16 oz. bottle)
3) 1
1/4
"x #8 wood screws (one lb. box)
4) Caulk gun and silicon caulk (two tubes)
5) Terminal cup (one per speaker) available at electronic parts stores
6) Speaker wire (2-4 ft.)
7) Carpet (optional)
8) Grills to protect your subwoofers (optional)
9) Solderless speaker connectors (available at electronic parts stores)
Designing Your Polk dX Subwoofer Enclosure Step By Step
1.) How much room do you have to work with in your car or truck?
When designing your subwoofer enclosure, the first thing you need to figure out is, just how
large an enclosure will fit in your vehicle. When an enclosure is going in the trunk of a car,
you first need to measure your trunk to find the maximum height, width, and depth you
can use. Pay attention to trunk hinges and tension bars. If your enclosure is going in an
area other than a trunk, make sure you check for similar obstructions. After measuring,
subtract 1.5" from each dimension. This compensates for the thickness of the material
you use (simply double the thickness, i.e.: if you’re using 3/4" material, subtract 1 1/2";
1" material, subtract 2", etc), and will give you your usable (internal) dimensions. Record
these dimensions here for future reference.
Maximum dimensions
Usable dimensions
Height:__________ inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Width:___________inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Depth:___________inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Usable volume=________cubic inches
Usable volume=________cubic feet
Multiply your usable Width x Height x Depth. The product will be the usable (internal)
volume of your enclosure in cubic inches. Divide this number by 1728 (the number of
cubic inches in a cubic foot). This will give you the internal volume in cubic feet. Divide
your internal cubic feet by 2 (only if you are using a pair of dX subwoofers). Compare
this number to the chart at the bottom of the technical sheet. Choose the recommended
enclosure which is closest in size or that fits your desired type of enclosure. Now that you
have all of your needed dimensions, you can begin cutting your wood. From the above
chart you can tell how big each piece of wood should be.
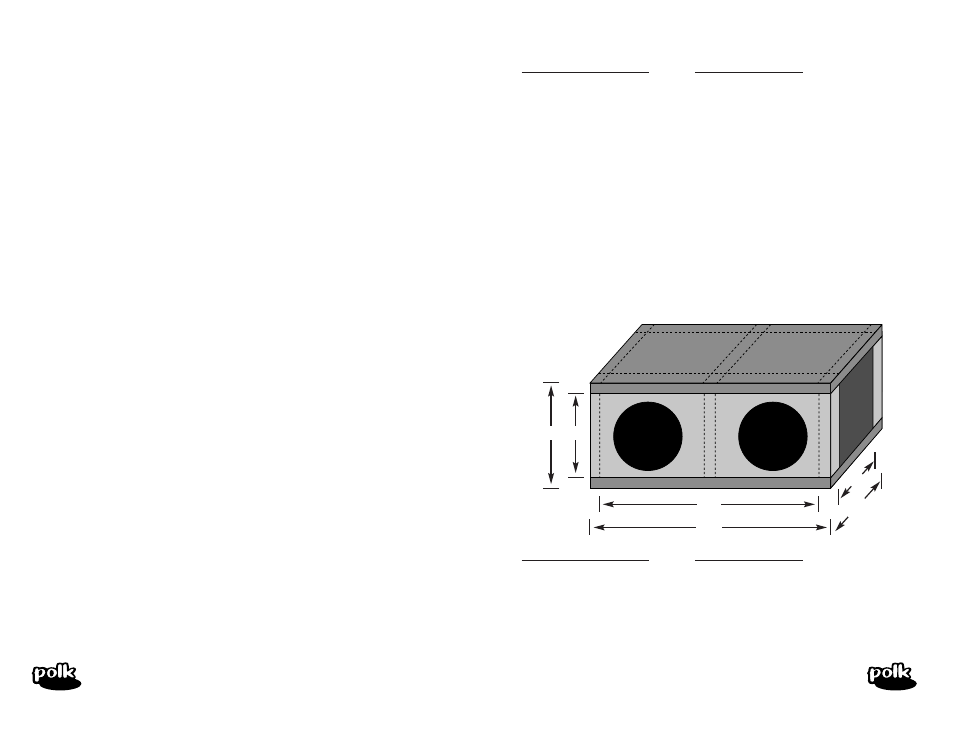
Here’s a sample enclosure:
Maximum dimensions
Usable dimensions
Height:__________ inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Width:___________inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Depth:___________inches
(Minus 1.5 inches)=______inches
Usable volume=________cubic inches
Usable volume=________cubic feet
15
1/2
"
14"
Hole diameter
dX8 = 7.26
dX10 = 9.30
dX12 = 11.16
28"
29
1/2
"
9"
10
1/2
"
15.5
29.5
10.5
14
28
9
3528
2.042
