Methods, Ease of use, Quality of the photographs: color-fidelity – Konica Minolta SLR User Manual
Page 3
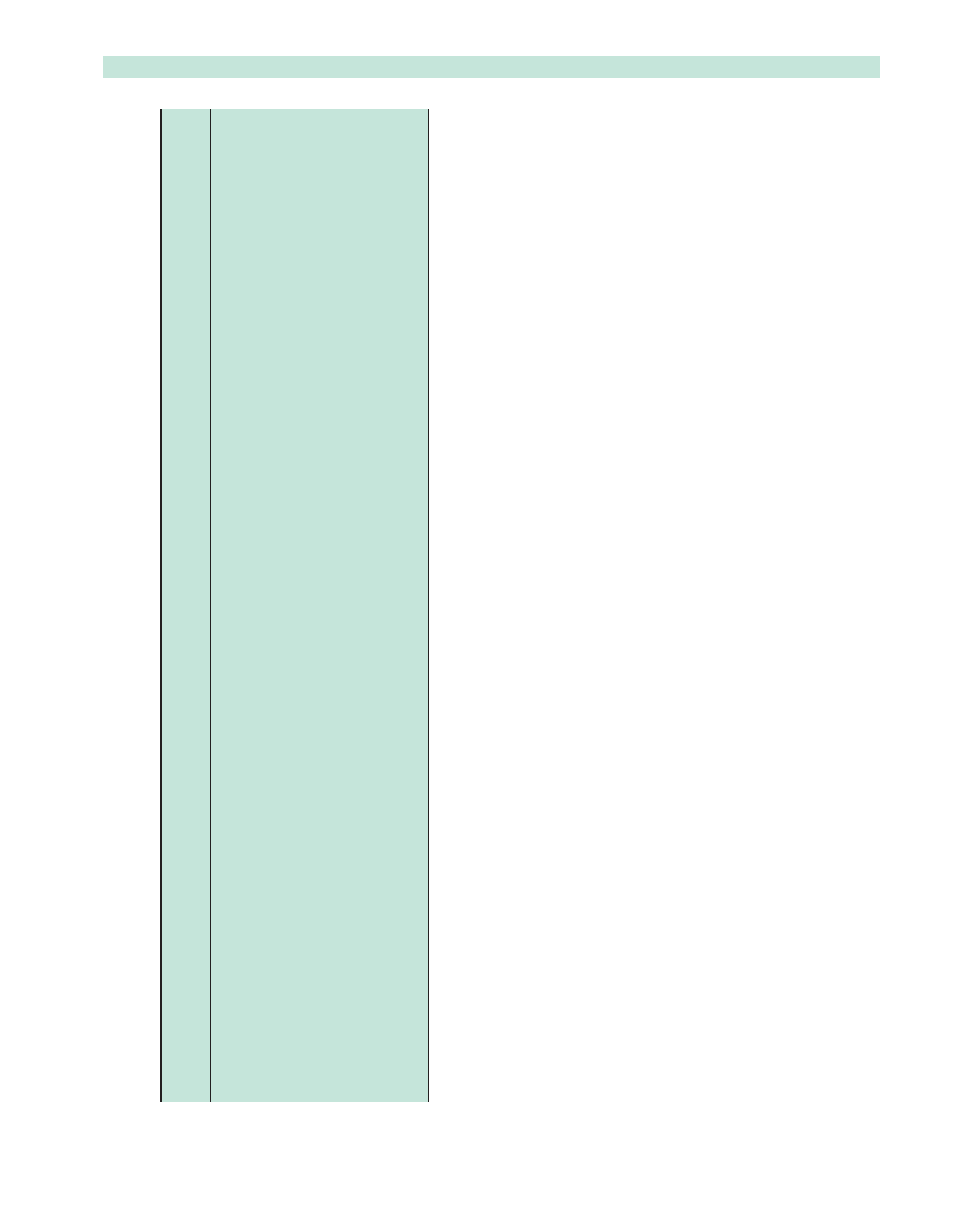
Pentax only produced the 100 mm macro-lens at the
time of testing,); Olympus only produces a 50 mm
macro-lens,
which
takes
magnification
differences
between analogue and digital formats into account.
The lenses chosen for this study were kept as close as
possible to a 100 mm equivalent (for 36 mm analogue
film). Nikon and Fujifilm use a small sensor, which does
not fill the 36 mm film-area. A magnification factor of
approximately 1.5 applies. This magnification factor was
adjusted by choosing a 60 mm macro-lens for those
cameras.
Methods
Ease of use
All cameras were initially set on automatic mode
(factory preset); with the flash turned on. The intra-oral
exposures were taken at approximately 1:2 magnifica-
tion. The aperture selected by the camera was recorded
and checked for suitability, particularly depth of field.
Homogeneity of illumination was checked for suitability
by assessing shadows on the image. There is a reverse
relationship between the f-setting and the aperture: the
larger the number of the f-setting the smaller the
aperture and the larger the depth of field. These settings
were found to be too small for all cameras (the aperture
was too large, giving poor depth of field) and were
therefore changed to aperture priority mode; the
aperture was closed to at least f522, which gives good
depth of field (Figure 2). The camera was then used for
extra-oral photography and the settings changed again
until appropriate, in this case an aperture of at least f58.
The number of changes necessary between the settings
was recorded. The camera was only considered metering
‘through the lens’ (TTL) if the flash settings did not need
to be changed.
Quality of the photographs: Color-fidelity
For consistency, intra-oral photographs (front, right
and left lateral views) were simulated by taking pictures
of a demonstration-model (Ormco), against a green
background (Figure 3). A non-clinical method was
preferred to taking images of a patient: the 10 cameras
were not all available at the same time and changes in
oral hygiene may have influenced color consistency over
time. Even if all cameras had been tested on one patient
on one occasion the discomfort would have been
considerable. The white balance selection was auto for
all cameras. The images were subsequently downloaded
on a
‘SONY
VAIO’ (Sony
Corporation,
Japan)
computer. The computer screen was adjusted to project
Journal
of
Or
thod
ontics
JOR
3338.3d
11/7/0
6
19
:17:05
The
Charlesworth
Group
,
Wakefield
+44(0)1924
369598
-
Rev
7.51n/W
(Jan
20
2003)
Table
1
Cam
eras
tested
and
specific
ations
Body
Canon
EO
S
350D
Canon
EOS
20D
Fujifilm
S3Pr
o
Konic
a
-
Mino
lta
7D
Nik
on
D100
Nikon
D70
s
Nik
on
D50
Olym
pus
E1
Olympus
E300
Pen
tax
*ist
DS
Meag
pixels
(r
ounded
fig
ure)
8
8
12
6
6
6
6
5
8
6
Body
(UK
list
price
wi
thout
VAT
in
Euro
)
770
1243
2206
1409
1348
858
746
1226
919
858
Fla
sh
MR-14
EX
MR-14
EX
SB
29S
R
1200
SB
29S
SB
29S
SB
29S
SRF
-
11
SRF
-
11
AF
140
C
Guide
numbe
r
14
14
11
12
11
11
11
11
11
14
Macr
o
Speed-lig
ht
(UK
list
pric
e
witho
ut
VAT
in
Euro)
490
490
466
490
466
466
466
662
662
515
Macr
o
-
Lens
100
mm
100
mm
60
mm
Nikko
r
100
mm
60
mm
Nikkor
60
mm
Nik
kor
60
mm
Nikkor
ED
50
mm
ED
50
mm
100
mm
Macr
o
-
Lens
(UK
list
pric
e
witho
ut
VAT
in
Euro)
588
588
539
919
539
539
539
453
453
551
Unit
-
W
eight
(in
gram
s
inclusive
batte
ries)
1612
1874
1891
2329
1765
1660
1605
1768
1688
1324
JO September 2006
Features Section
Comparison of digital SLR cameras
3
