Alarm zones and modes – Swann SW347-WA2 User Manual
Page 12
12
12
12
Alarm Zones and Modes
Modes:
The Wireless Alarm System has two main modes of operation, the Home Mode
and Out Mode. These zones do not refer to where the sensors are placed, but
where you are at any given time.
For example, when you are in your home, you should set the alarm system to
“Home”. Home Mode should include your Window/Door Sensor(s) and any other
sensors you want to be active while there are people in the house. For this reason,
we suggest not assigning any of the PIR motion sensors inside your home to a zone
which is armed in Home Mode - it will give you many ‘false’ alarms.
Arming “Out Mode” will arm all zones on the alarm system. Thus, this should only
be armed when there is to be no-one in the house.
Zones:
The Wireless Alarm System has eight discreet zones, named 1 through 8. Any (or
all, or none) of these zones can be assigned to the Home Mode. All zones are
always associated with Out Mode.
Thus, arming Home Mode will arm only the zones you have assigned to Home
Mode. We suggest that the Window/Door Sensor works well assigned to Home
Mode.
Activating Out Mode will arm all the sensors attached to your alarm system, those
located both inside and outside the home.
To briefl y summarize:
Home Mode
Home Mode
Will arm all of the zones which you’ve assigned to Home
Will arm all of the zones which you’ve assigned to Home
Mode. This is intended for use when there are people
Mode. This is intended for use when there are people
in the home who want the perimeter to be secure (for
in the home who want the perimeter to be secure (for
example, while they are sleeping).
example, while they are sleeping).
Out Mode
Out Mode
Will arm sensors in all eight zones. This mode is intended
Will arm sensors in all eight zones. This mode is intended
to be activated whilst there is nobody in the house.
to be activated whilst there is nobody in the house.
You can change the Zone and Mode that a sensor is assigned to
when you pair it with the Keypad Alarm Control Unit.
See the sensor pairing instructions on page 13.
9
9
Important:
Any obstructions in the environment will reduce the sensors effectiveness. It
•
can’t see through walls! Even a thin sheet of glass will signifi cantly impair the
range of the sensor, as glass blocks more infrared radiation than visible light.
Small animals (such as a cat or similar) can, under some circumstances, trigger
•
the PIR motion sensors. Therefore, we suggest that the PIR motion sensors are
not suited to areas where pets are routinely kept.
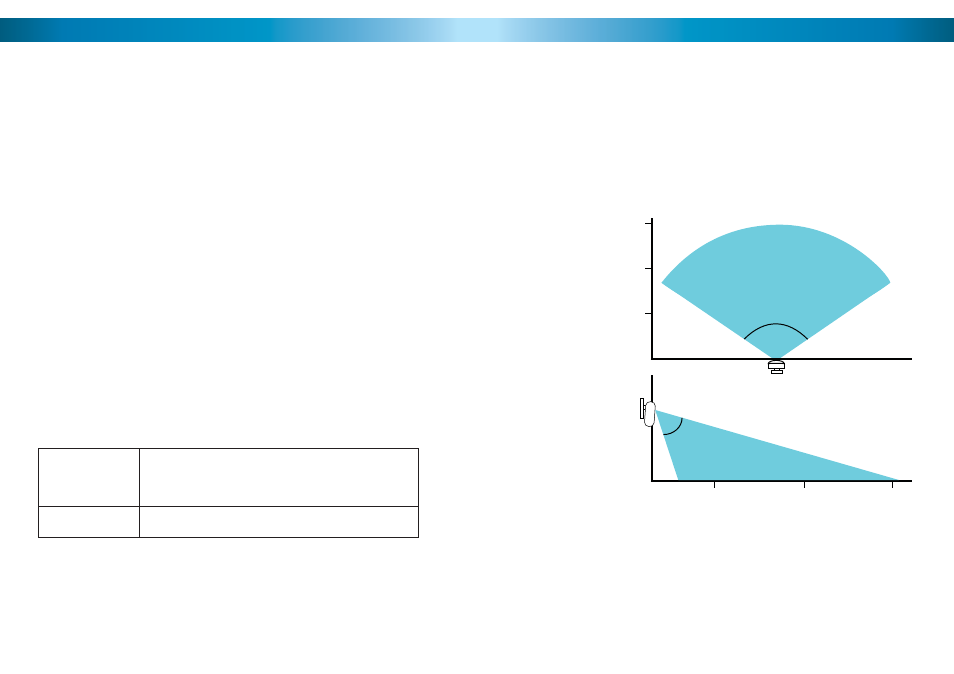
This diagram
shows a typical
coverage area
for an evenly
heated space
with an ambient
temperature of
approximately
68°F/20ºC with
low relative
humidity.
Higher humidity
or higher/lower
temperatures will
alter the effective
range of the
sensor.
Placing the PIR motion sensors
The PIR motion sensors have an effective range of between 16ft/5m and 50ft/15m
depending on the specifi c conditions of the environment. Typically, the sensor will
have a longer range in colder conditions, or in evenly heated environments. The
opposite is also true - environments with uneven temperatures (such as part of the
area in sunlight and other areas in shade) or consistently high temperatures will
lower the effective range of the sensor.
Under typical circumstances, the effective range of the PIR motion sensor is
approximately 50ft/15m. Multiple sensors can be used in conjunction with one
another to cover larger spaces.
Feet / Meters
5f
t/1.8m - 7f
t/2.4m
16ft/5m
16ft/5m
32ft/10m
32ft/10m
50ft/15m
50ft/15m
110°
70°
