2 i2c eeprom, Datasheet, C eeprom – SMSC USB2512Ai User Manual
Page 24
Industrial Temperature Rated USB 2.0 Hi-Speed 2-Port Hub Controller
Datasheet
Revision 1.97 (08-11-08)
24
SMSC USB2512Ai
DATASHEET
4.2.1.22
Register FFh: Status/Command
4.2.2
I
2
C EEPROM
The I
2
C EEPROM interface implements a subset of the I
2
C Master Specification (Please refer to the
Philips Semiconductor Standard I
2
C-Bus Specification for details on I
2
C bus protocols). The Hub’s I
2
C
EEPROM interface is designed to attach to a single “dedicated” I
2
C EEPROM, and it conforms to the
Standard-mode I
2
C Specification (100kbit/s transfer rate and 7-bit addressing) for protocol and
electrical compatibility.
Note: Extensions to the I
2
C Specification are not supported.
The Hub acts as the master and generates the serial clock SCL, controls the bus access (determines
which device acts as the transmitter and which device acts as the receiver), and generates the START
and STOP conditions.
4.2.2.1
Implementation Characteristics
The Hub will only access an EEPROM using the Sequential Read Protocol.
4.2.2.2
Pull-Up Resistor
The Circuit board designer is required to place external pull-up resistors (10K
Ω recommended) on the
SDA/SMBDATA & SCL/SMBCLK/CFG_SELO lines (per SMBus 1.0 Specification, and EEPROM
manufacturer guidelines) to Vcc in order to assure proper operation.
4.2.2.3
I
2
C EEPROM Slave Address
Slave address is 1010000.
Note: 10-bit addressing is NOT supported.
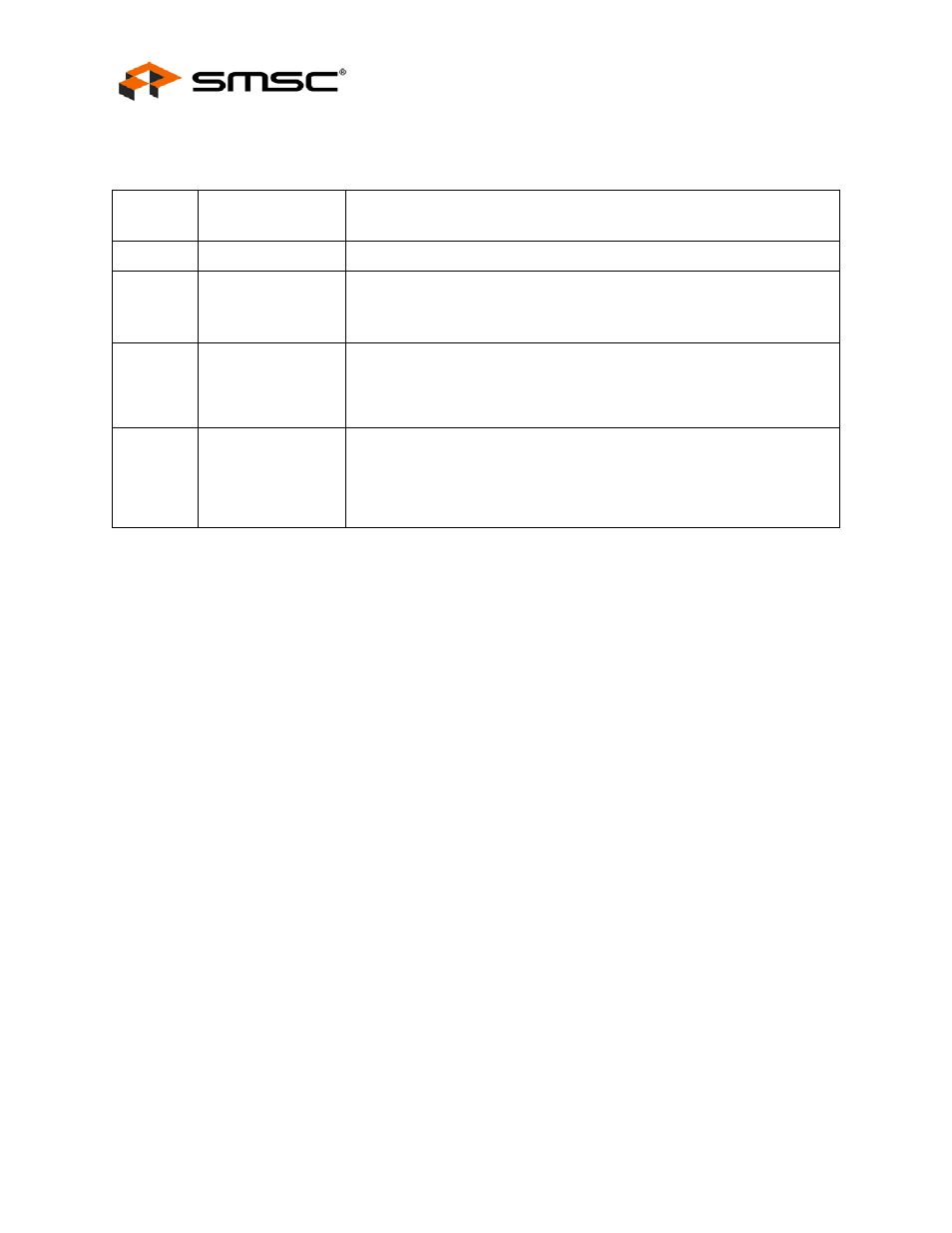
BIT
NUMBER
BIT NAME
DESCRIPTION
7:3
Reserved
Reserved
2
INTF_PW_DN
SMBus Interface Power Down
‘0’ = Interface is active
‘1’ = Interface power down after ACk has completed
1
RESET
Reset the SMBus Interface and internal memory back to RESET_N
assertion default settings.
‘0’ = Normal Run/Idle State
‘1’ = Force a reset of registers to their default state
0
USB_ATTACH
USB Attach (and write protect)
‘0’ = SMBus slave interface is active
‘1’ = Hub will signal a USB attach event to an upstream device, and the
internal memory (address range 00h-FEh) is “write-protected” to prevent
unintentional data corruption.
