MSI ATX Motherboard G52-MA00362 User Manual
Page 82
A-3
Glossary
DMA (direct memory access)
A transfer mode between the main memory and the peripheral devices
that without passing through the CPU. Using the DMA controller, data
is transferred much faster.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
A most common type of computer memory. It usually uses one transistor
and a capacitor to represent a bit. As the development of technology, the
memory type and specification used in computer becomes variety, such
as SDRAM, DDR SDRAM, and RDRAM. For further instruction, please
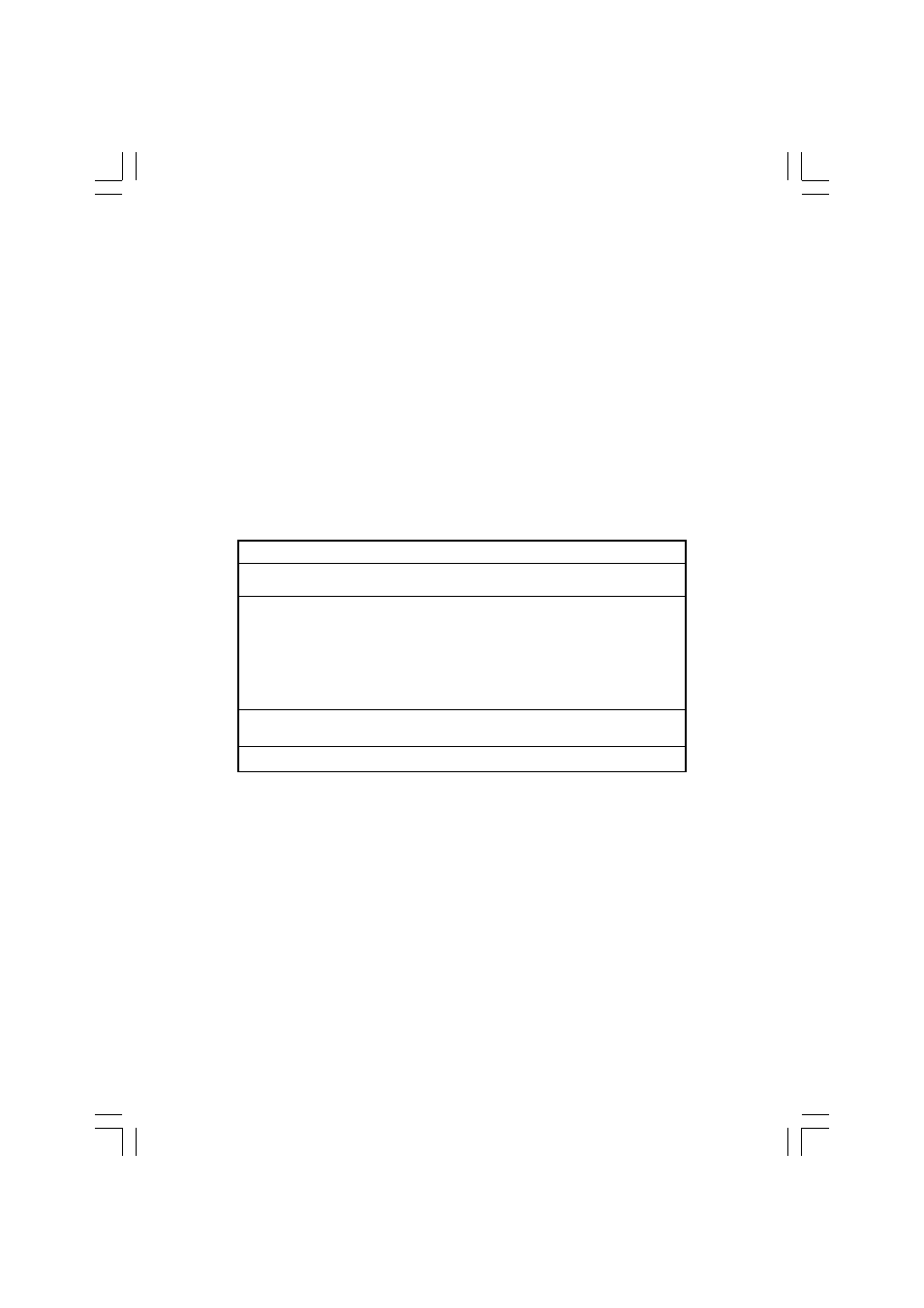
see the table below:
ECC Memory (error correcting code memory)
A type of memory that contains special circuitry for testing the accuracy
of data and correcting the errors on the fly.
IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics)
A type of disk-drive interface widely used to connect hard disks, CD-
ROMs and tape drives to a PC, in which the controller electronics is
integrated into the drive itself, eliminating the need for a separate adapter
card. The IDE interface is known as the ATA (AT Attachment)
specification.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Memory Technologies
Type
FPM (60,70ns)
EDO (50,60,70ns)
SDRAM (66MHz)
SDRAM (100MHz)
SDRAM (133MHz)
RDRAM (Direct Rambus)
DDR SDRAM (100MHz)
DDR SDRAM (133MHz)
First Used
1990
1994
1996
1998
1999
1999
2000
2000
Clock Rate
25MHz
40MHz
66MHz
100MHz
133MHz
400MHz
100MHz
133MHz
Bus* Width
64 bits
64 bits
64 bits
64 bits
64 bits
16 bits
64 bits
64 bits
Bandwidth
200 MBps
320 MBps
528 MBps
800 MBps
1.1 GBps
1.6 GBps
1.6 GBps
2.1 GBps
Volts
5v
5v
3.3v
3.3v
3.3v
2.5v
3.3v
3.3v
Peak
* Memory channel width (64 bits started with 75MHz Pentium)
Source: Computer Desktop Encyclopedia
