Connecting to weld output terminals, Selecting weld cable sizes, 8. connecting to weld output terminals – Miller Electric Big Blue 452P User Manual
Page 33: 9. selecting weld cable sizes
OM-496 Page 27
Return To Table Of Contents
5-8.
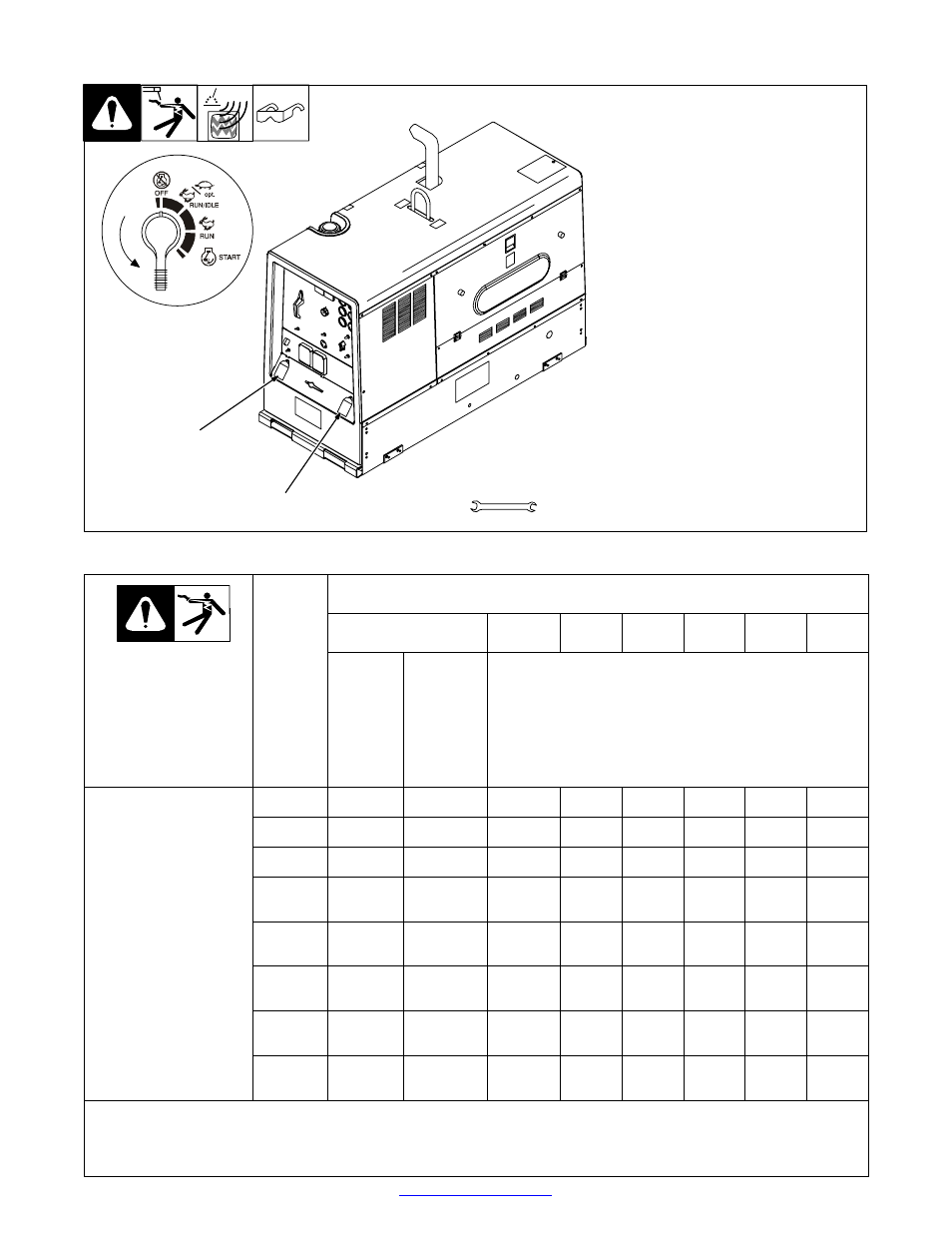
Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
802 311
Tools Needed:
2
3/4 in
1
Y
Stop engine.
1
Positive (+) Weld Output Terminal
2
Negative (−) Weld Output Terminal
Stick and TIG Welding
For Stick and TIG welding Direct Current Elec-
trode Positive (DCEP), connect electrode
holder cable to Positive (+) terminal on left and
work cable to Negative (−) terminal on right.
For Direct Current Electrode Negative
(DCEN), reverse cable connections.
If equipped with optional Polarity switch or op-
tional Polarity/AC switch, connect electrode
holder cable to Electrode (+) terminal on left
and work cable to Work (−) terminal on right.
MIG and FCAW Welding
For MIG and FCAW welding Direct Current
Electrode Positive (DCEP) on CC/CV models,
connect wire feeder cable to Positive (+) termi-
nal on left and work cable to Negative (−) ter-
minal on right. Use Process/Contactor switch
to select type of weld output (see Section 7-3).
For Direct Current Electrode Negative
(DCEN), reverse cable connections.
If equipped with optional Polarity switch or op-
tional Polarity/AC switch, connect wire feeder
cable to Electrode (+) terminal on left and
work cable to Work (−) terminal on right.
5-9.
Selecting Weld Cable Sizes*
Weld Cable Size** and Total Cable (Copper) Length in Weld Circuit
Not Exceeding***
100 ft (30 m) or Less
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
300 ft
(90 m)
350 ft
(105 m)
400 ft
(120 m)
Weld Output
Terminals
Y
Stop engine before
connecting to weld out-
put terminals.
Y
Do not use worn, dam-
aged, undersized, or
poorly spliced cables.
Welding
Amperes
10 − 60%
Duty
Cycle
60 − 100%
Duty
Cycle
10 − 100% Duty Cycle
100
4 (20)
4 (20)
4 (20)
3 (30)
2 (35)
1 (50)
1/0 (60)
1/0 (60)
150
3 (30)
3 (30)
2 (35)
1 (50)
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
3/0 (95)
200
3 (30)
2 (35)
1 (50)
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
4/0 (120)
250
2 (35)
1 (50)
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
300
1 (50)
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
350
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
400
1/0 (60)
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
500
2/0 (70)
3/0 (95)
4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
*
Chart is a general guideline and may not suit all applications. If cables overheat (normally you can smell it), use next size larger cable.
**Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere.
( ) = mm
2
for metric use
S-0007-E−
***For distances longer than those shown in this guide, call a factory applications representative at 920-735-4505.
