Configuration mode, Management network settings, Configuration mode management network settings – Ubiquiti Networks Rockeac User Manual
Page 20: Bridge mode
17
Chapter 4: Network
airOS®7 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
• In Advanced view, any interface can be selected as the
WAN or the LAN, but typical functionality is as follows:
•
Station
The WLAN functions as the WAN, and the
Ethernet port functions as the LAN.
•
Access Point
The Ethernet port functions as the
WAN, and the WLAN functions as the LAN.
• Each wired or wireless interface on the WAN or LAN has
its own IP address.
• For example, Router mode is used in a typical Customer
Premises Equipment (CPE) installation. The device acts
as the demarcation (demarc) point between the CPE
and Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP), with the
wireless interface of the device connecting to the WISP.
There can be only one WAN interface, but there can be
many LAN interfaces.
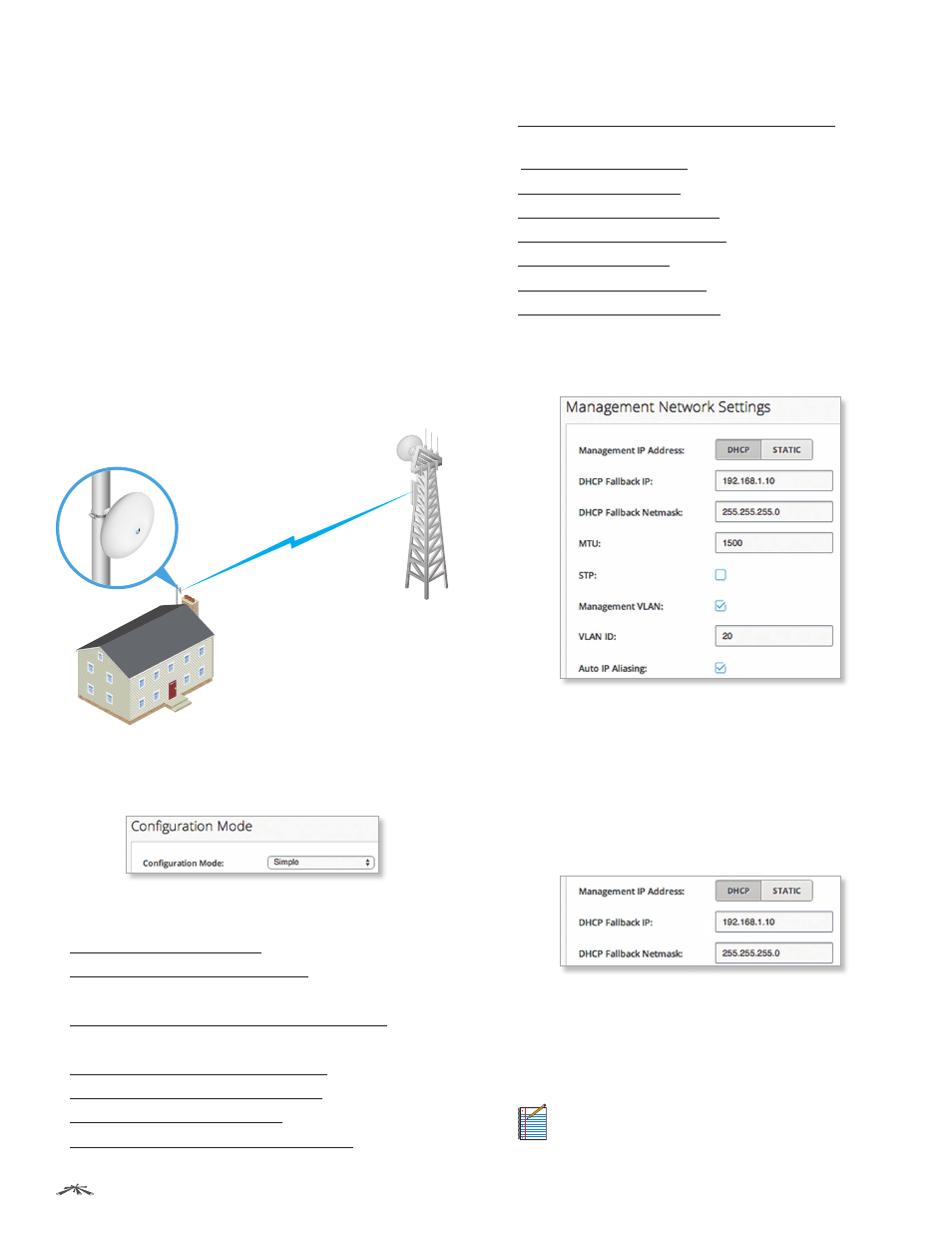
The following diagram shows the NanoBeam ac at a
residence wirelessly connecting to a WISP tower.
NanoBeam ac
WISP Tower
Configuration Mode
The Network page has two views, Simple and Advanced.
Simple
The following basic configuration settings are
available (advanced configuration settings are hidden):
• “Network Role” on page 16)
• “Configuration Mode” on page 17)
The following settings are available in Bridge mode only:
• “Management Network Settings” on page 17)
The following settings are available in Router mode only:
• “WAN Network Settings” on page 18
• “LAN Network Settings” on page 22
• “Port Forwarding” on page 26
• “Multicast Routing Settings” on page 27
Advanced
Displays the advanced configuration settings,
in addition to the basic configuration settings:
• “Management Network Settings” on page 17)
(Router mode only)
• “Interfaces” on page 23
• “IP Aliases” on page 23
• “VLAN Network” on page 24
• “Bridge Network” on page 24
• “Firewall” on page 25
• “Static Routes” on page 26
• “Traffic Shaping” on page 28
Management Network Settings
Bridge Mode
Management Interface
(Available in Advanced view.)
Select the interface used for management.
Management IP Address
Keep the default, DHCP, if the
device obtains an IP address from its DHCP server, or click
Static if the device uses a static IP address.
•
DHCP
The local DHCP server assigns a dynamic IP
address, gateway IP address, and DNS address to the
device.
-
DHCP Fallback IP
Enter the IP address for the device
to use if a DHCP server is not found.
-
DHCP Fallback Netmask
Enter the netmask for the
device to use if a DHCP server is not found.
•
Static
Assign static IP settings to the device.
Note:
IP settings should be consistent with the
address space of the device’s network segment.
