Bell & Gossett P81875G Series HSC-S Centrifugal Pump User Manual
Page 10
13. DOWELING
Dowel the pump and driving unit as follows:
a. Drill holes through diagonally opposite feet and into the
base. Holes must be of a diameter
1
/
64
inch less than the
diameter of the dowel pins. Clean out the chips.
b. Ream the holes in feet and base to the proper diameter for
the pins (light push fit). Clean out the chips.
c. Insert pins to be approximately flush with feet.
14. SUCTION AND DISCHARGE PIPING
General
When installing the pump piping, be sure to observe the fol-
lowing precautions:
Piping should always be run to the pump.
Do not move pump to pipe. This could make final alignment
impossible.
Both the suction and discharge piping should be supported
independently near the pump and properly aligned, so that no
strain is transmitted to the pump when the flange bolts are
tightened. Use pipe hangers or other supports at necessary
intervals to provide support. When expansion joints are used
in the piping system, they must be installed beyond the piping
supports closest to the pump. Tie bolts should be used with
expansion joints to prevent pipe strain. Do not install expan-
sion joints next to the pump or in any way that would cause a
strain on the pump resulting from system pressure changes. It
is usually advisable to increase the size of both suction and
discharge pipes at the pump connections to decrease the loss
of head from friction.
Install piping as straight as possible, avoiding unnecessary
bends. Where necessary, use 45-degree or long sweep
90-degree fitting to decrease friction losses.
Make sure that all piping joints are air-tight.
Where flanged joints are used, assure that inside diameters
match properly.
Remove burrs and sharp edges when making up joints.
Do not “spring” piping when making any connections.
Provide for pipe expansion when hot fluids are to be pumped.
Suction Piping
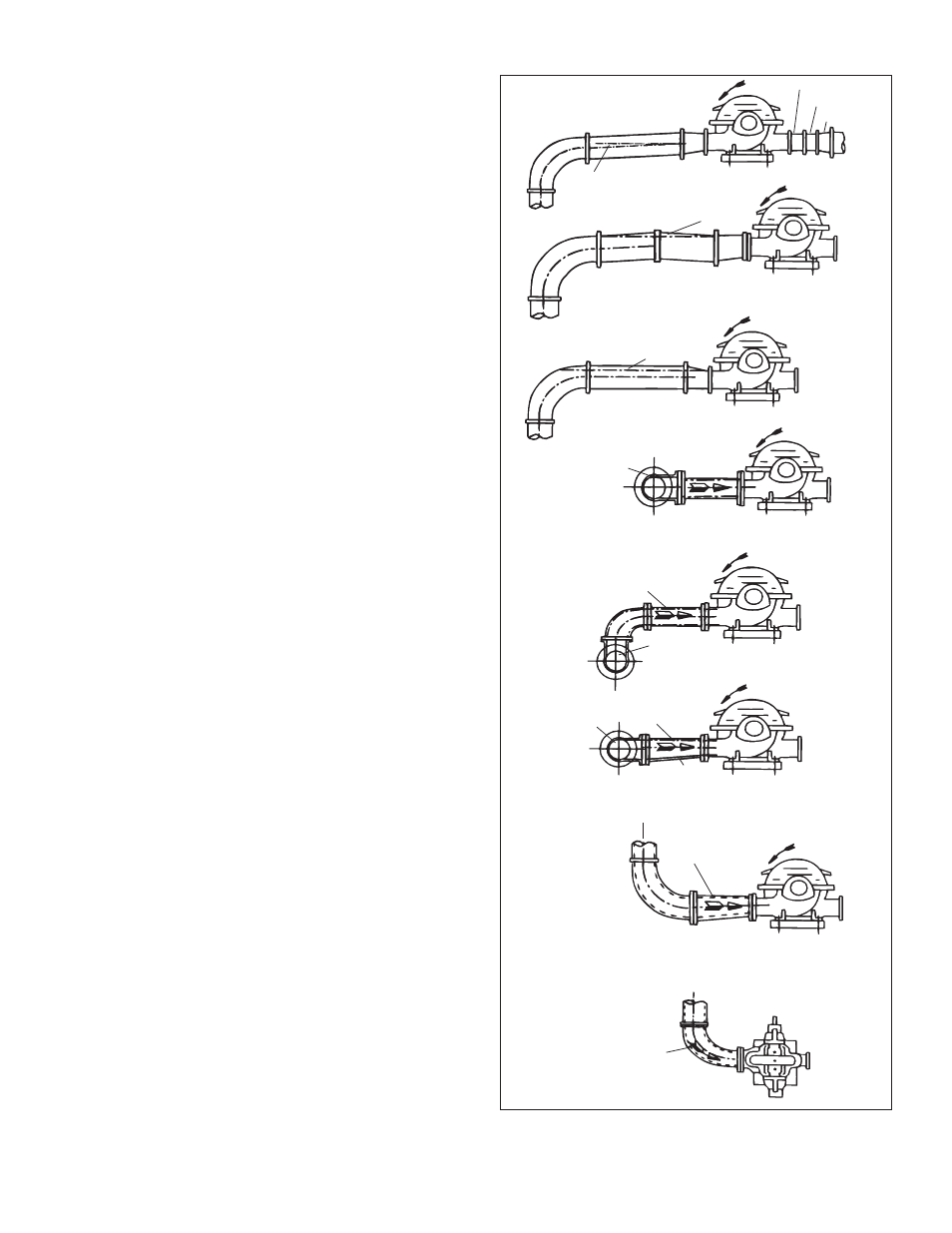
When installing the suction piping, observe the following
precautions (See Illustration 7).
The sizing and installation of the suction piping is extremely
important. It must be selected and installed so that pressure
losses are minimized and sufficient liquid will flow into the
pump when started and operated. Many NPSH (Net Positive
Suction Head) problems can be attributed directly to improper
suction piping systems.
Friction losses caused by undersized suction piping can
increase the fluid’s velocity into the pump. As recommended
by the Hydraulic Institute Standard ANSI/HI 1.1-1.5-1994, suc-
tion pipe velocity should not exceed the velocity in the pump
suction nozzle. In some situations pipe velocity may need to
be further reduced to satisfy pump NPSH requirements and to
control suction line losses. Pipe friction can be reduced by
using pipes that are one to two sizes larger than the pump
suction nozzle in order to maintain pipe velocities less than
5 feet/second.
Illustration 7 – Suction Pipe Installations
(Piping Supports Not Shown)
CHECK VALVE
GATE VALVE
INCREASER
CORRECT
C OF PIPE
SUCTION PIPE INSTALLED WITH
A GRADUAL RISE TO PUMP
L
LEVEL
AIR POCKET
INCORRECT
AIR POCKET
INCORRECT
AIR POCKET
INCORRECT
GRADUAL RISE
TO PUMP
NO AIR
POCKETS
CORRECT
NO AIR
POCKETS
GRADUAL RISE
TO PUMP
ECCENTRIC
REDUCER
CORRECT
DISTANCE PLUS
ECCENTRIC REDUCER
STRAIGHTENS FLOW
CORRECT
PATH OF
WATER
INCORRECT
10
