Spi pins and connections, Logic level shifting and conditioning circuit – Intelligent Motion Systems MForce PowerDrive Plus MForce Series Microstepping PowerDrive User Manual
Page 45
27
Part 2: Interfacing and Configuring
SPI Pins and Connections
+5 VDC OUT
19
15
2 3 4
PC Parallel/SPI Port
P1
10
12
7
9
11
MASTER OUT/SLAVE IN
MASTER IN/SLAVE OUT
SPI CLOCK
8
CHIP SELECT
COMM GND
12-Pin Locking Wire Crimp
For Use ONLY
with IMS Parameter
Setup Cable
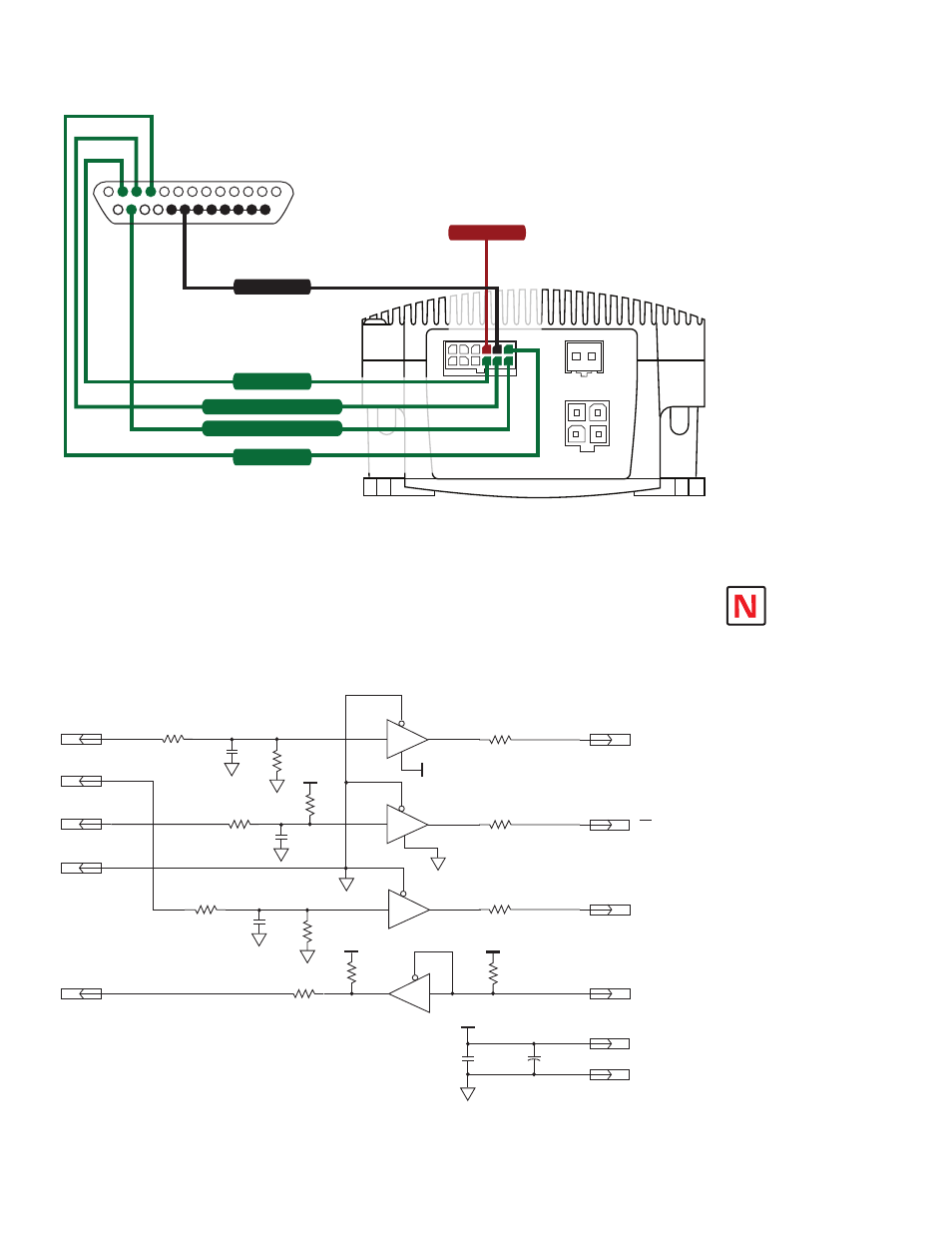
Figure 2.5.2: SPI Pins and Connections, 12-Pin Wire Crimp
Logic Level Shifting and Conditioning Circuit
The following circuit diagram is of a Logic Level shifting and conditioning circuit. This circuit should be
used if you are making your own parameter cable and are using a laptop computer with 3.3 V output parallel
ports.
U1:A
U1:B
U1:D
U1:C
HCT125
HCT125
HCT125
HCT125
2
1
14
4
5
7
13
12
11
10
8
9
6
3
2
R1
100
+5V
R2
49.9
P2: 8
CLK
+5V
P2: 4
P2: 7
P2: 10
P2: 6
P2: 5
CS
MOSI
MISO
+5 VDC
GND
5
6
10
7
4
8
3
4
19
DB25: 2
DB25: 3
DB25: 4
DB25: 19
DB25: 15
15
C3
330pF
R9
100K
R10 100K
R4
49.9
R6
49.9
C4
330pF
R3
100
R5
100
C5
330pF
R11
100K
+5V
R12 100K
+5V
R8
4.9K
R7
49.9
+5V
C1
C2
.1µF
1µF
25V
+
Figure 2.5.3: Logic Level Shifting and Conditioning Circuit
NOTE: If making your
own parameter setup
cable, be advised
the 3.3V output
parallel ports on some laptop
PC’s may not be sufficient to
communicate with the device
without use of a logic level
shifting and conditioning
Interface.
