2 suction pressure, Table 15 suction pressures, 3 discharge pressure – Emerson Liebert Deluxe System/3 DH User Manual
Page 60: Table 16 discharge pressures, 4 suction superheat, 5 thermostatic expansion valve, Operation, Suction pressure, Discharge pressure, Suction superheat
Component Operation and Maintenance, Checks and Adjustments
52
7.4.2 Suction Pressure
Suction pressure will vary with load conditions. The low pressure switch will shut the compressor
down if suction pressure falls below the cut-out setting. On the other hand, high suction pressure
reduces the ability of the refrigerant to cool compressor components and can result in compressor
damage. Minimum (pressure switch cut-out setting) and maximum (design operating) suction pres-
sures are listed in the following table.
7.4.3 Discharge Pressure
Discharge Pressure can be increased or decreased by load conditions or condenser efficiency. The high
pressure switch will shut the compressor down at its cut-out setting. Refer to the table below.
7.4.4 Suction Superheat
Superheat can be adjusted by the Thermostatic Expansion Value (TEV).
To determine superheat:
1. Measure the temperature of the suction line at the point the TEV bulb is clamped.
2. Obtain the gauge pressure at the compressor suction valve.
3. Add the estimated pressure drop between bulb location and suction valve.
4. Convert the sum of the two pressures to the equivalent temperature.
5. Subtract this temperature from the actual suction line temperature. The difference is superheat.
7.4.5 Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Operation
The thermostatic expansion valve performs one function. It keeps the evaporator supplied with
enough refrigerant to satisfy load conditions. It does not effect compressor operation.
Proper valve operation can be determined by measuring superheat. If too little refrigerant is being fed
to the evaporator, the superheat will be high; if too much refrigerant is being supplied, the superheat
will be low. The correct superheat setting is between 10 and 15°F (5.6 and 8.3°C).
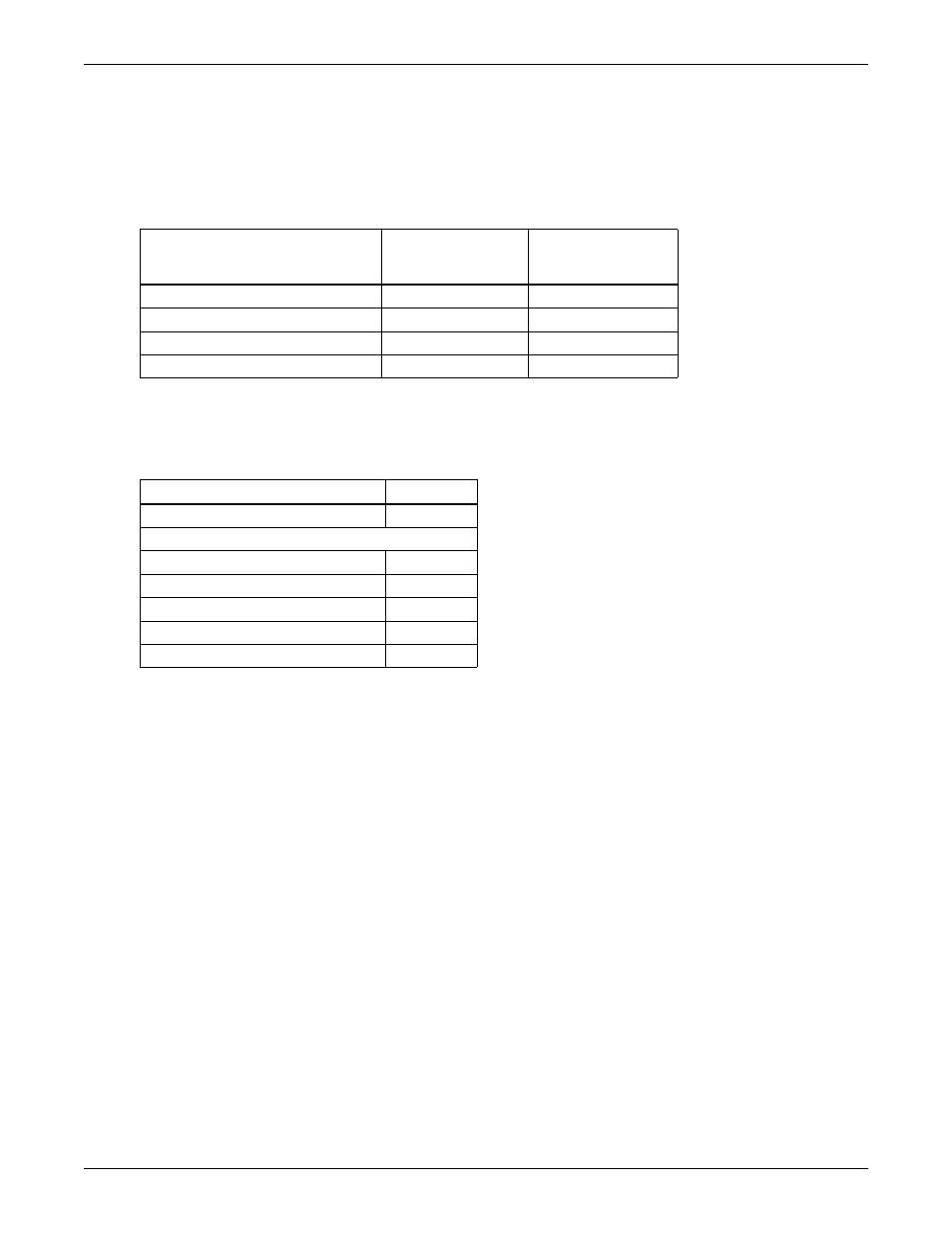
Table 15
Suction pressures
System
Minimum Pressure
PSIG (kPa)
R–22
Maximum Pressure
PSIG (kPa)
R–22
Air FSC
15 (103)
90 (620)
Floodback head pressure control
20 (137)
90 (620)
Water Cooled
20 (137)
90 (620)
Glycol Cooled
20 (137)
90 (620)
Table 16
Discharge pressures
System Design
PSIG (kPa)
Air Cooled
260 (1795)
Water Cooled
65 to 75°F water (18 to 24°C)
210 (1450)
85°F water (29°C)
225 (1550)
Glycol Cooled
295 (2035)
Maximum
330 (2275)
High Pressure Cut-Out
360 (2480)
