Verilink 1250 (CG) Configuration/Installation Guide User Manual
1250 power and alarm card, Configuration guide, Chassis address selection
T
R
A
N
S
P
O
R
T
®
1250 Power and Alarm Card
Configuration Guide
Part Number 45- 00007
Revision 2.0
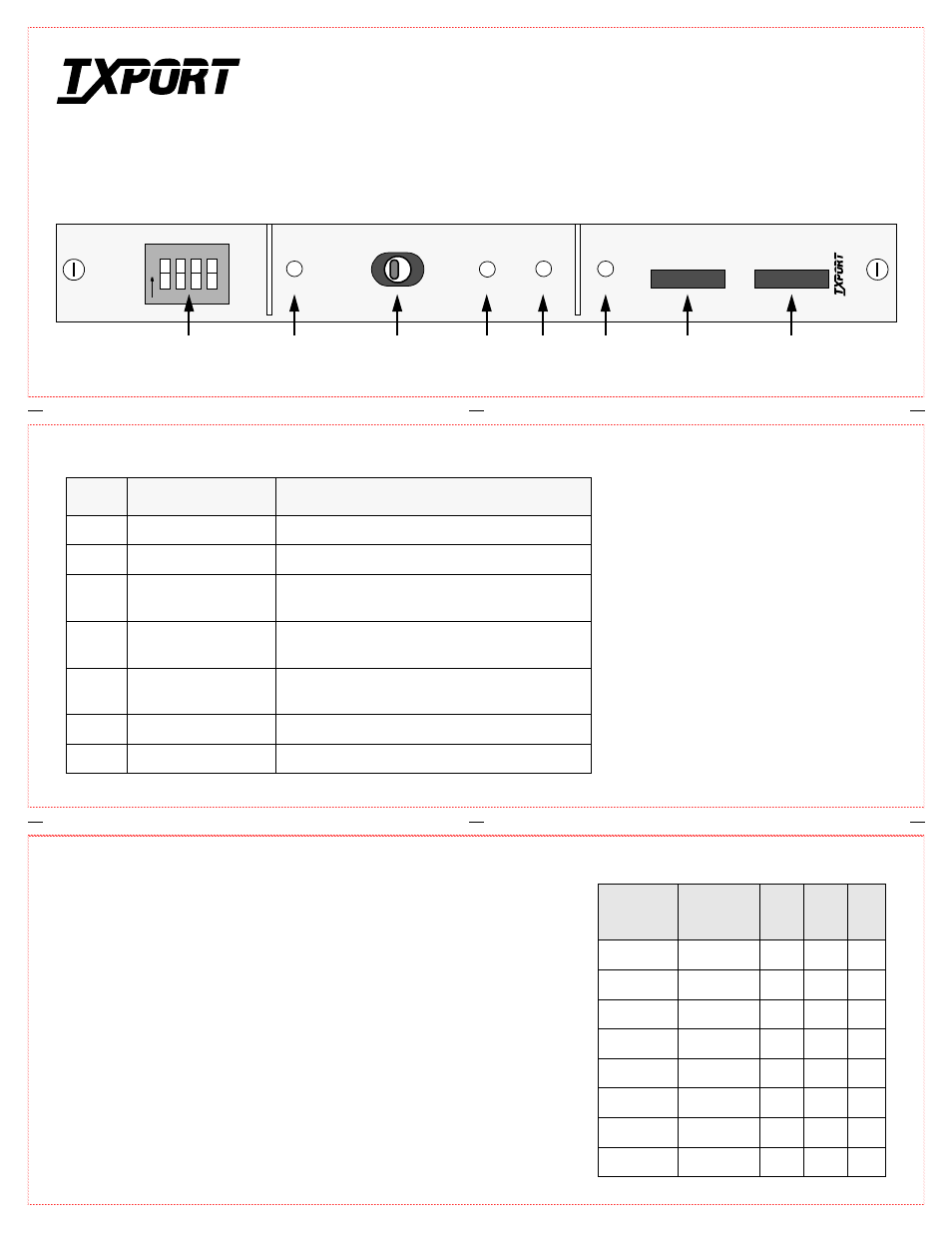
1250 Controls and Indicators
Index
Indicator
Description
1
CHASSIS ADDRESS
DIP switch which provides up to 8 chassis addresses.
2
POWER
Indicates that power is being supplied to the unit.
3
NORMAL/SILENT
Normal enables the ACO (Alarm Cut Off).
Silent disables the ACO.
4
ACO
The Alarm Cut Off LED indicates that the alarm
relay contacts are disabled.
5
ALARM
This LED indicates that an APS shelf alarm has
occurred.
6
FUSE ALARM
This LED indicates that a bus fuse has blown.
7
3 AMP GMT
Two 3 Amp fuse for power source A/B.
Chassis Addresses
Chassis
Number
Base
Address
S2
S3
S4
1
0 to 27
0
0
0
2
32 to 59
0
0
1
3
64 to 91
0
1
0
4
96 to 123
0
1
1
5
128 to 155
1
0
0
6
160 to 187
1
0
1
7
192 to 219
1
1
0
8
224 to 251
1
1
1
Chassis Address Selection
Each APS chassis must be assigned a block of addresses for its 1557 APS
cards so that the 1559 APS Manager may communicate with them. The DIP
switch located on the front panel of the 1250 Alarm and Power Card is used
to provide up to 8 chassis addresses. These addresses are used by the APSM
to poll and send commands to the 1557 cards.
Three out of the four switches (S2, S3, and S4) are set to one of the 8 pos-
sible address codes as shown in the table to the right. The DIP switch posi-
tions are number S1 through S4, with S1 on top and S4 on bottom. Note that
S1 is not used.
The first unit address (1557 card) in the chassis is the base address plus 1.
For example, if S2, S3, and S4 were all set to 0, the first unit address in the
chassis would be ‘1’ (0 + 1).
AL
ARM
&
PO
WE
R
CH
AS
S
IS
ADDRES
S
1
2
3 4
O
N
1
2
3
–
PO
WER
NORMAL
SILENT
AC
O
ALARM
FU
S
E
ALA
R
M
A
B
3 A
M
P
GM
T
12
50
TRANSPORT
®
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
7
1250 Front View
NOTES: 1250 cards that are Rev. 2.63 or
higher add the capability to maintain alarm
card functions (front panel indicators, switch
functions, and relay operation) even when
Fuse A and B are open. This is possible be-
cause these cards have the alarm circuitry
wired to the ‘hot’ side of the incoming A and
B external power source(s). In early revi-
sions, the 1250 alarm functions were only op-
erational if one or more of the front panel
fuses were functional (not blown).
Earlier versions of the 1250 card were called
1555P cards. The function of each card is the
same.
