Fc100 - floating point fast fourier transform, Streaming io architecture – Sundance FC100 v.2.3 User Manual
Page 8
FC100 - Floating Point Fast Fourier Transform
v2.3
Fast Fourier Transform product manual
October 2005
www.sundance.com
- 8 -
The output data bank is either A or B. The number of passes through the core will help to
determine which one is the output data bank. Table 3 shows the number of passes in
function of the transform length. If the number is odd for a given transform length, the
FFT results will be in data bank B. If even, the results will be stored in data bank A.
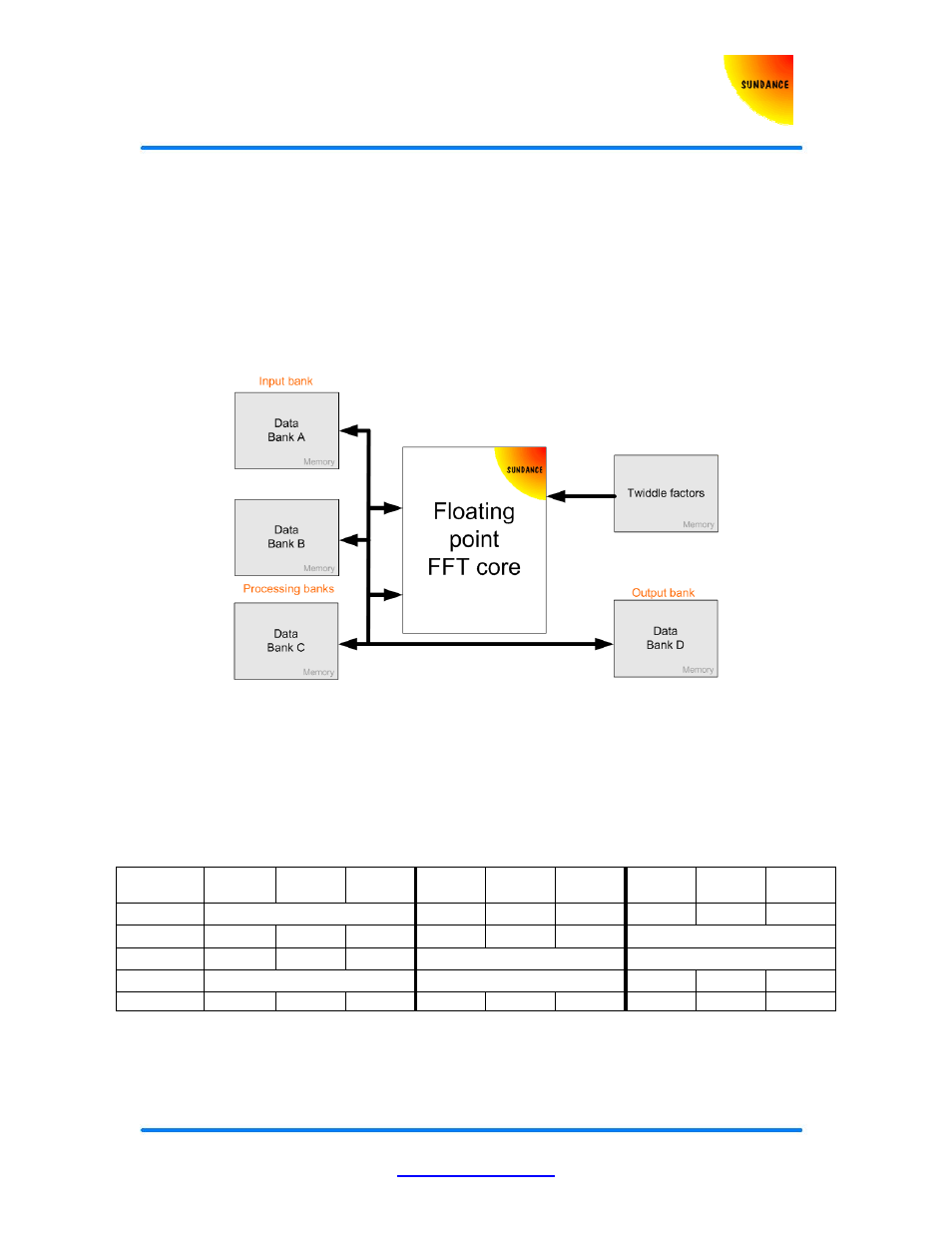
Streaming IO architecture
A streaming IO architecture is presented below for continuous data processing. Please
note that a system using Dual Port Memory or QDR SRAM will only require two data
banks.
Figure 2 : Streaming IO memory architecture
Streaming IO processing with concurrent data input and data output requires 5 memory
banks to be connected to the FFT core. In this type of architectures, the maximum
continuous throughput depends on the number of passes through the FFT engine and the
clock rate is it running at. The table below shows how the memory banks are used when
performing several transforms in a row.
Bank Pass
1
FFT 1
Pass 2
FFT 1
Pass 3
FFT 1
Pass 1
FFT 2
Pass 2
FFT 2
Pass 3
FFT 2
Pass 1
FFT 3
Pass 2
FFT 3
Pass 3
FFT 3
D
ata A
Write input data for FFT 2
FFT read
FFT write
FFT read
FFT write
FFT read
FFT write
D
ata B
FFT read
FFT write
FFT read
FFT write
FFT read
FFT write
Read output results of FFT 2
D
ata C
FFT write
FFT read
FFT write
Read output results of FFT 1
Write input data for FFT 4
D
ata D
Read output results of FFT 0
Write input data for FFT 3
FFT read
FFT write
FFT read
Twiddles
read read read read read read read read read
Table 4 : Memory banks for a streaming IO architecture
