Fluke Biomedical 18-222 User Manual
Page 13
2-5
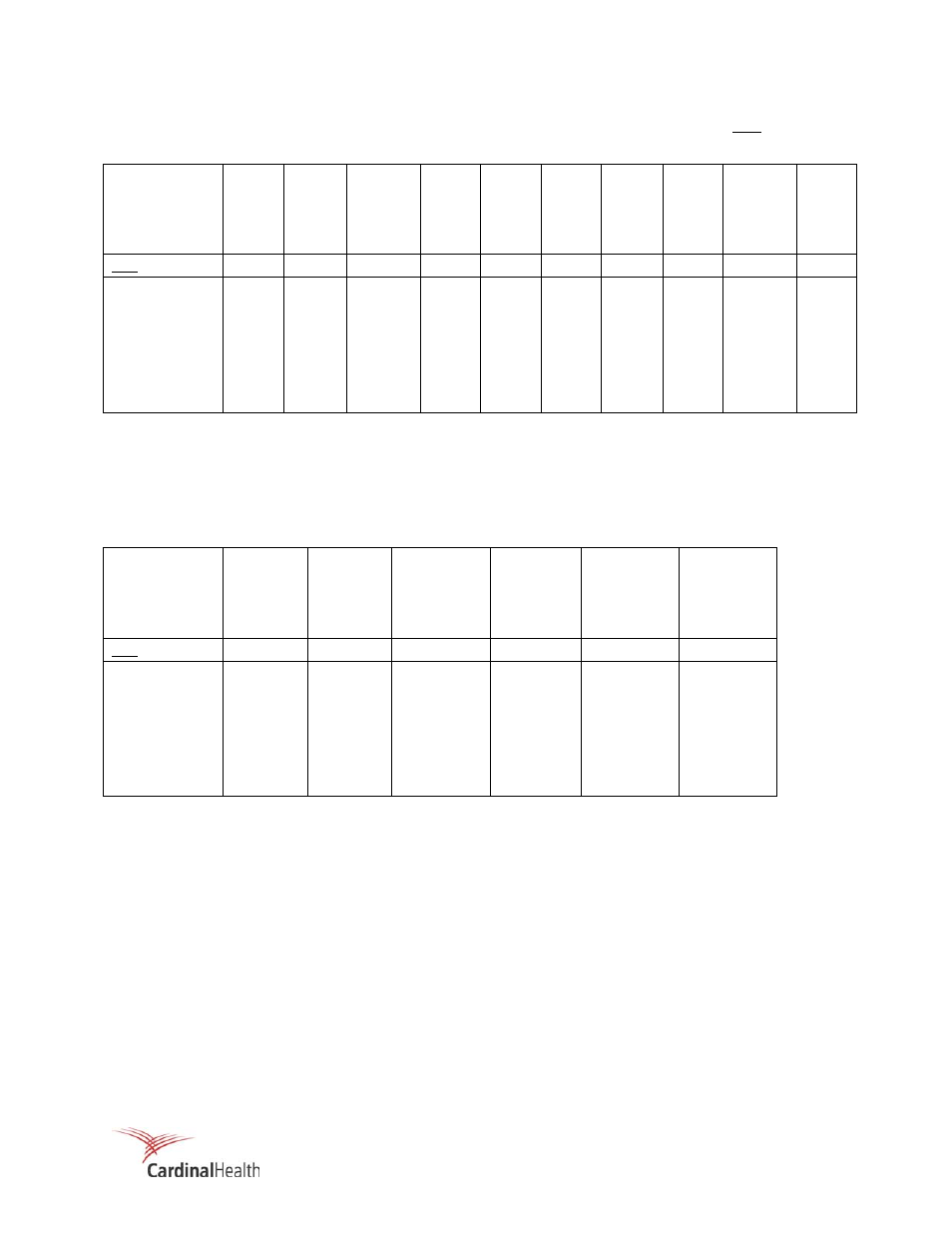
Table 2-3. Attenuation Comparison (
µ
x) for Uses in the Well Known Relationship Various
Phantom Densities and Sizes
Tissue:
Acrylic Acrylic Acrylic BR-12 50/50 30/70 50/50 30/70 50/50 20/80
Thickness:
4.4 cm
5.0 cm
4.55 cm
4.5 cm
4.0 cm
4.5 cm
4.5 cm
5.0 cm
5.0 cm
6.0 cm
MFGR:
ACR
MFR #1
MFR #2
NAD
NAD
NAD
NAD
NAD
NAD
NAD
Fat Layer:
No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
keV
10 15.542
17.769
16.995
15.942
13.703
14.257 15.514 15.889 17.325 18.294
15 5.127
5.891
5.608
5.298
4.601
4.803 5.207 5.352 5.814 6.175
20 (28 kVp)
2.705
3.103
2.936
2.728 2.392 2.523 2.706 2.811 3.021 3.251
30 1.477
1.691
1.582
1.402
1.251
1.346 1.412 1.498 1.573 1.758
40 1.162
1.328
1.236
1.062
.956
1.042 1.078 1.159 1.201 1.371
50 1.033
1.179
1.095
.925
.836
.918 .944 1.021 1.051 1.211
This chart compares the composite attenuation for various phantom size/density compositions.
The linear attenuation coefficient (
µ) for each type of material (wax/lucite/gland/fat/etc.) applied to the thickness of
the material in each phantom design permits calculation of total attenuation for each phantom design.
Actual Breast Tissue per Hammerstein
Tissue
70/30 50/50 50/50 50/50 30/70 20/80
Thickness:
4.0 cm
4.0 cm
4.5 cm
5.0 cm
5.0 cm
6.0 cm
MFGR:
Actual Actual Actual Actual Actual Actual
Fat Layer:
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
keV
10 15.689
14.411
16.317
18.223
16.578
18.996
15 5.066
4.697
5.314
5.931
5.446
6.271
20 (28 kVp)
2.571
2.411
2.725
3.038
2.829
3.279
30 1.307
1.254
1.414
1.574
1.502
1.762
40 .989
.961
1.082
1.204
1.165
1.375
50 .862
.843
.949
1.055
1.028
1.217
I
-
µx
I
O
= e
