5 dubbing studio, Dubbing studio -4 – Dolby Laboratories 737 User Manual
Page 22
Model 737 Soundtrack Loudness Meter - Leq(m)
Cat. No. 448B Input Adapter Board
3-4
3.5
Dubbing studio
Dubbing Studio set-ups may vary depending upon location. Contact a Dolby sound
consultant or Dolby office to resolve any uncertainties. Installation of the Cat. No. 448B
can be optimized using the logic map in Table 3-1 and Figure 3-4, the Cat. No. 448B
schematic diagram. The following examples are two common configurations.
Example 1
A typical UK setup uses the DA20 or dubbing interface (Cat. No. 448) output switched
to the CP65-S. The Cat. No. 448B should take this unbalanced six-track signal as the main
input (grounding the negative inputs) and the two-track signal from the Cat. No. 150
via the auxiliary input. OPT and MAT should be fed from either the FA line of the
CP65 or the MAT line of the dubbing interface and SR should be grounded. Follow
the installation steps in Section 3.4.2 on page 2. The six-track input is paralleled from
the 300 mV input to the CP65 after any switching between the monitor bus and DA20.
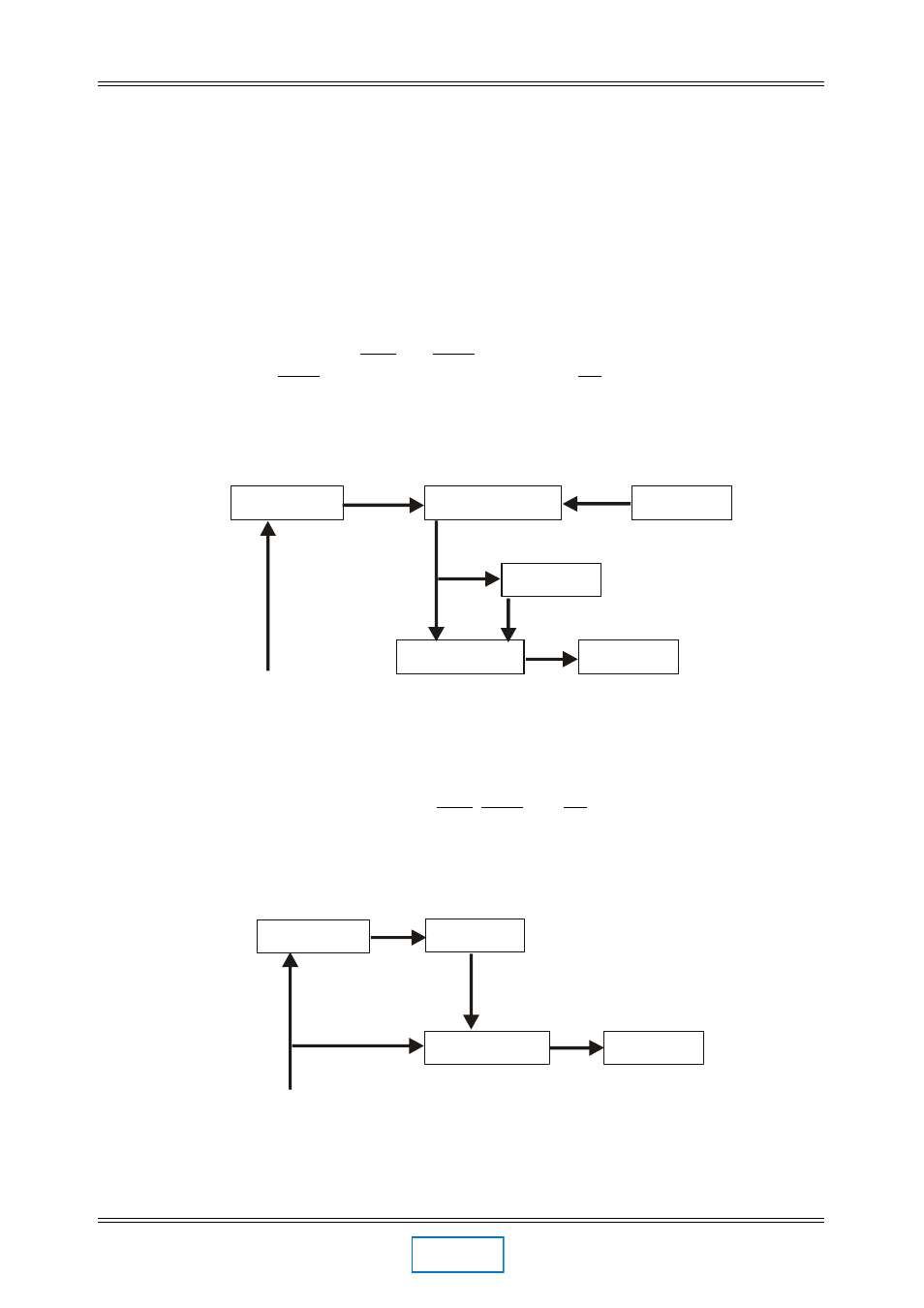
Figure 3-3 Typical UK setup
Example 2
The six-track main inputs are balanced and the two-track inputs are derived from the
main input channels 1&3 or 2&3. OPT, MAT, and SR lines are fed from the dubbing
interface. The DA20 output should be routed at the calibrated level to the main monitor
buses of the studio before the dubbing interface.
C a t. N o . 4 4 8
C a t. N o . 4 4 8 B
M od e l 7 3 7
C P 6 5
6 p 2w S w itch e r
D A 1 0 /2 0
S tu d io m o n ito r b u s
x6 (b a l.)
x2 L t/R t - o pt
x6 (u n b a l.)
x6 (u n b a l.)
C a t. N o . 4 4 8
C a t. N o . 4 4 8 B
M od e l 7 3 7
C P 6 5
S tu d io m o n ito r b u ss
x6 (b a l.)
x2 L t/R t - o pt
x6 (u n b a l.)
MAIN
