Winco AS480 User Manual
Page 2
© Cummins 2008
2
TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
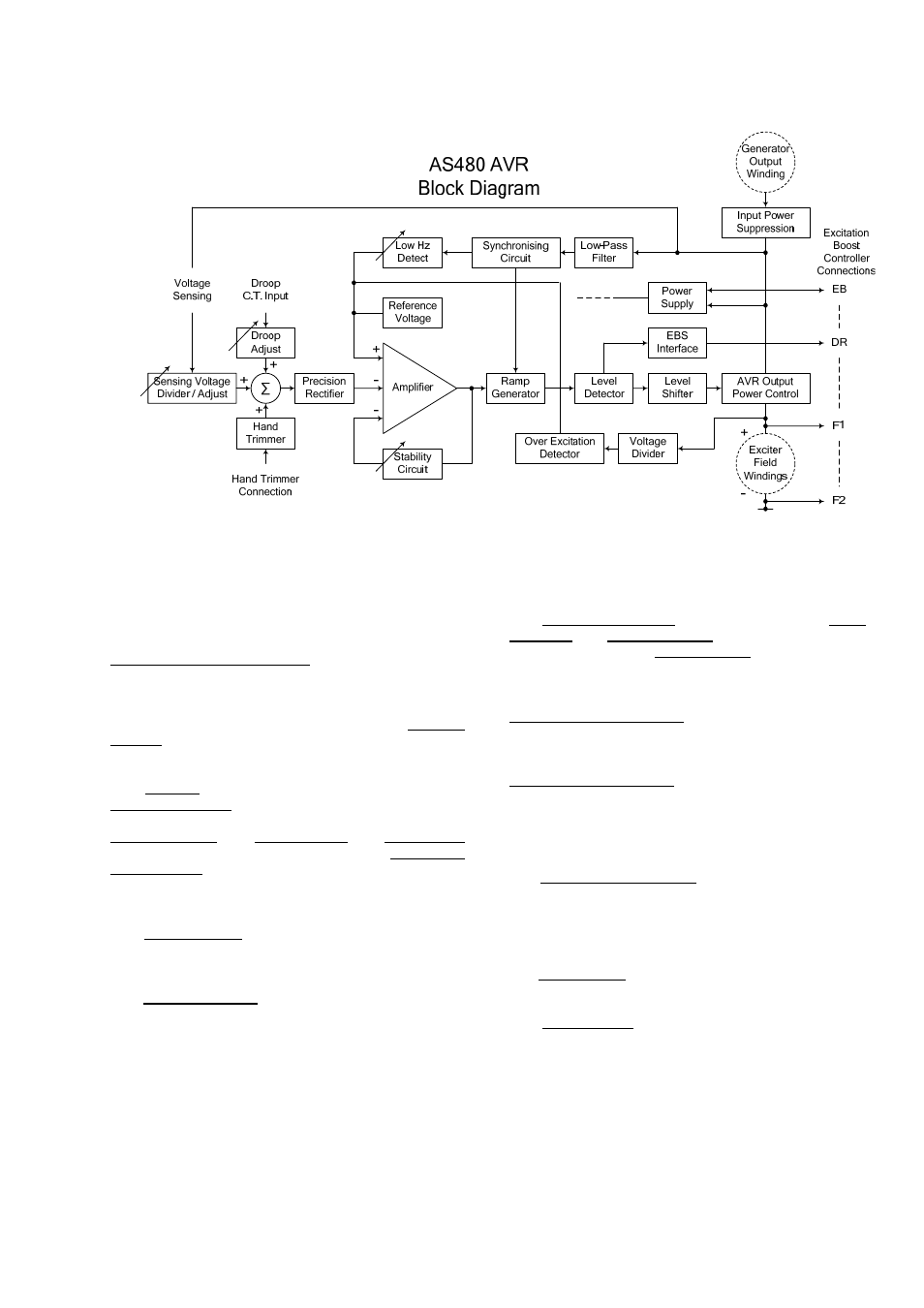
The AVR Circuit Description
The main functions of the AVR are:
Sensing Voltage Divider / Adjust takes a proportion of the
generator output voltage and attenuates it. The potential
divider is adjustable by the AVR Volts potentiometer and
external hand trimmer (when fitted). The output from the
droop CT is also added to this signal. A Precision
Rectifier converts the a.c. input signal into d.c. for further
processing.
The Amplifier compares the sensed voltage to the
Reference Voltage and amplifies the difference (error) to
provide a controlling signal for the power devices. The
Ramp Generator and Level Detector and Level Shifter
infinitely control the conduction period of the AVR Output
Power Control devices. This provides the exciter field
windings with the variable power necessary to maintain
the generator voltage within specified limits.
The Stability Circuit provides adjustable feedback to
ensure good steady state and transient performance of
the control system.
The Low Hz Detector measures the period of each
electrical cycle and causes the reference voltage to be
reduced approximately linearly with speed below a pre-
settable threshold. A Light Emitting Diode gives indication
that the circuit is activated by the low-speed running
condition.
The Synchronising circuit is used to keep the Ramp
Generator and Low Hz Detector locked to the generator
waveform period. The Low Pass Filter prevents distorted
waveforms affecting the operation of the AVR control
circuit.
AVR Output Power Control devices vary the amount of
exciter field current in response to the error signal
produced by the Amplifier.
Input Power Suppression components are included to
prevent load generated voltage transients from damaging
the AVR components and also to reduce the amount of
conducted radio-frequency noise on the generator
terminals.
The Over Excitation Detector continuously monitors the
exciter field voltage and provides the signal required to
collapse the output voltage. This protection circuit
triggers only if an over excitation condition persists for a
specific amount of time.
The Power Supply provides the required voltages for the
AVR circuitry.
The EBS Interface provides the signals necessary to
control the excitation boost generator (EBG). The EBG
responds to the level of excitation provided by the AVR
and supplies additional power as it is needed to support
the overload.
