Power supply, Blood pressure - general information – Dyras BPSS-4129 User Manual
Page 5
EN
BPSS-4129
BPSS-4129
8
9
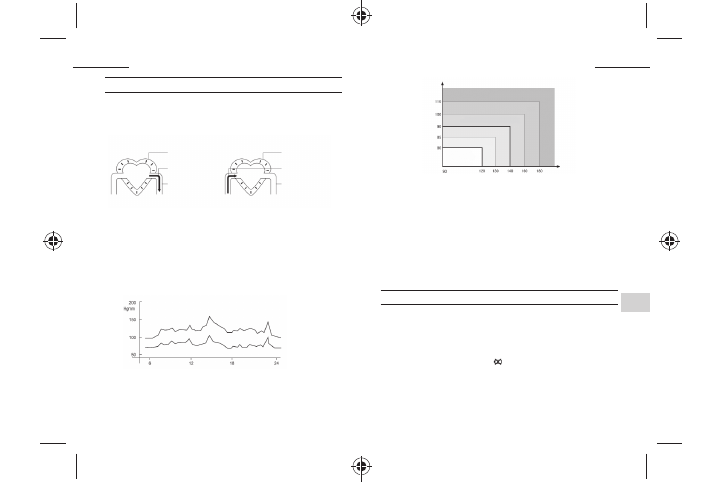
Diastolic blood pressure
(Hgmm)
Seriously high blood pressure
High blood pressure
Rather high blood pressure
Normal systolic value
Normal blood pressure
Optimum blood
pressure
(target value)
Systolic blood pressure
(Hgmm)
If the average of the blood pressure values measured by you differs from the normal values given in the table, or
the measured values show significant fluctuations and thus they frequently differ from the healthy values, we
advise you to consult your doctor. Only specialist doctors can make a correct diagnosis, based on measurements
made with medical instruments. Furthermore, we recommend that you take your blood pressure monitor with
you, as it is necessary to check the calibration of your device from time to time.
In addition to the medical treatment prescribed by your doctor you can promote efficient reduction of your blood
pressure by observing the following suggestions:
- Slimming course or diet that would reduce the level of harmful cholesterol (LDL)
- Reducing the consumption of drinks containing alcohol and caffeine
- Giving up smoking
- Moderate salt consumption
- Regular exercise
POWER SUPPLY
The device operates on 2 x 1.5 V AAA batteries.
1. Slide the battery compartment cover as shown by the arrow, then remove it.
2. Insert the batteries in the battery holder according to the marked polarity.
3. Finally replace the battery compartment cover,making sure it is securely fitted.
•
Batteries must be replaced when the battery icon
appears on the display. Both batteries must be
replaced by a new ones. You must use alkali batteries only. Ni-Cd/Ni-MH batteries have an output voltage not
exceeding 1.2V, which is insufficient to operate the blood pressure measuring instrument.
BLOOD PRESSURE - GENERAL INFORMATION
Blood circulation ensures an appropriate supply of oxygen to the body. Blood pressure is the pressure the blood
exerts on the artery wall. The systolic value (upper value) can be measured when the myocardium contracts and
forces blood into the arteries. The diastolic value (lower value) is measured when the myocardium relaxes and
blood flows from the veins into the heart.
Myocardium contracts
Blood flows out
Pressure rises in
the blood vessels
Higher pressure
Myocardium relaxes
Blood flows back to the heart
Pressure decreases
in the blood vessels
Lower pressure
Systolic blood pressure
Diastolic blood pressure
In the human body, blood pressure increases naturally with age. This is the result of aging of the blood vessels.
Increased blood pressure can be further aggravated by smoking, regular consumption of alcohol and drinks
containing caffeine, extreme salt consumption, stress and lack of regular exercise. Also latent diseases such
as problems with the kidneys or a high level of cholesterol (LDL) can cause increased blood pressure, because
they result in the blood vessels losing flexibility. High blood pressure increases the risk of a stroke or myocardial
infarction. Due to the fact that high blood pressure causes symptoms that can remain unnoticed for a long time,
it is necessary to check our blood pressure regularly, to make sure that it is within the healthy range. A person’s
blood pressure fluctuates during the day, as a result of exercise or changes in our mood, and this is why only the
average of several measurements or the number of changes can give us meaningful results.
Upper curve: Systolic blood pressure values
Lower curve: Diastolic blood pressure values
The average of the measured blood pressure values can be evaluated on the basis of the figure below. Systolic
values below 90 indicate low blood pressure.
User'sManual for BPSS-4129.indd 8-9
User'sManual for BPSS-4129.indd 8-9
2013.01.22. 10:39:08
2013.01.22. 10:39:08
