Principle of pump operation, Model specific – Versa-Matic 3 Elima-Matic Metallic Food Processing - ATEX (E3) User Manual
Page 8
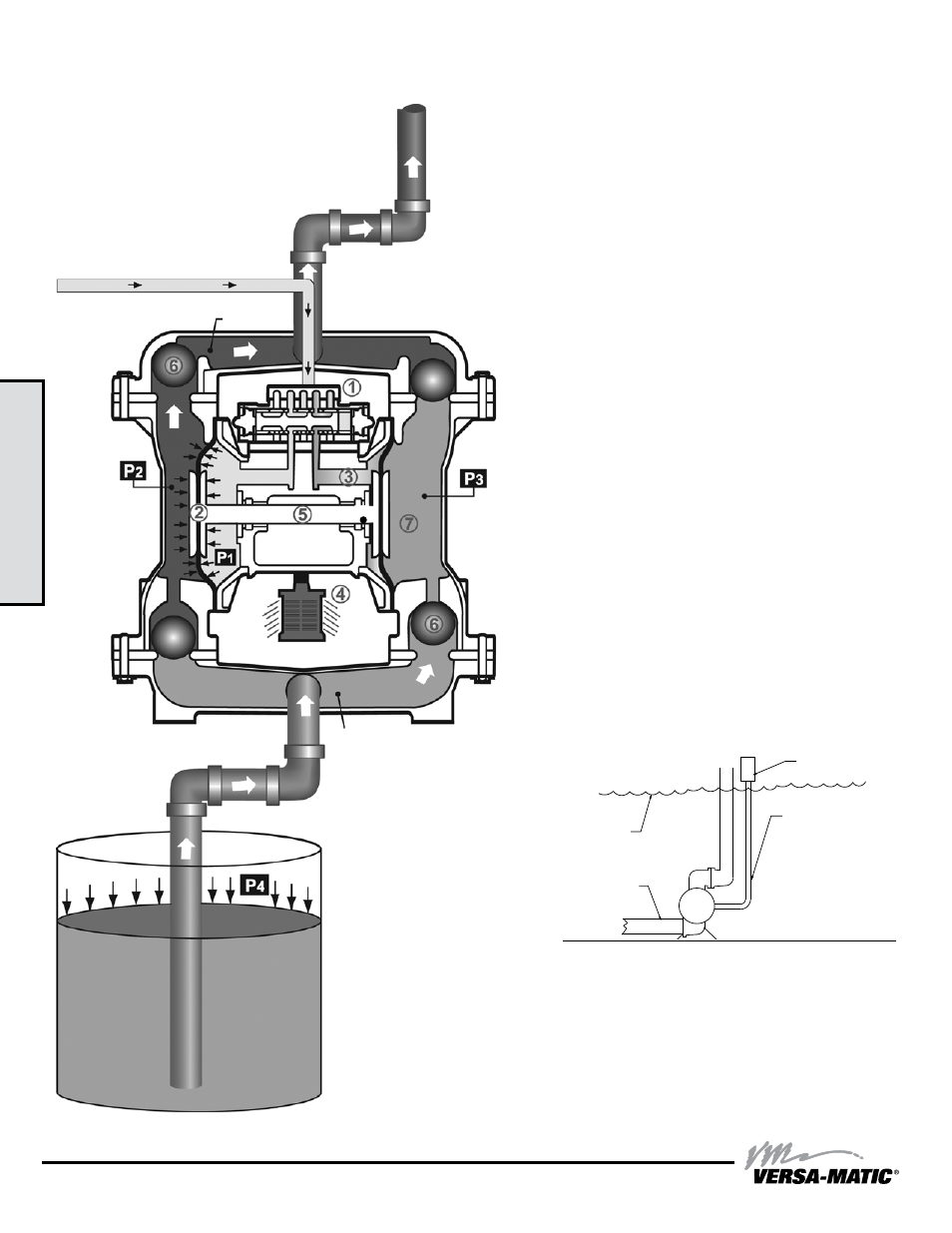
e3mdlCsmATEXFP-rev0514
5
• Model E3 Metallic Food Processing
www
.
versamatic
.
com
Air-Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) pumps are powered
by compressed air or nitrogen.
The main directional (air) control valve
①
distributes
compressed air to an air chamber, exerting uniform pressure
over the inner surface of the diaphragm
②
. At the same time,
the exhausting air
③
from behind the opposite diaphragm
is directed through the air valve assembly(s) to an exhaust
port
④
.
As inner chamber pressure
(P1)
exceeds liquid chamber
pressure
(P2)
, the rod
⑤
connected diaphragms shift
together creating discharge on one side and suction on the
opposite side. The discharged and primed liquid’s directions
are controlled by the check valves (ball or flap)
⑥
orientation.
The pump primes as a result of the suction stroke. The
suction stroke lowers the chamber pressure
(P3)
increasing
the chamber volume. This results in a pressure differential
necessary for atmospheric pressure
(P4)
to push the fluid
through the suction piping and across the suction side check
valve and into the outer fluid chamber
⑦
.
Suction (side) stroking also initiates the reciprocating
(shifting, stroking or cycling) action of the pump. The suction
diaphragm’s movement is mechanically pulled through its
stroke. The diaphragm’s inner plate makes contact with an
actuator plunger aligned to shift the pilot signaling valve.
Once actuated, the pilot valve sends a pressure signal to the
opposite end of the main directional air valve, redirecting the
compressed air to the opposite inner chamber.
Principle of Pump Operation
SAFE AIR
EXHAUST
DISPOSAL
AREA
PUMP INSTALLATION AREA
1" DIAMETER AIR
EXHAUST PIPING
1" DIAMETER AIR
EXHAUST PIPING
1" DIAMETER AIR
EXHAUST PIPING
MUFFLER
LIQUID
LEVEL
SUCTION
LINE
LIQUID
LEVEL
SUCTION
LINE
MUFFLER
MUFFLER
SUBMERGED ILLUSTRATION
Pump can be submerged if the pump materials of construction
are compatible with the liquid being pumped. The air exhaust
must be piped above the liquid level. When the pumped product
source is at a higher level than the pump (flooded suction
condition), pipe the exhaust higher than the product source to
prevent siphoning spills.
MODEL SPECIFIC
2: INST
AL
& OP
