Gorman-Rupp Pumps 112G60-B 1214462 and up User Manual
Page 11
OM−05174
10 SERIES
PAGE B − 4
INSTALLATION
trained air to escape from the liquid before it is
drawn into the suction inlet.
If two suction lines are installed in a single sump,
the flow paths may interact, reducing the efficiency
of one or both pumps. To avoid this, position the
suction inlets so that they are separated by a dis-
tance equal to at least 3 times the diameter of the
suction pipe.
Suction Line Positioning
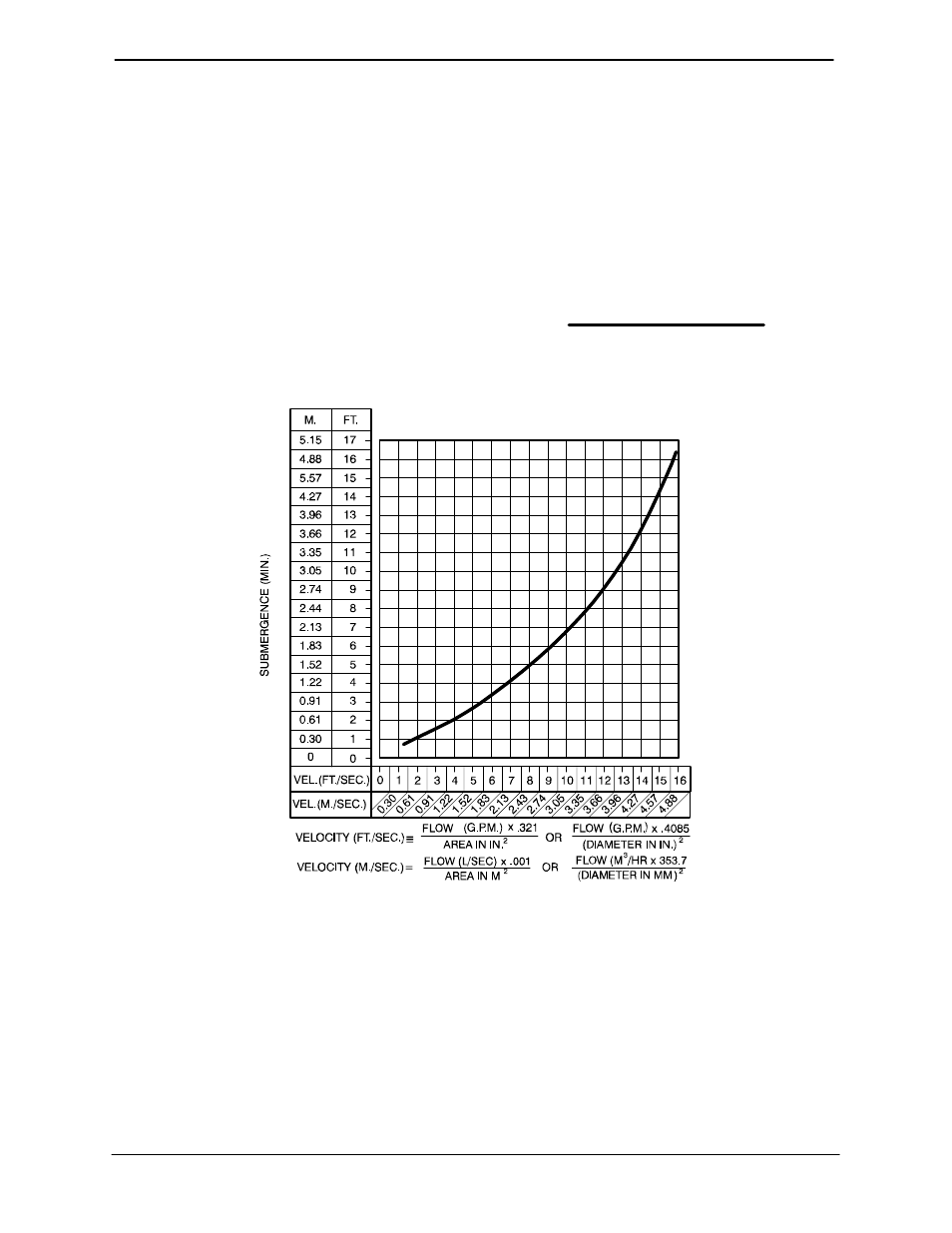
The depth of submergence of the suction line is
critical to efficient pump operation.
Figure B−2
shows recommended minimum submergence vs.
velocity.
NOTE
The pipe submergence required may be reduced
by installing a standard pipe increaser fitting at the
end of the suction line. The larger opening size will
reduce the inlet velocity. Calculate the required
submergence using the following formula based
on the increased opening size (area or diameter).
Figure B−2. Recommended Minimum Suction Line Submergence vs. Velocity
DISCHARGE LINES
Siphoning
Do not terminate the discharge line at a level lower
than that of the liquid being pumped unless a si-
phon breaker is used in the line. Otherwise, a si-
phoning action causing damage to the pump
could result.
Valves
If a throttling valve is desired in the discharge line,
use a valve as large as the largest pipe to minimize
friction losses. Never install a throttling valve in a
suction line.
A check valve in the discharge line is normally rec-
ommended, but it is not necessary in low dis-
charge head applications.
