3B Scientific Hoffmann Electrolysis Apparatus User Manual
Page 3
6
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com • Technical amendments are possible
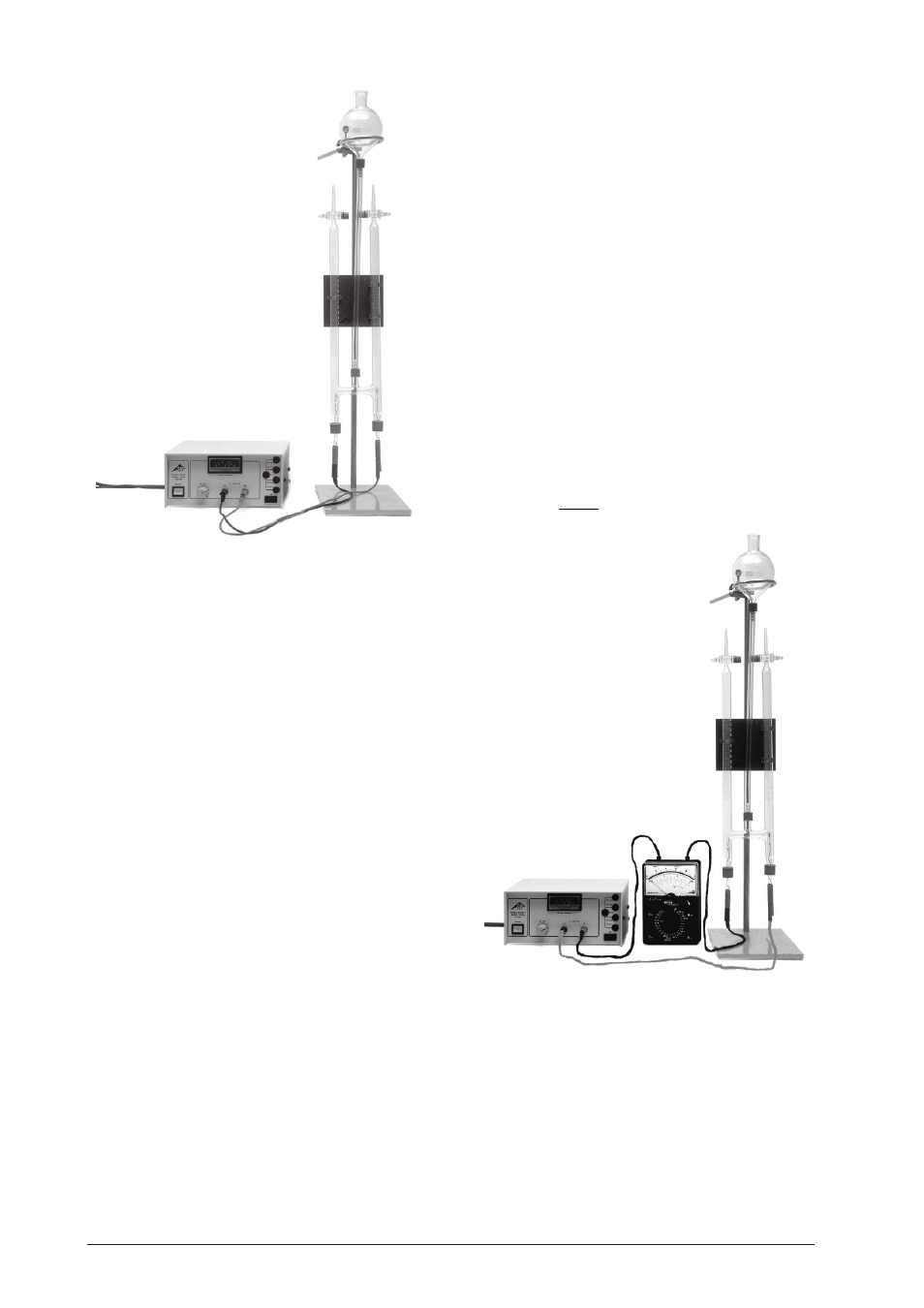
Fig. 1
3.2 Determining the Faraday constant
Required equipment:
Water-decomposition apparatus
Voltage supply (e.g. U11760 AC/DC Power supply)
Ammeter (e.g. U13000 multimeter)
Connecting leads
Distilled water
Sulfuric acid
Stopwatch
Thermometer
Barometer
Hydrometer
Experiment procedure:
•
Set up the experiment according to Figure 2.
•
Pour distilled water into the leveling bulb with both
stopcocks open.
Fill the gas collection tubes completely by altering
the height of the leveling bulb.
•
Close the glass stopcocks. The water level in the
leveling bulb should be higher than that in the col-
lection tubes.
•
Check the apparatus for leaks and tighten where
necessary.
•
Turn on the power supply and set the voltage so
that approximately 1 A of current flows. Check to
see that gas is being emitted into both tubes.
•
Turn the power supply off again, open the stop-
cocks and release the gas.
•
Close the glass stopcocks. Turn on the power sup-
ply and the stopwatch at the same time.
•
When the glass collection tube at the negative pole
(cathode) is nearly full, turn off the power supply
and the stopwatch together and record the time.
•
Determine the volumes of gas. The hydrostatic pres-
sure should be equalized in order to do this.
•
Measure the air pressure and room temperature.
Calculation:
•
For a known current
Ι
(A), time t (s), air pressure p
(Nm
–2
), temperature T (K), volumes of gas VH
2
, VO
2
(m
3
) and universal gas constant R (8.3 J mol
–1
K
–1
)
the Faraday constant F is given by
F
Q R T
p V
= ⋅ ⋅
⋅ ⋅
2
Fig. 2
