3B Scientific Kolbe's Electroscope User Manual
Page 2
3B Scientific GmbH ▪ Rudorffweg 8 ▪ 21031 Hamburg ▪ Germany ▪
www.3bscientific.com
Rights to amend technical specifications reserved
© Copyright 2013 3B Scientific GmbH
4. Friction rods and rubbing material
Friction
rods
Rubbing
material
Charge
polarity
PVC
Plastic foil
+
Acrylic
glass
Plastic foil
-
Glass tube
Newspaper,
leather
+
Plastic rod
Wool, textile
fibers
-
5. Operation
5.1 General notes
•
Make sure that the insulator is always clean
and dry. If necessary use alcohol or spirits
for cleaning.
•
At high humidity and after transporting the
unit from a cool room into a warmer one, dry
the electroscope in a stream of hot air (e.g.
a hair dryer).
5.2
Charging up the electroscope by
touching it with a statically charged body
•
Attach the capacitor plate to the
electroscope.
•
Rub the friction rod (e.g. 1002709) with the
suitable material (PVC or acrylic rods e.g.
with plastic foil).
•
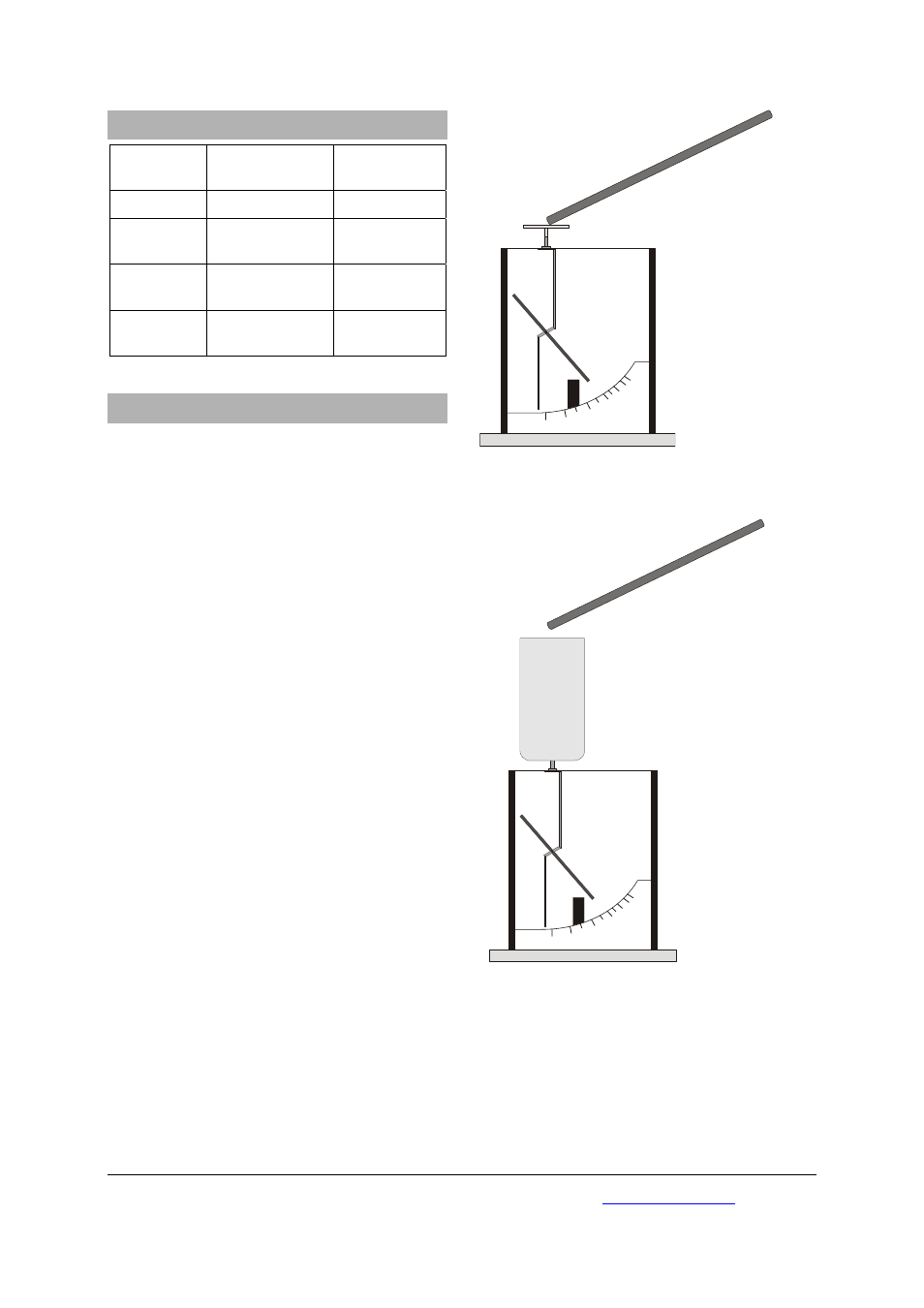
Touch the capacitor plate with the charged
rod. The pointer deflects.
•
Remove the friction rod, the pointer remains
deflected.
•
Touch the capacitor plate with your hand.
The pointer returns to normal.
5.3 Using electrostatic induction to charge
up the electroscope
•
Approach but do not touch the capacitor
plate with the statically charged friction rod.
The pointer deflects.
•
Remove the friction rod. The pointer returns
to normal.
•
Again approach the capacitor plate with the
statically charged friction rod. Once again
the pointer deflects.
•
Briefly touch the capacitor plate with your
finger to discharge it. The pointer deflection
disappears and returns to normal.
•
Now remove the friction rod. The pointer
again shows deflection.
0 1
2
3
4
5
6
Fig. 1 Charging the electroscope using a statically-
charged friction rod
0 1
2
3
4
5
6
Fig. 2 Charging a Faraday cup (1000972)
