Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX7425 User Manual
Page 11
MAX7418–MAX7425
5th-Order, Lowpass,
Switched-Capacitor Filters
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
Internal Clock
When using the internal oscillator, the capacitance
(C
OSC
) on CLK determines the oscillator frequency:
where
k = 87 x 10
3
for the
MAX7418/MAX7421/MAX7422/MAX7425
and
k = 110 x 10
3
for the
MAX7419/MAX7420/MAX7423/ MAX7424.
Since C
OSC
is in the low picofarads, minimize the stray
capacitance at CLK so that it does not affect the inter-
nal oscillator frequency. Varying the rate of the internal
oscillator adjusts the filter’s corner frequency by a
100:1 clock-to-corner frequency ratio. For example, an
internal oscillator frequency of 2.2MHz produces a
nominal corner frequency of 2.2kHz.
Input Impedance vs. Clock Frequencies
The MAX7418–MAX7425s’ input impedance is effective
as a switched-capacitor resistor and is inversely propor-
tional to frequency. The input impedance values deter-
mined by the equation represents the average input
impedance, since the input current is not continuous.
As a rule, use a driver with an output resistance less
than 10% of the filter’s input impedance.
Estimate the input impedance of the filter by using the
following formula:
where f
CLK
= clock frequency and C
IN
= 1pF.
Low-Power Shutdown Mode
The MAX7418–MAX7425 have a shutdown mode that is
activated by driving SHDN low. In shutdown mode, the
filter supply current reduces to 0.2µA, and the output of
the filter becomes high impedance. For normal opera-
tion, drive SHDN high or connect to V
DD
.
Applications Information
Offset (OS) and Common-Mode (COM)
Input Adjustment
COM sets the common-mode input voltage and is
biased at midsupply with an internal resistor-divider. If
the application does not require offset adjustment, con-
nect OS to COM. For applications in which offset
adjustment is required, apply an external bias voltage
through a resistor-divider network to OS, as shown in
Figure 4. For applications that require DC level shifting,
adjust OS with respect to COM. (Note: Do not leave OS
unconnected.) The output voltage is represented by
these equations:
where (V
IN
- V
COM
) is lowpass filtered by the SCF and
OS is added at the output stage. See the Electrical
Characteristics table for the input voltage range of COM
V
V
V
V
V
V
typ
OUT
IN
COM
OS
COM
DD
(
)
(
)
=
−
+
=
2
Z
1
(f
C )
IN
CLK
IN
=
×
fOSC(kHz)
k
COSC(pF)
=
V
DD
V
SUPPLY
IN
CLK
GND
INPUT
OUTPUT
50k
50k
50k
OUT
0.1
µF
0.1
µF
0.1
µF
CLOCK
SHDN
COM
OS
MAX7418–
MAX7425
Figure 4. Offset Adjustment Circuit
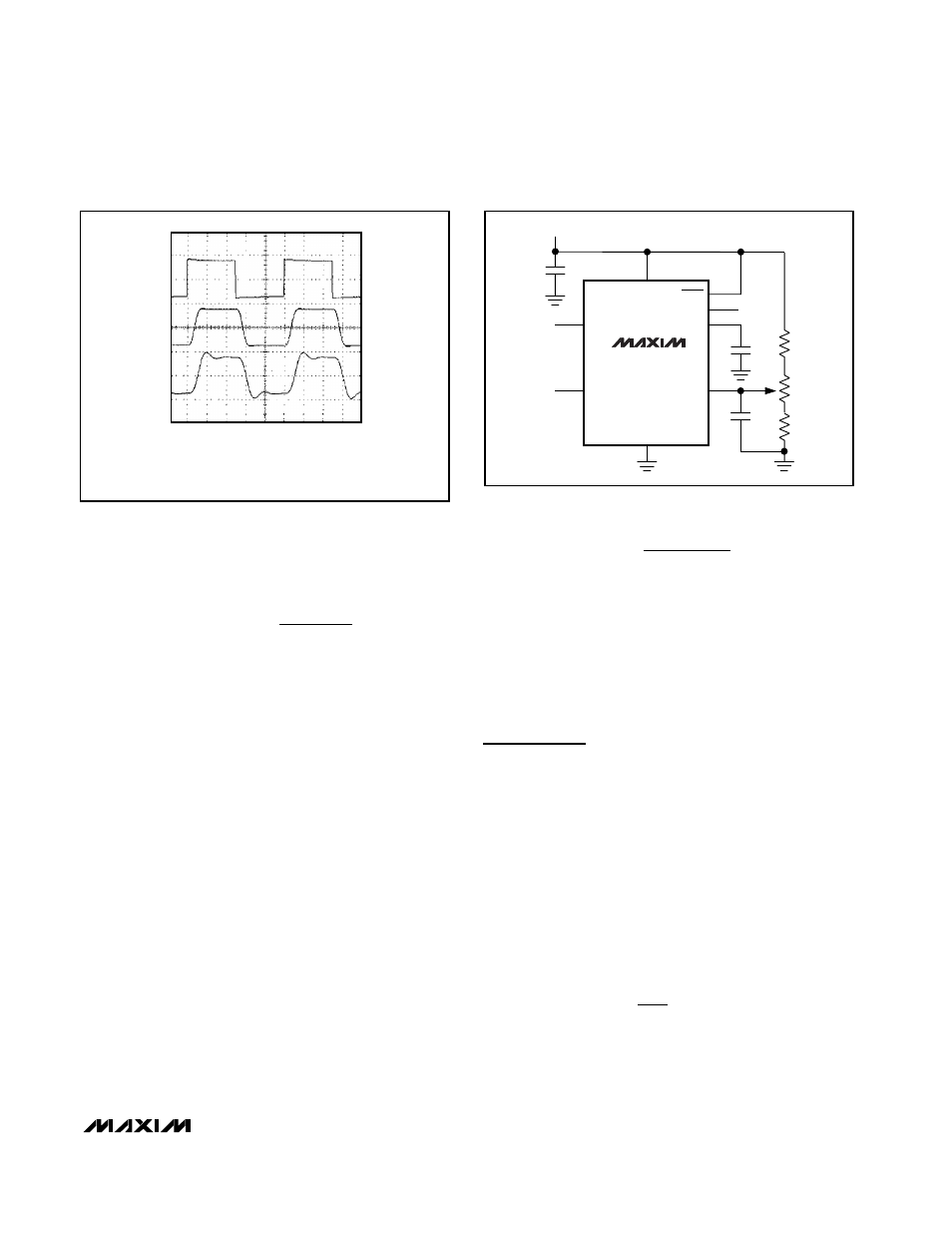
A
2V/div
2V/div
2V/div
C
A: 1kHz INPUT SIGNAL
B: MAX7419 BESSEL FILTER RESPONSE; f
C
= 5kHz
C: MAX7420 BUTTERWORTH FILTER RESPONSE; f
C
= 5kHz
B
200
µs/div
Figure 3. Bessel vs. Butterworth Filter Response
