Nokia T66280 User Manual
Page 20
E
Copyright Nokia Networks Oy
C33906002SE_00
19
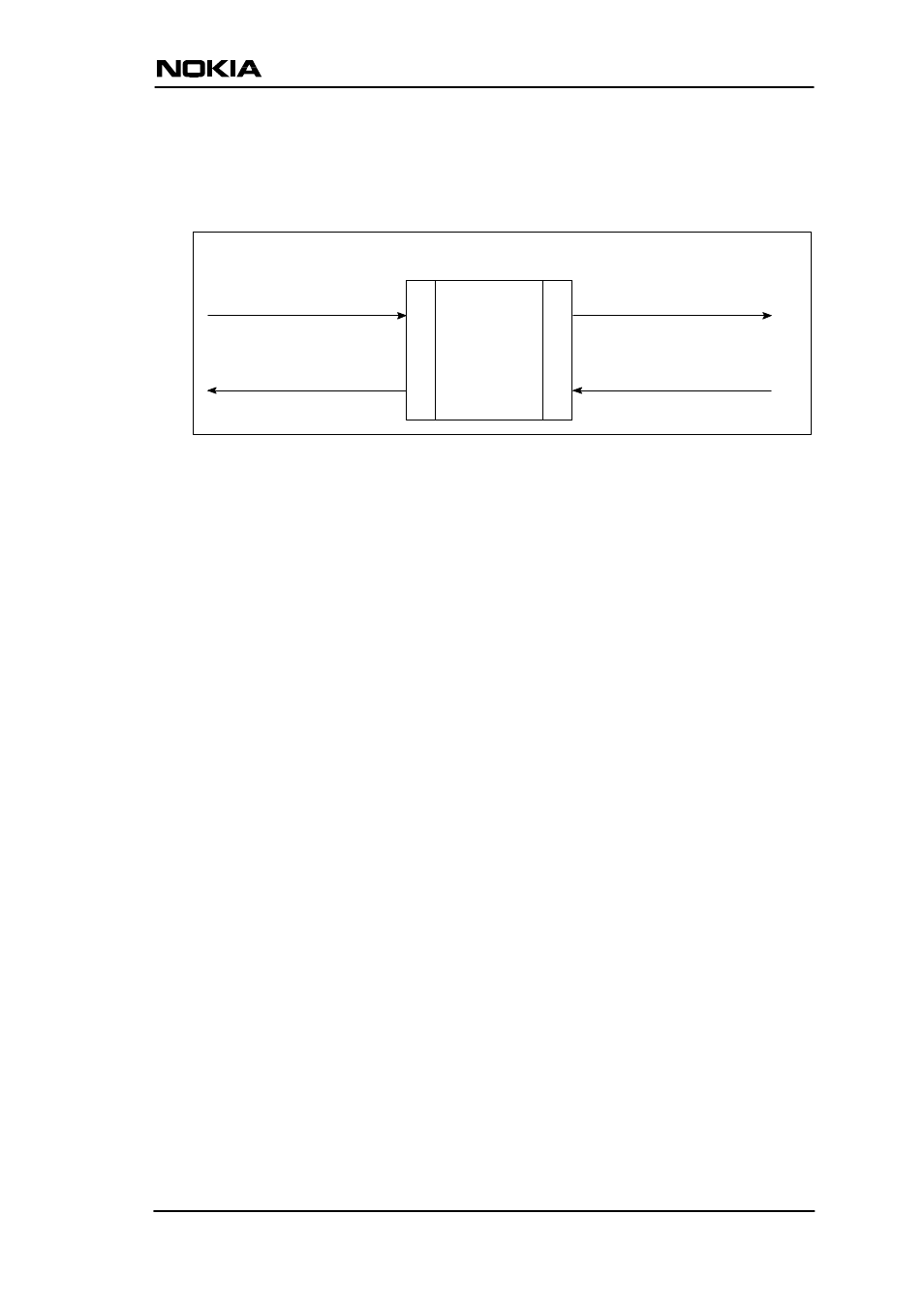
single VCC IP address to the public network. The principle of Network
Address Port Translation is presented in Figure 15.
NAPT router
192.168.1.254
195.1
12.12.161
src:192.168.1.112:1228
dst:194.112.11.111:80
src:194.112.11.111:80
dst:192.168.1.112:1228
src:195.112.12.161:50001
dst:194.112.11.111:80
src:194.112.11.111:80
dst:195.112.12.161:50001
Home network (LAN)
Internet (WAN)
Figure 15
Principle of Network Address Port Translation
NAPT may restrict the operation of some IP applications. NAPT also
operates as a simple IP firewall because translation is only allowed
when the first packet is transmitted from the LAN. This means that the
NAPT table entry is created only when a packet is sent from the home
network to the Internet. With server support capability, the user can
add static entries to the NAPT table allowing the translation always in
both directions. This capability is used to add servers (HTTP, NNTP,
and FTP), which are visible to the public IP network via the VCC, on
the LAN subnet.
NAPT supports most IP-based protocols. Because NAPT operates on
the IP and transport layer, the application that includes IP address and
port within the payload will not work properly through NAPT. In many
cases, these applications can be passed through the NAPT using
Application Layer Gateway functionality (ALG). M1122 has ALG for
the following protocols/applications:
D
ICMP
D
FTP
D
H.323 including NetMeeting
D
CUSeeMe
D
PPTP
D
IRC
D
IPSEC ESP tunnel mode and IKE
Note, that most IPSEC implementations will fail when passed through
NAPT. A typical reason is that the identification may fail if the
identification is based on IP address. Also, only tunnel mode without
Authentication Header (AH) works.
