Halogen basics & benefits, Halogen basics, Bulb shapes – Satco Products Halogen Lamps User Manual
Page 3: How it works, Un der pressu re • un der pre ssu re, Base types
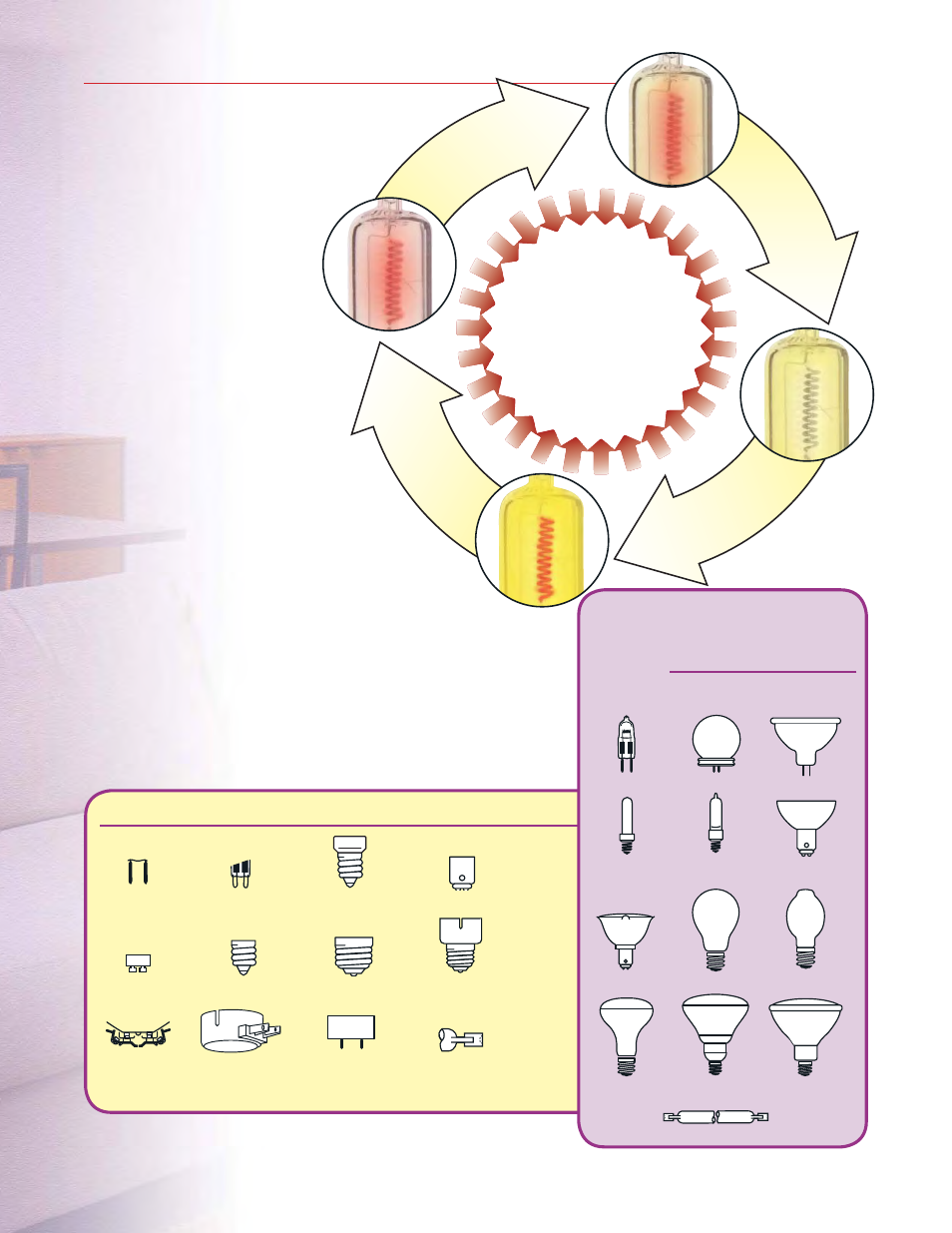
Halogen Basics
Halogen light bulbs operate
on the same principle as
standard incandescents
heating the tungsten
filament until it glows
but from there,
halogens improve
upon the process.
HOW IT WORKS
Operation of halogen lamps
is based on the “Halogen Cycle”
(see right). Tungsten particles from
the bulb’s filament evaporate.
The evaporated tungsten collides
with the halogen gas. The particles
chemically bond with the halogen
gas. Tungsten is then redeposited
back to the filament and the gas
is re-released.
The operating temperature is a significant
factor to ensure that the halogen cycle
performs properly. The interior wall of the bulb
must be above 250° C and less than 1,100° C.
Additionally, the filament of the lamp must reach
at least 2,000° C. To reach this temperature, the
interior wall must be in close proximity to the
tungsten filament.
ev
ap
or
a t
e
.
T
u
n
g
st
en
pa
rti
cle
s
fr
o
m
th
e
fil
a m
ent
E
va
p
o
ra
te
d
tu
n
g
s
te
n
co
llid
e
s
w
ith
th
e
ha
lo
g
e
n
g
a
s
.
P
a rti
cle
s
ch
em
ic
a
lly
bond
w it
h t
he
ha
lo
ge
n
ga
s
T
u
n
g
s
te
n
is
re
d
e
p
o
sit
ed
b
a
c
k
in
to
th
e
fil
a
m
e
n
t
a
nd
th
e
g
a
s
is
re
le
a
se
d.
•
UN
DER
PRESSU
RE
•
UN
DER
PRE
SSU
RE
In order for the
halogen cycle to function
properly, the gas must be
inserted into the quartz envelope at
a very high level of pressure, and it
must be sealed off and
maintained at the same level.
For safety reasons, a particle
barrier is required.
Bulb
shapes
JC
JCGV
MR
JD
Krypton
JD
ALR
AR
A
BT
R
BR
PAR
T
Base Types
Bi Pin
Double Loop
E11
DC Bay.
GU10
Euro (E14)
Medium (E26)
Medium Skirted
Screw Term.
Side Prong
Mog. End Prong
R7s
