SpectraLink NetLink Wireless Telephones Best Practices White Paper Wireless Telephone User Manual
Page 17
White Paper
Page 16
5.5 Virtual
Private
Networks
(VPNs)
Virtual Private Networks are secured private network connections.
VPNs typically employ some combination of encryption, digital
certificates, strong user authentication and access control to provide
security to the traffic they carry. They usually provide connectivity to
many devices behind a VPN concentrator. The network can be broken
into two portions, protected and unprotected:
1. The area behind the VPN server is referred to as the “protected”
portion of the network. Sensitive, private network equipment
such as file servers, email servers and databases would reside
in this portion.
2. The area in front of the VPN server is referred to as the
“unprotected” or demilitarized zone (DMZ), where the wireless
APs and less sensitive network equipment may reside.
Utilizing VPNs can be an extremely effective method of securing a
wireless network. Many customers have been implementing VPNs to
maintain the integrity of their wireless LANs by requiring wireless users
who need access to the protected portion of the network to connect
through a firewall.
Voice devices, such as the NetLink Wireless Telephone do not require
access to the protected portion of the network. Placing the NetLink
Wireless Telephones, NetLink SVP Server(s), and NetLink Telephony
Gateways in the demilitarized zone, and requiring data users to utilize
the VPN ensures that the network is protected against hackers seeking
to access sensitive information within the network core.
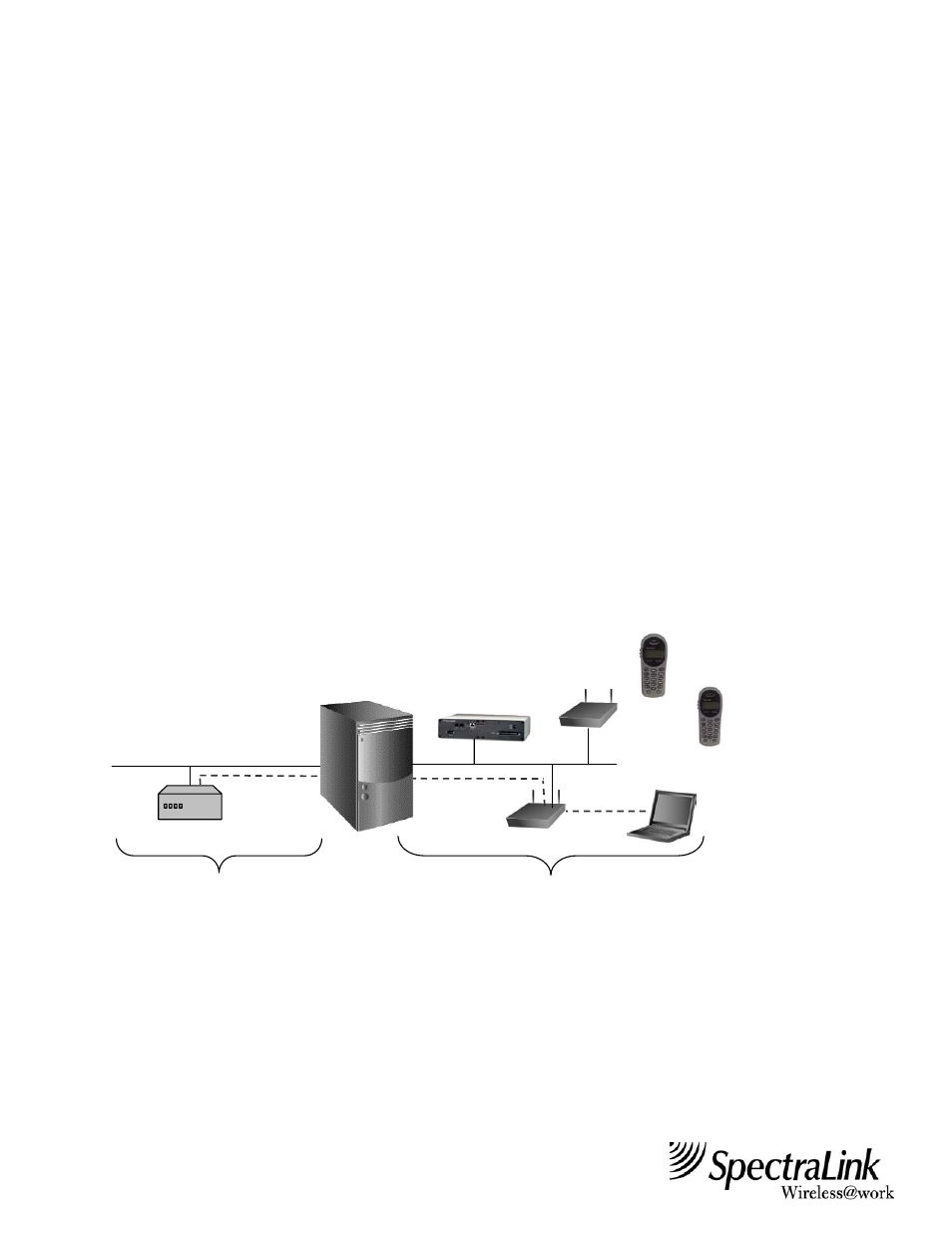
Deploying NetLink Wireless Telephones with a VPN
NetLink Wireless
Telephones
Unprotected DMZ
Protected Network Core
Devices that
require access to
the network core
utilize a secure
VPN connection
(dashed line).
VPN Concentrator
NetLink
Telephony
Gateway
