Next generation cdma 2000 solution, Ultrawave cdma – ADC UltraWAVE 2000 User Manual
Page 5
6/08
•
106330AE
Next
Generation
CDMA
2000
Solution
5
w w w . a d c . c o m
•
+ 1 - 9 5 2 - 9 3 8 - 8 0 8 0
•
1 - 8 0 0 - 3 6 6 - 3 8 9 1
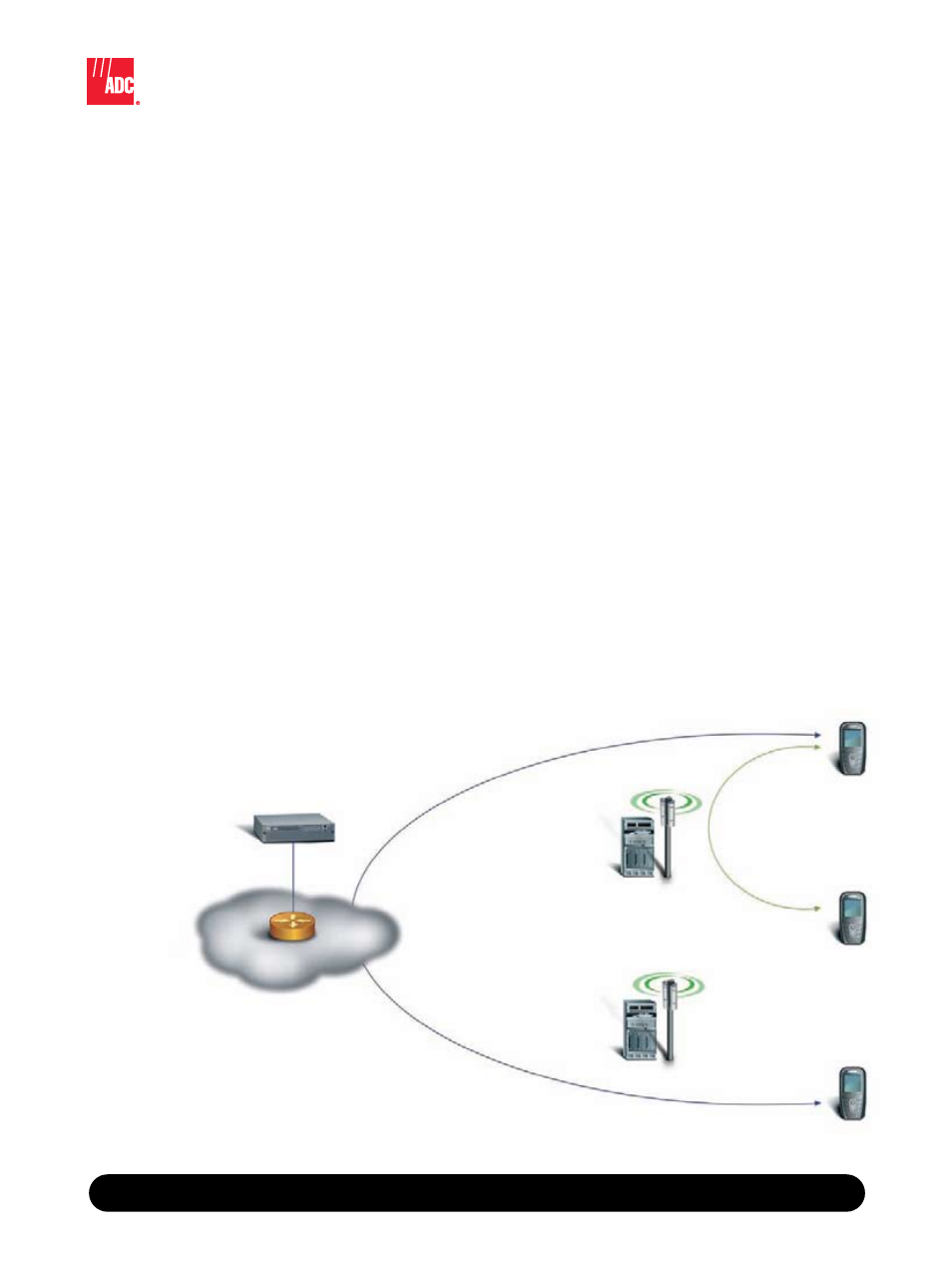
UltraWAVE CDMA
Next Generation CDMA 2000 Solution
BS Plus
IP Network
Softswitch
CDMA2000
BS Plus
CDMA2000
Flexible IP Architecture
for Today and Tomorrow
UltraWAVE CDMA’s distributed architecture
effectively integrates legacy BSC and the BTS into
a single compact unit. As a result, UltraWAVE
CDMA is the ideal solution for rural areas and
sparsely populated towns. This architecture also
minimizes carriers’ initial investment for larger
network roll-outs, while ensuring rapid return on
investment. Taking advantage of the attractive
economics of standard IP-based infrastructure
technologies, UltraWAVE CDMA cuts the total
cost of the network. This design approach also
enhances system flexibility in addressing various
network configurations, including V5.2, SS7 and
PRI as well as combinations of them.
Both new and established fixed carriers
and mobile operators benefit from deploying
UltraWAVE CDMA. The all-IP architecture allows
operators an easier migration path to MMD, IMS,
and NGN. While new operators can immediately
establish next generation networks (NGN),
established carriers can build upon their
legacy systems now with seamless migration
in the future.
Furthermore, the all-IP based architecture
facilitates the introduction of IP transmission
between the RAN and the CN for operators
who are planning ahead for IP-based
multimedia services.
Local Switching
A major part of any operator’s OPEX is the cost
of backhauling traffic from the radio access
network (RAN) to the core network (CN). Due
to UltraWAVE CDMA’s unique capability to
offer local switching, substantial savings can
be achieved. The key benefit is that calls that
are terminated intra cell or inter cells can be
switched locally so that the payload does not
occupy any bandwidth over the backhaul system.
Only the signalling is carried between the RAN
and the CN. The result is significant reductions
in backhaul bandwidth requirements and lower
OPEX (via satellite or leased line) and CAPEX
(via procured terrestrial backhaul).
In addition to cost savings on the backhaul,
the introduction of local switching means
less consumption of switching resources. This
translates into less investment in trunk capacity.
UltraWAVE CDMA Local Switching Configuration
