Regulator ics ba3938 – Rainbow Electronics BA3938 User Manual
Page 6
189
Regulator ICs
BA3938
F
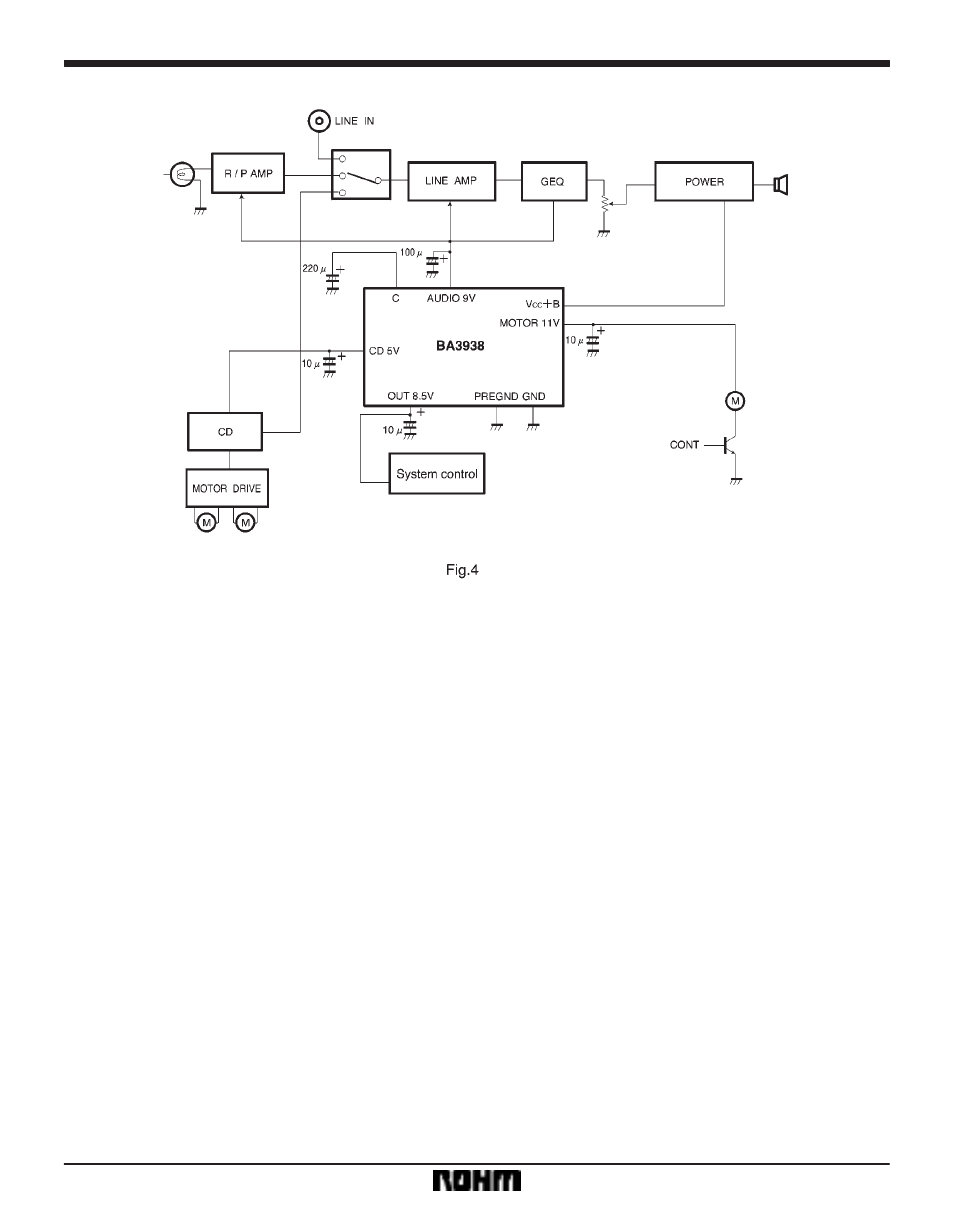
Application example
F
Operation notes
(1)
Operating power supply voltage
When operating within proper ranges of power supply
voltage and ambient temperature, most circuit functions
are guaranteed. Although the rated values of electrical
characteristics cannot be absolutely guaranteed, char-
acteristic values do not change drastically within the
proper ranges.
(2)
Power dissipation (Pd)
Refer to the heat reduction characteristics (Fig. 5) and
the rough estimation of IC power dissipation given on a
separate page. If power dissipation exceeds the allow-
able limit, the functionality of IC will be degraded (such
as reduction of current capacity by increased chip tem-
perature). Make sure to use the IC within the allowable
range of power dissipation with a sufficient margin.
(3)
Preventing oscillation at each output
To stop oscillation of output, make sure to connect a ca-
pacitor having a capacitance of 10
µ
F or greater between
GND and each output pin. Oscillation can occur if capaci-
tance is susceptible to temperature. We recommend us-
ing a tantalum electrolytic capacitor with minimal
changes in capacitance. Also, output can be further sta-
bilized by connecting a bypass capacitor between V
CC
and GND.
(4)
Overcurrent protection circuit
An overcurrent protection circuit is installed in each out-
put system, based on the respective output current. This
prevents IC destruction by overcurrent, by limiting the
current with a curve shape of “7” in the voltage-current
graph (a curve shape of “inverted -L” for V
CC
)
B). The
IC is designed with margins so that current flow will be re-
stricted and latching will be prevented even if a large cur-
rent suddenly flows through a large capacitor. Note that
these protection circuits are only good for preventing
damage from sudden accidents. Make sure your design
does not cause the protection circuit to operate continu-
ously under transitional conditions (for instance, if output
is clamped at 1V
F
or higher, short mode circuit operates
at 1V
F
or lower). Note that the circuit ability is negatively
correlated with temperature.
